Can a single investment vehicle provide both diversification and cost efficiency? Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have transformed portfolio management with their innovative structure. This transformative power has made ETFs indispensable in modern investment strategies.
ETFs, having first emerged in the early 1990s, now command a substantial portion of the investment market. With over $6 trillion in assets under management, the growth of ETFs underscores their role in portfolio diversification and risk management. Their ability to track indices, sectors, or commodities offers a versatile tool for investors.
Unpacking Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
The Origin of ETFs
ETFs began in the early 1990s, offering a new way for investors to diversify. The first ETF, called SPDR, tracked the S&P 500 index. Today, ETFs have grown to manage trillions of dollars in assets.
Their creation allowed everyday investors to access market segments previously reserved for the wealthy. Initially, they were popular in the U.S., but now they are a global phenomenon. ETFs have brought more transparency and efficiency into the market.
This growth wasn’t without challenges. Early ETFs faced regulatory hurdles and skepticism. Over time, their benefits won over critics and expanded their appeal.
The Fundamental Structure of ETFs
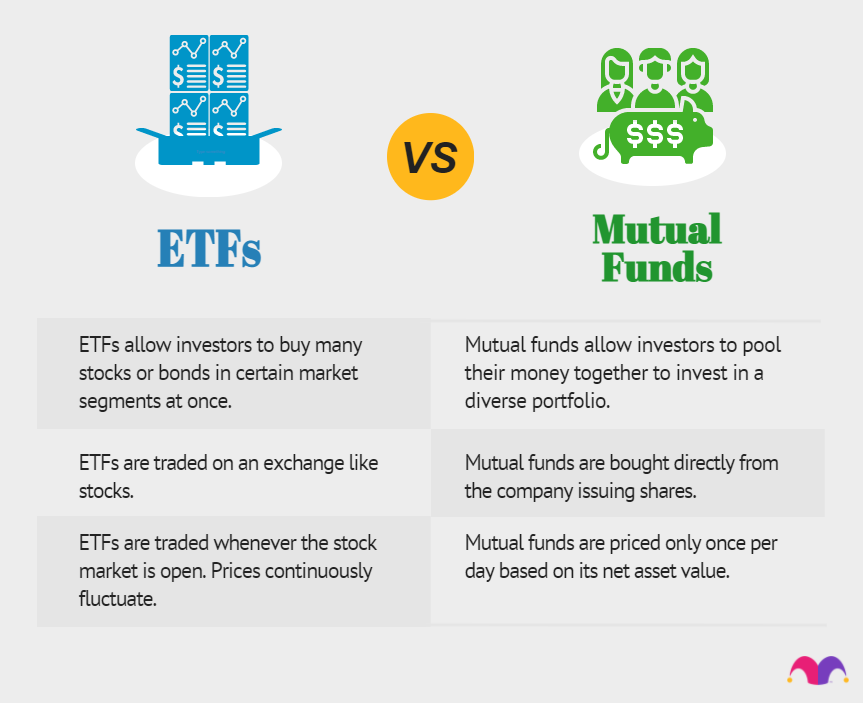
At its core, an ETF is a basket of assets. These assets could include stocks, bonds, or commodities. Investors can buy shares of this basket, which trade on stock exchanges.
One key feature is their ability to trade like a stock. This means you can buy and sell ETFs throughout the trading day. Their prices can fluctuate, offering liquidity and flexibility.
Additionally, ETFs often have lower fees compared to mutual funds. This cost-efficiency makes them attractive to both individual and institutional investors. Their transparency allows investors to see exactly what they own.
The Future Outlook on ETFs
The innovation in ETFs shows no sign of slowing down. New types of ETFs are being developed to cater to diverse investment needs. Sustainable and sector-specific ETFs are gaining popularity.
Technology is playing a significant role in their future. Automated trading and robo-advisors often include ETFs in their services. This trend is making investing more accessible.
Laws and regulations also continue to adapt. Policies that favor ETF growth are being implemented. The future looks promising for this versatile investment tool.
The Origin of ETFs
ETFs started with a groundbreaking launch in 1993. The first ETF, named SPDR, was designed to track the S&P 500 index. This was a significant innovation in the financial world.
This new investment tool democratized access to a broader market. Before ETFs, replicating the performance of market indices was costly and complex. ETFs simplified this process for individual investors.
Over time, the appeal of ETFs expanded globally. Their cost-efficiency and adaptability made them a popular choice. Today, they are an essential part of diversified portfolios worldwide.
The early success of ETFs paved the way for further innovation. Different types of ETFs emerged, catering to various investment strategies. From niche markets to broad sectors, ETFs are now prevalent everywhere.
Early Development and Adoption
ETFs faced initial skepticism and regulatory challenges. The concept of trading a basket of assets like a stock was new and untested. However, the early adopters saw the advantages and pushed for more options.
By the late 1990s, ETFs gained traction in investment circles. New ETFs started to track different indices, sectors, and commodities. This period marked rapid growth and wider acceptance.
The adaptability of ETFs helped overcome early barriers. Their ability to fit various investment strategies drove their popularity. Today, ETFs are an industry standard.
The Role of Innovation
Innovation has been central to the evolution of ETFs. New types such as sector-specific and thematic ETFs have emerged. Technology and algorithmic trading added more layers of efficiency.
Financial institutions continually develop smarter, more focused ETFs. These newer versions cater to both specialized and general investment needs. The versatility of ETFs is a key factor in their success.
The introduction of robo-advisors further expanded ETF usage. These automated platforms often incorporate ETFs for their efficiency. Innovation continues to shape the future of ETFs.
Global Expansion
After initial success in the U.S., ETFs started to capture global interest. Countries like Canada, Europe, and Asia began adopting ETFs in their markets. This global expansion added another layer of credibility.
Various financial regulations were adjusted to accommodate ETFs on a global scale. This helped in harmonizing the trading and management of ETFs worldwide. Investor education also played a role in promoting global adoption.
Today, ETFs are a common feature in investment portfolios around the world. Their ease of access and wide range of options appeal to a diverse range of investors. The origin of ETFs laid the groundwork for this global phenomenon.
The Fundamental Structure of ETFs
ETFs are composed of various assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities. These assets are pooled together to form a single investment fund. Investors can purchase shares of this fund on the stock market.
One of the standout features of an ETF is its flexibility. Unlike mutual funds, ETFs trade throughout the day like individual stocks. This allows investors to buy and sell them at market prices.
ETFs are also known for their cost-efficiency. They often have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds. This makes them an attractive option for long-term investors.
Transparency is another key aspect. Most ETFs disclose their holdings daily, letting investors know exactly what they own. This level of transparency helps build investor trust and confidence.
The Significance of ETFs in Investment Strategy
ETFs play a crucial role in modern investment strategies. They provide a simple way to achieve diversification. Investors can gain exposure to a wide range of assets with a single purchase.
One significant benefit of ETFs is their cost-effectiveness. They often come with lower fees compared to mutual funds. This makes ETFs an attractive option for cost-conscious investors.
ETFs also offer flexibility and liquidity. You can trade them throughout the day at market prices, just like stocks. This flexibility makes them suitable for both long-term and short-term strategies.
Another key point is transparency. Most ETFs provide daily updates on their holdings. This transparency allows investors to know exactly what they are investing in.
The ability to track specific indices, sectors, or commodities adds another layer of versatility. Investors can target specific market segments easily. This helps in executing more precise investment strategies.
ETFs also allow for efficient tax management. They are structured to minimize capital gains tax. This tax efficiency can enhance overall investment returns.
Versatility of ETFs: Tracking Indices, Sectors, and Commodities
ETFs offer exceptional versatility in investment strategies. They can track a variety of indices, providing broad market exposure. This means you can invest in the entire market or specific segments with ease.
When it comes to sector-specific investing, ETFs shine. You can select ETFs that focus solely on technology, healthcare, or finance. This targeted approach allows for precise allocation of resources.
ETFs also provide opportunities to invest in commodities. Commodity ETFs include assets like gold, silver, or crude oil. These ETFs allow investors to diversify beyond traditional stocks and bonds.
- Tracking major indices like the S&P 500
- Focusing on specific sectors like technology or healthcare
- Investing in commodities such as gold or crude oil
This flexibility makes ETFs suitable for various investment goals. Whether you’re looking for broad exposure or a niche market, there’s likely an ETF for you. The range of options gives investors the tools they need to execute diverse strategies.
Another advantage is the ease of access. Most ETFs can be traded on major stock exchanges. This accessibility allows investors to buy and sell with minimal complications.
Cost-effectiveness and Accessibility of ETFs
ETFs are known for their low cost. They typically have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds. This makes them attractive for cost-conscious investors seeking to maximize returns.
Another advantage is the lack of minimum investment requirements. You can buy a single share of an ETF, making it accessible for investors of all sizes. This opens the door to new investors.
ETFs also provide easy access to a variety of markets. Most ETFs are traded on major stock exchanges. This provides liquidity and flexibility, allowing for quick buying and selling.
- Low expense ratios
- No minimum investment requirements
- Traded on major stock exchanges
This combination of low cost and high accessibility makes ETFs a popular choice. Both new and seasoned investors can benefit. ETFs offer a simple way to build a diversified portfolio.
Their structure also allows for tax efficiency. ETFs often generate fewer capital gains, enhancing their appeal. This tax advantage adds another layer to their cost-effectiveness.
Optimization of Investment Portfolios with ETFs
ETFs play a crucial role in optimizing investment portfolios. They offer an easy way to diversify, reducing risk by spreading investments across multiple assets. This helps create a balanced portfolio.
The flexibility of ETFs allows for precise asset allocation. You can tailor your exposure to specific sectors, regions, or commodities. This targeted approach meets various investment goals.
Another benefit is the ease of rebalancing. ETFs can be bought and sold quickly on the stock exchange. This makes it simple to adjust your portfolio as market conditions change.
- Diversification across multiple assets
- Targeted sector and regional exposure
- Easy rebalancing options
ETFs also offer tax advantages that aid optimization. They generally incur fewer capital gains taxes compared to mutual funds. This tax efficiency can enhance overall returns.
The low fees associated with ETFs further contribute to their appeal. Over time, these cost savings add up, benefiting long-term investors. This combination of low cost and high efficiency is hard to beat.
The transparency provided by ETFs aids in strategic planning. You always know what you’re invested in, which helps make informed decisions. This level of control is invaluable for serious investors.
Diversification and Balancing Portfolios
Diversification is a key strategy in reducing investment risk. By spreading investments across various assets, ETFs help in this diversification. This reduces the impact of any single asset’s poor performance.
Balancing a portfolio involves maintaining a mix of assets that align with your risk tolerance. ETFs make this easier by offering exposure to different sectors and asset classes. This balance helps in achieving a steady growth.
Another advantage of ETFs is their ability to provide international exposure. You can invest in foreign markets without the complexities. This adds another layer of diversification to your portfolio.
- Exposure to multiple asset classes
- Access to different sectors
- International investment opportunities
ETFs also facilitate periodic rebalancing. They can be easily bought or sold based on market conditions. This ensures your portfolio remains aligned with your investment strategy.
Lastly, ETFs help in managing risk through targeted investments. You can choose ETFs that focus on low-risk sectors, like utilities or government bonds. This targeted approach aids in achieving a balanced, diversified portfolio.
The Future Outlook on ETFs in Investment
The future of ETFs looks bright with ongoing innovations. New types of ETFs are emerging, focusing on areas like sustainability and technology. These innovative products cater to the evolving needs of investors.
One exciting trend is the development of sustainable or ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) ETFs. These ETFs enable investors to put their money in companies that prioritize ethical practices. This aligns investments with personal values.
Technology is another driving force. AI and automated trading systems are increasingly incorporating ETFs. This not only enhances efficiency but also broadens accessibility.
- Emerging sustainable ETFs
- Technology-driven ETF products
- Greater integration with AI and automation
Financial regulations are also evolving to support ETF growth. Governments and regulatory bodies are making it easier for new ETFs to enter the market. This fosters innovation and expands investment opportunities.
Finally, investor education is playing a crucial role. More resources are available to help investors understand and use ETFs effectively. This growing awareness is contributing to the widespread adoption of ETFs.
All these factors indicate a promising future for ETFs. They will likely continue to be a valuable tool in investment portfolios. Their adaptability ensures they remain relevant as market conditions change.
Innovation and Emerging ETF Trends
Innovation is rapidly transforming the ETF landscape. One significant trend is the rise of thematic ETFs. These funds focus on specific themes like clean energy, technology, or healthcare.
Sustainable investing is also gaining momentum. ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) ETFs allow investors to support companies with ethical practices. This aligns investment strategies with personal values.
Another emerging trend is the use of smart beta ETFs. These funds use advanced strategies to select stocks. This can potentially enhance returns while managing risks.
- Thematic ETFs
- ESG-focused ETFs
- Smart beta ETFs
Technology is playing a pivotal role in ETF advancements. Automated trading systems and robo-advisors often include ETFs due to their efficiency. This integration makes investing more accessible.
Regulatory changes are also fostering innovation. Governments are adapting rules to facilitate the introduction of new ETFs. This encourages continuous growth and diversification.
Finally, investor education is becoming a priority. More resources are available to help people understand complex ETF strategies. This increased knowledge is fueling the demand for innovative ETFs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some frequently asked questions about the role and benefits of ETFs in investment portfolios. These answers aim to help you understand how ETFs can enhance your investment strategy.
1. What is an ETF?
An ETF, or Exchange-Traded Fund, is a type of investment fund that holds a collection of assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities. Unlike mutual funds, ETFs trade on stock exchanges just like individual stocks.
This allows investors to buy and sell shares throughout the trading day. ETFs offer diversification, cost efficiency, and liquidity, making them versatile tools for both novice and experienced investors.
2. How do ETFs provide diversification?
ETFs pool various assets into one fund, allowing investors to own small portions of multiple securities. This reduces risk by spreading investments across different sectors or asset classes.
For example, holding an ETF that tracks the S&P 500 index gives exposure to all 500 companies in the index. This broad spectrum lowers the risk associated with any single company’s poor performance.
3. Are there tax advantages to investing in ETFs?
Yes, ETFs often have tax advantages because they usually generate fewer capital gains than mutual funds. This is due to their unique structure and in-kind creation/redemption process.
This means investors may owe less in taxes when they hold or sell ETF shares compared to mutual fund shares. Lower taxation can lead to higher overall returns over time.
4. What types of assets can be included in an ETF?
ETFs can include various assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and even currencies. Some specialized ETFs focus on specific sectors like technology or healthcare.
This flexibility allows investors to build diversified portfolios tailored to their financial goals and risk tolerance. Commodity-based ETFs might include assets like gold or oil, providing further diversification options.
5. How does liquidity benefit an ETF investor?
The liquidity of an ETF refers to how easily its shares can be bought or sold on the market without affecting its price significantly. High liquidity means transactions are smooth and quick.
This benefit allows investors to enter or exit positions rapidly based on market conditions or personal financial needs. It also ensures that there’s a ready market for buying and selling shares at fair prices.
The Role of ETFs in Diversifying Your Investment Portfolio Hey everyone! 🌟 Let’s talk about how Exc
Conclusion
ETFs have revolutionized the investment landscape, offering a versatile and cost-effective way to diversify portfolios. Their ability to track a wide range of assets, coupled with lower fees, makes them an attractive option for investors. ETFs provide transparency, liquidity, and tax advantages.
As the market continues to innovate, the role of ETFs is expected to grow even further. They will remain a fundamental tool for both individual and institutional investors. With their myriad benefits, ETFs are set to play a pivotal role in future investment strategies.
