Have you ever considered that the difference between two neighboring countries’ economic prosperity could hinge on the macroeconomic growth model they adopt? The nuances of these models, from classical to Keynesian, shape nations’ destinies. This exploration isn’t merely academic; it’s a journey through policy decisions that impact billions of lives.
Macroeconomic growth models have evolved significantly since the days of Adam Smith and the Wealth of Nations. Historical models such as the Solow-Swan model emphasize the role of capital accumulation and technological progress. Interestingly, a study by the World Bank found that countries adopting more inclusive growth models experienced a 1.5% higher annual GDP growth rate over a decade. These variations reveal the power of aligning economic theory with practical governance.
Exploring the Foundations of Macroeconomic Growth Models
Macroeconomic growth models help explain why some economies expand faster than others. They provide a framework for understanding economic performance. These models are crucial for policymakers and economists.
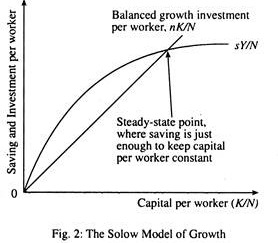
One of the earliest models was created by Robert Solow in the 1950s. His model, known as the Solow-Swan model, emphasizes the role of technological progress. It also highlights the importance of capital accumulation.
Another important model is the endogenous growth model. This model focuses on how investments in human capital and innovation drive growth. Developed in the 1980s, it offered new insights into how policies can influence economic development.
These models are not just theoretical; they have real-world applications. Countries use these frameworks to shape their economic policies and strategies. Understanding these models can help address issues like poverty and inequality.
Historical Overview of Macroeconomic Models
The history of macroeconomic models dates back to Adam Smith’s time. In his 1776 book, “The Wealth of Nations,” Smith introduced ideas that influenced later models. His work laid the foundation for classical economics.
In the 20th century, John Maynard Keynes developed the Keynesian model. This model emphasizes government intervention to stabilize the economy. During the Great Depression, Keynesian ideas gained significant traction.
More recent models have shifted focus to include globalization and technological changes. These modern theories account for the interconnectedness of global economies. They also consider the rapid pace of technological advancements.
The Importance of Macroeconomic Models for Economic Growth
Macroeconomic models are essential tools for predicting economic trends. Governments and businesses use these predictions to make informed decisions. They guide policy development and economic planning.
Without these models, understanding economic growth would be much harder. They help identify which factors contribute most to economic prosperity. This knowledge is invaluable for creating effective economic policies.
The models also aid in tackling economic challenges. By understanding the dynamics of growth, we can better address issues like inflation. Effective use of these models can lead to more stable and prosperous economies.
Historical Overview of Macroeconomic Models
Macroeconomic models have evolved over centuries, shaping how economies are understood and managed. From classical to modern theories, each model offers unique insights. These developments reflect the changing priorities and conditions of different eras.
Classical Economics and Adam Smith
Adam Smith, known as the father of economics, introduced classical economic ideas in the 18th century. His book, “The Wealth of Nations,” laid the foundation for free-market principles. Smith’s ideas emphasized minimal government intervention.
Classical economics focuses on supply and demand as the main drivers of economic growth. It suggests that markets are self-regulating and tend to reach equilibrium. This model was dominant until the 20th century
Despite its age, classical economics still influences modern theories. Economists continue to draw from Smith’s principles to understand market behavior. This longevity demonstrates its foundational importance.
Keynesian Revolution and its Impact
In the 1930s, John Maynard Keynes introduced a new way of thinking about economics. His ideas, known as Keynesian economics, emerged during the Great Depression. Keynes argued for active government intervention to stabilize the economy.
Keynesian economics focuses on total spending in the economy and its effects on output and inflation. This approach provided solutions during economic downturns. Keynes’s theories gained widespread acceptance during and after World War II.
Many governments adopted Keynesian policies to manage their economies. These policies helped lift countries out of recession and promote growth. Even today, Keynesian ideas remain vital in economic discussions.
Emergence of Modern Growth Theories
Modern growth theories emerged in the mid-20th century, offering new insights. The Solow-Swan model, developed in the 1950s, introduced the role of technology in growth. This model highlighted the importance of capital accumulation and labor productivity.
In the 1980s, endogenous growth theory added another layer to understanding economic progress. It emphasized the role of innovation, human capital, and knowledge. This theory suggested that investments in these areas lead to sustained economic growth.
Modern growth theories continue to evolve with globalization and technological advancements. Economists study how interconnected markets and rapid tech developments impact growth. This ongoing evolution ensures economic models remain relevant.
The Importance of Macroeconomic Models for Economic Growth
Macroeconomic models are essential tools for understanding how economies function. They help policymakers predict trends and make informed decisions. Using these models, governments can craft effective industrial and fiscal policies.
These models break down complex economic dynamics into manageable components. By analyzing factors such as GDP, unemployment, and inflation, they provide a clearer picture. This clarity aids in identifying strengths and weaknesses in an economy.
One of the significant benefits is their ability to forecast potential issues. Early warnings about economic downturns or inflation spikes can guide timely interventions. This proactive approach helps stabilize economies and prevent crises.
Macroeconomic models also play a crucial role in long-term planning. They inform strategies for sustainable growth and development. By understanding these models, nations can better navigate economic challenges and opportunities.
How Different Economies Utilize Macroeconomic Growth Models
Different economies tailor macroeconomic growth models to suit their specific needs and conditions. For instance, emerging markets often focus on rapid industrialization and employment. These countries use models that promote investment in infrastructure and education.
Developed economies, like the United States and Germany, adopt more complex models. They incorporate advanced technology and innovation as central components. This helps maintain their competitive edge in the global market.
In contrast, some economies prioritize social welfare alongside growth. Scandinavian countries such as Sweden and Norway use models that balance economic growth with social benefits. This approach helps ensure a high quality of life for all citizens.
Resource-rich countries, like Saudi Arabia and Russia, focus on utilizing natural resources efficiently. They align their models to capitalize on resource extraction while diversifying their economies. This helps mitigate the risks associated with dependency on a single resource.
Asian economies like China and India use hybrid models. These models mix elements from both market-based and government-controlled approaches. This flexibility allows them to adapt to changing global economic conditions.
By considering these diverse approaches, we can see how adaptable and vital macroeconomic models are. They are not one-size-fits-all but are tailored to meet specific economic goals and realities.
The Influence of Macroeconomic Models on Emerging Economies
Emerging economies leverage macroeconomic models to accelerate development and reduce poverty. These models guide policies that promote investment and infrastructure growth. This helps attract foreign direct investment, boosting financial stability.
Countries like India and Brazil use these models to enhance their industrial sectors. By focusing on manufacturing and technology, they create job opportunities and improve living standards. This strategy also diversifies the economy, reducing dependency on agriculture.
Education and healthcare are also prioritized in the macroeconomic models. Investments in these sectors lead to a more skilled workforce. A healthier, more educated population drives long-term economic growth.
Emerging economies often face high inflation rates. Macroeconomic models can help manage this by suggesting appropriate monetary policies. For example, controlling the money supply and adjusting interest rates can stabilize prices.
Global partnerships also play a role. Developing nations often collaborate with international organizations for financial aid and technical support. These collaborations enhance the effectiveness of their macroeconomic strategies.
By adopting tailored macroeconomic models, emerging economies can navigate challenges and seize opportunities. This adaptability is key to sustainable growth and development.
Shifts in Macroeconomic Models in Developed Economies
Developed economies continually adjust their macroeconomic models to stay competitive. Over the decades, these shifts have reflected changes in global and domestic conditions. Understanding these shifts can reveal much about economic strategies in advanced nations.
In the aftermath of World War II, many developed economies adopted Keynesian policies. These policies emphasized government spending to boost economic activity. This approach paved the way for unprecedented post-war growth.
By the 1980s, many countries shifted toward neoliberal models. These models prioritize free markets, deregulation, and privatization. Countries like the United States and the United Kingdom led this transition.
The 2008 financial crisis prompted another shift. Economists and policymakers recognized the need for more balanced approaches. Increased focus on financial regulations and government intervention became evident.
Today, developed economies are incorporating sustainability into their models. Environmental concerns and social equity are becoming central to economic planning. This shift aims for long-term sustainability rather than short-term gains.
As these economies evolve, their macroeconomic models will continue to adapt. Emerging technologies and shifting global dynamics will play critical roles. This adaptability helps maintain stability and growth in an ever-changing world.
Analysing the Impacts of Macroeconomic Growth Models
Macroeconomic growth models have significant effects on national economies. By guiding economic policies, they shape a country’s financial health. Their impact can be felt across various sectors, from employment to industry.
These models help determine how resources are allocated. Efficient allocation can lead to higher productivity and growth. However, poor implementation may result in inequality and stagnation.
One notable impact is on employment levels. Models that focus on industrial growth typically generate more jobs. This boosts incomes and improves living standards for many people.
Environmental sustainability is another crucial area influenced by these models. Some models promote green technologies to balance growth with ecological conservation. This helps ensure long-term economic health while protecting natural resources.
Consumer behavior also changes due to macroeconomic policies derived from these models. For example, tax cuts can increase consumer spending, boosting the economy. Higher taxes might reduce spending but fund essential public services.
Understanding these impacts helps policymakers make better decisions. It enables them to create balanced strategies that promote overall well-being and sustainable development.
The Role of Macroeconomic Models in Economic Disparity
Macroeconomic models can significantly influence economic disparity within a country. These models guide policies that impact wealth distribution. When implemented poorly, they can widen the gap between rich and poor.
For instance, models focusing on rapid industrial growth may neglect rural areas. Urban areas benefit from investment and job creation, leaving rural communities behind. This urban-rural divide contributes to socioeconomic disparity.
Tax policies derived from macroeconomic models also play a crucial role. Progressive tax systems aim to reduce inequality by taxing the wealthy more. Conversely, regressive taxes can exacerbate income inequality.
Educational investments often depend on these economic models. Higher spending on education in disadvantaged areas can reduce long-term inequality. By ensuring equal access to quality education, these models can help level the playing field.
Healthcare access is another critical factor influenced by these models. Policies promoting universal healthcare can reduce economic disparity. Healthier populations are more productive, contributing positively to the economy.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for creating balanced economic policies. By addressing the root causes of inequality, macroeconomic models can promote a more equitable society.
Evaluating Success and Failures of Various Macroeconomic Models
Evaluating macroeconomic models involves looking at their successes and failures. These assessments help refine economic theories and policies. Understanding what works and what doesn’t can guide future decisions.
One of the clear successes is the Keynesian model, especially during economic downturns. This model’s emphasis on government spending helped revive many economies after the Great Depression. It also played a significant role during the 2008 financial crisis.
However, the Keynesian model has its shortcomings. Critics argue that excessive government intervention can lead to high inflation. This was evident during the 1970s when many economies faced stagflation.
The neoliberal model, popular in the 1980s, brought about significant growth. By promoting free markets and reducing regulations, countries saw increased efficiency. Yet, this model also led to increased income inequality and financial instability.
More recently, the focus has shifted to sustainable growth models. These models aim to balance economic development with environmental protection. While promising, they face challenges in implementation and global cooperation.
By evaluating these models, we gain insights into their practical applications. Continuous assessment ensures that economic policies evolve and adapt to changing circumstances.
Future Trends in Macroeconomic Growth Models
Future trends in macroeconomic growth models are shifting towards sustainability and inclusivity. Economists are considering environmental factors to ensure long-term growth. This shift aims to balance economic development with ecological preservation.
Another significant trend is the integration of technology in economic models. Advancements in artificial intelligence and big data are shaping new economic theories. These technologies enable more accurate forecasts and efficient resource allocation.
Globalization has also influenced future macroeconomic models. Economies are becoming more interconnected, necessitating models that account for international trade and cooperation. This interconnectedness helps in understanding global economic dynamics.
Social equity is gaining attention in these models. Policies are being designed to address income inequality and provide equal opportunities for all citizens. Inclusive growth models aim to lift everyone, not just a select few.
Climate change is forcing a reevaluation of existing models. Governments are adopting green policies to mitigate environmental impacts. This trend ensures that economic growth does not come at the expense of the planet.
The future of macroeconomic models will likely involve a blend of these elements. Continuous adaptation and innovation will be key to addressing new challenges and opportunities. This approach ensures resilient and sustainable economic growth.
Emerging Macroeconomic Models and Theories
New macroeconomic models and theories are emerging to address current global challenges. These models incorporate fresh ideas and technologies to better understand economic realities. They aim to provide more practical and effective solutions.
One emerging theory is the concept of the circular economy. This model focuses on recycling and reusing resources to create sustainability. It contrasts with the traditional linear economy, which often leads to waste.
Another promising model is behavioral economics. This field studies how human behavior impacts economic decisions. By understanding behavior, policymakers can design better interventions to guide economic activities.
Some models emphasize the importance of social capital. They consider how relationships and social networks impact economic outcomes. These models focus on community development and social cohesion.
Technological advancements are also inspiring new theories. The application of big data and AI is revolutionizing economic forecasting. These tools provide more accurate predictions, helping to shape better policies.
Emerging macroeconomic models continue to evolve, reflecting the dynamic nature of the global economy. This evolution keeps economic theories relevant and useful. Continuous innovation ensures that these models address future challenges effectively.
The Intersection of Macroeconomic Models and Globalization
Globalization has a profound impact on macroeconomic models. These models must now account for international trade, capital flow, and global supply chains. The interconnectedness of economies makes accurate modeling more complex.
Many countries benefit from open markets and free trade. For example, nations with strong exports see significant economic growth. This interdependence has led to the development of trade-focused macroeconomic models.
However, globalization can also create vulnerabilities. Economic downturns in one country can ripple through others. Models that consider these global risks are essential for building resilient economies.
Technology plays a crucial role in globalization. Advanced models use big data to track global economic trends. This technology allows for better prediction and management of economic fluctuations.
International policies and agreements influence macroeconomic models as well. Organizations like the World Trade Organization set rules that countries must follow. These rules shape how nations design their economic strategies.
Understanding the intersection of these factors helps in crafting more effective macroeconomic policies. It ensures that economies can thrive in a globalized world. Continuous adaptation keeps these models relevant and robust.
Frequently Asked Questions
Macroeconomic growth models are essential tools in understanding economic development. Here are some common questions and answers that provide insights into the key aspects of these models.
1 What is the Solow-Swan model?
The Solow-Swan model, developed in the 1950s, focuses on capital accumulation, labor, and technological progress. It explains long-term economic growth based on these three factors. The model suggests that technological advancement is the main driver of sustained growth.
This theory has been influential in shaping economic policies globally. Policymakers use it to understand how investments in technology can spur economic development over time.
2 How do endogenous growth models differ from exogenous ones?
Endogenous growth models emphasize internal factors like innovation and human capital as drivers of economic growth. Unlike exogenous models, which focus on external factors such as technological advances occurring outside the economy, endogenous theories see these as results of economic activities.
This approach helps explain why some countries grow faster than others when they invest in education and innovation. This makes policy recommendations more actionable for governments seeking sustainable growth.
3 Why is technological progress important for economic growth?
Technological progress boosts productivity by making processes more efficient and creating new industries. According to macroeconomic theories like the Solow-Swan model, it’s a key factor for sustained long-term growth.
Countries investing heavily in research and development often experience rapid economic expansion. These investments lead to innovations that can revolutionize industries and improve living standards.
4 What role does human capital play in macroeconomic growth?
Human capital refers to the skills, knowledge, and experience possessed by individuals contributing to economic activities. Models like endogenous growth theories highlight its importance for increasing productivity and fostering innovation.
A well-educated workforce is crucial for adapting to new technologies and driving future advancements. This underscores why nations focus on improving education systems as a pathway to better economic outcomes.
5 How do policy decisions impact macroeconomic models?
Policy decisions shape how effectively an economy can implement recommendations from macroeconomic models. Policies related to taxes, infrastructure investment, education, and research directly affect variables considered by these models.
An example includes government incentives for R&D boosting technological progress within an endogenous framework. Effective policies can catalyze investments critical for achieving sustainable long-term economic growth.
Conclusion
Macroeconomic growth models are vital tools for understanding and driving economic development. They provide insights into how various factors like technology, human capital, and policy decisions shape economic outcomes. These models guide policymakers in crafting effective strategies for sustainable growth.
From the Solow-Swan model to modern endogenous theories, each framework offers unique perspectives. Understanding these variations helps nations address their specific economic challenges. As globalization and technological advancements continue, these models will evolve, remaining essential for navigating future economic landscapes.
