When the financial crisis of 2008 hit, it was more than just Wall Street that felt the shockwaves. Consumers, businesses, and even global markets were affected dramatically. This event starkly highlighted the deep interconnection between the U.S. economy and its financial markets.
The relationship between the U.S. economy and financial markets is not a new concept. Historically, the health of the financial markets has been a bellwether for economic performance. For instance, a study shows that changes in the stock market can often predict economic downturns. This symbiotic relationship underlines the critical role of financial markets in economic stability and growth.
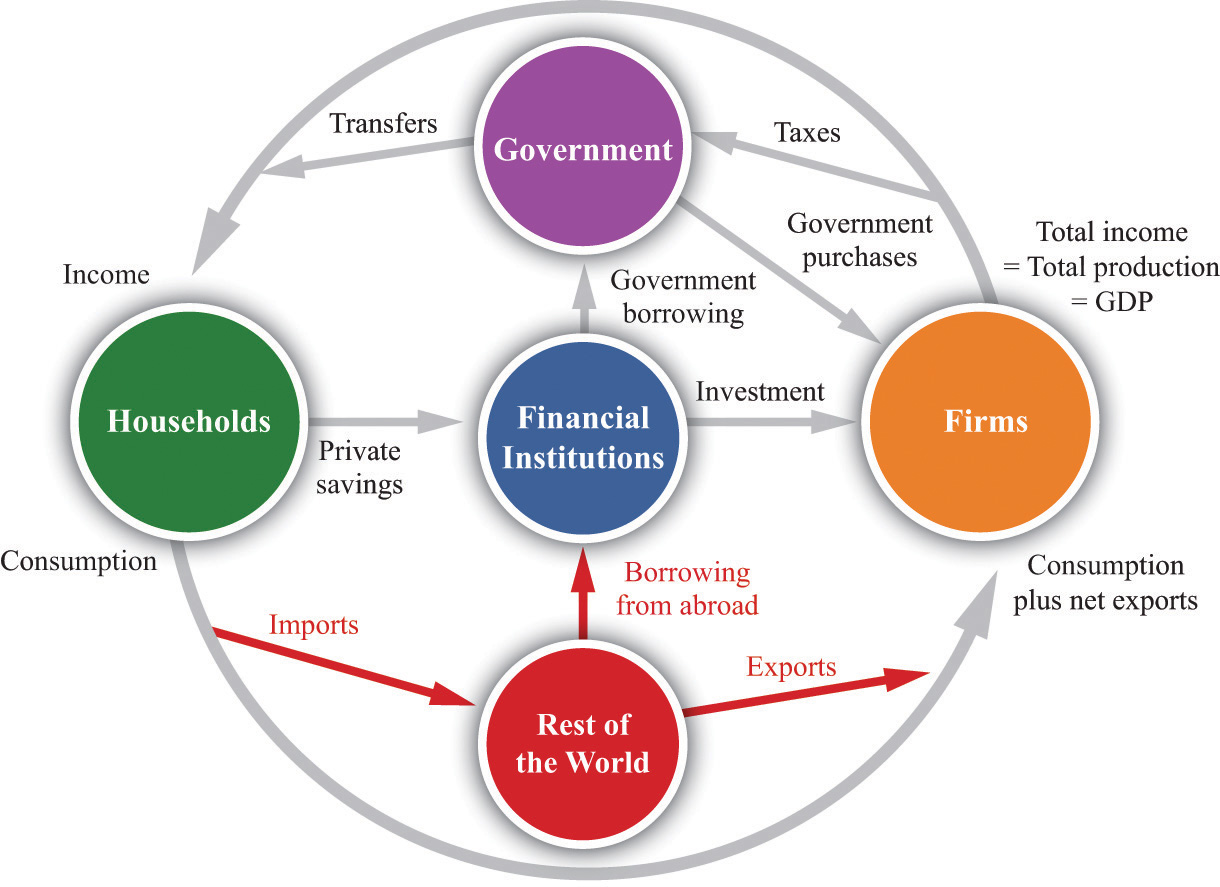
Exploring the Bond between U.S. Economy and Financial Markets
The U.S. economy and financial markets are deeply connected. When the economy grows, stock prices usually rise. This relationship is vital for understanding both fields.
Financial markets reflect the economy’s health. For instance, if the economy is booming, markets thrive. Similarly, economic downturns lead to market declines.
Investors often look at economic indicators. These include employment rates and consumer spending. They help predict market movements.
Changes in the financial markets influence the economy. A strong stock market can boost consumer confidence. This increased confidence, in turn, drives more spending and investment.
The Influence of Financial Markets on the U.S. Economy
The financial markets have a significant impact on the U.S. economy. These markets include stocks, bonds, and commodities. Their movements can shape the direction of economic growth.
Stock Market and Economic Growth
The stock market is often seen as a barometer for economic health. When stock prices rise, companies can raise more capital. This allows businesses to expand and hire more workers.
Economic growth is often boosted by a thriving stock market. Investors gain confidence and spend more money. This can lead to increased consumer demand.
A declining stock market can signal trouble. Falling stock prices might reduce wealth and spending. This can slow down economic growth.
Bond Market and Interest Rates
The bond market plays a crucial role in determining interest rates. When bond prices rise, interest rates usually fall. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper.
Cheaper borrowing helps stimulate economic activity. Businesses can invest in new projects. Consumers might take out loans for big purchases like homes and cars.
Conversely, high interest rates can stifle economic growth. More expensive borrowing can reduce spending and investment. This can lead to a slowdown in economic activity.
Commodities Market and Inflation
Commodities like oil, gold, and agricultural products also influence the economy. Changes in their prices can affect inflation rates. For instance, rising oil prices can increase transportation costs.
Higher commodity prices can lead to higher inflation. This can reduce consumer purchasing power. Businesses might also face increased costs, affecting their profitability.
On the other hand, falling commodity prices can help lower inflation. This can increase disposable income. It often leads to higher consumer spending.
The Impact of the U.S. Economy on its Financial Markets
The state of the U.S. economy can greatly influence financial markets. When the economy is strong, people tend to invest more. This drives up stock prices and market indices.
Economic indicators like GDP and employment rates have a direct effect on the markets. High GDP growth shows a robust economy, boosting investor confidence. Conversely, rising unemployment rates can cause stock market declines.
Consumer spending is another crucial factor. Increased spending often leads to higher corporate profits. This, in turn, makes stocks more attractive to investors.
Government policies also play a key role in impacting financial markets. Tax cuts and spending programs can stimulate economic growth. These actions often result in positive market reactions.
Key Drivers of the U.S. Economy and their Role
The U.S. economy is powered by various key drivers that interact in complex ways. One of these drivers is consumer spending. It accounts for about 70% of economic activity and indicates overall economic health.
Business investments are another crucial factor. Companies invest in projects and infrastructure, boosting productivity. This creates jobs and stimulates further economic growth.
Government policies also have a significant impact. These can include tax laws, spending programs, and regulations. Such policies can either fuel economic growth or hold it back.
Trade is equally important for the U.S. economy. Exports bring in revenue, while imports provide goods and services. Trade balances can affect currency value and economic stability.
The labor market is yet another driver. High employment rates mean more people have disposable income. This leads to higher consumer spending and further economic growth.
Innovation and technology serve as the backbone of economic advancement. New technologies can create entirely new industries. This fosters a cycle of continuous improvement and growth.
How Financial Markets Reflect the Health of the U.S. Economy
Financial markets act as a mirror for the U.S. economy’s health. When the economy is doing well, stock prices generally rise. This indicates strong business performance and investor confidence.
Stock market indices like the S&P 500 are key indicators. A rising S&P 500 often signals economic growth. Conversely, a declining index can warn of economic trouble.
Bonds also provide insights into economic health. When bond prices are high, it’s often a sign of low interest rates and economic stability. On the flip side, falling bond prices can indicate rising interest rates and economic uncertainty.
Commodity prices reflect various economic conditions. For example, rising oil prices might indicate increased industrial activity. Conversely, a drop in commodity prices can signal a slowdown.
The performance of financial markets can influence public sentiment. Strong markets boost consumer and investor confidence, leading to higher spending. This, in turn, further stimulates economic growth.
By monitoring financial markets, one can gauge the overall health of the economy. This is why markets are closely watched by policymakers and investors alike. They provide real-time data on economic conditions.
The Role of Monetary Policy in Bridging Economy and Financial Markets
Monetary policy plays a critical role in linking the economy and financial markets. The Federal Reserve (Fed) uses various tools to manage this relationship. These tools can include adjusting interest rates and controlling the money supply.
Interest rates are a primary tool. When the Fed lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper. This encourages spending and investment, which can boost the economy.
Higher interest rates, on the other hand, can slow down economic activity. They make borrowing more expensive. Investors might then move their money into safer investments like bonds.
The Fed also uses open market operations. This involves buying or selling government securities to influence the money supply. By doing this, the Fed can either increase or decrease liquidity in the financial system.
An increase in the money supply can lead to more spending and investment. Conversely, a decrease can help control inflation. These actions directly impact both the economy and financial markets.
Monetary policy also affects exchange rates. A strong U.S. dollar can make exports more expensive. This can influence trade balances and economic growth.
Anticipating Economic Health through Market Trends
Market trends are essential for predicting economic health. Investors and analysts closely watch these trends. They offer clues about where the economy is headed.
Stock market performance is a key indicator. When stock prices rise, it suggests economic growth. Conversely, falling stock prices can indicate potential trouble ahead.
Bond yields also provide valuable insights. High bond yields might signal strong economic confidence. Low yields could mean that investors are seeking safer options due to economic uncertainty.
| Indicator | Economic Signal |
|---|---|
| Rising Stock Prices | Economic Growth |
| Falling Stock Prices | Economic Decline |
| High Bond Yields | Economic Confidence |
| Low Bond Yields | Eeconomic Uncertainty |
Commodity prices are another important factor. Higher commodity prices can indicate increased industrial activity. Lower prices may suggest weakening demand and economic slowdown.
The housing market also provides vital clues. Rising home sales and prices generally point to a healthy economy. On the other hand, a slump in the housing market often signals economic problems.
If you keep an eye on these market trends, you’ll have a better understanding of future economic conditions. This knowledge helps in making informed investment and policy decisions.
The Ripple Effect: How U.S. Economic Changes Impact Global Markets
The U.S. economy holds a significant place in the global arena. When it experiences changes, the effects are felt worldwide. This ripple effect is seen in various international markets.
Stock markets around the globe closely follow U.S. economic indicators. A strong U.S. economy often boosts investor confidence globally. Conversely, economic downturns in the U.S. can lead to foreign market declines.
Currency markets are also impacted. The U.S. dollar is a cornerstone of global trade. Fluctuations in the dollar’s value can affect exchange rates worldwide.
- Higher U.S. interest rates often strengthen the dollar.
- Conversely, lower interest rates can weaken the dollar.
Changes in the U.S. economy also influence global trade. When the U.S. economy is strong, demand for imports rises. This can benefit exporting countries.
Commodities like oil and gold are impacted by U.S. economic shifts. A thriving U.S. economy can drive up commodity prices. Conversely, an economic slowdown can reduce demand for these resources.
International policymakers closely monitor U.S. economic trends. Changes in U.S. fiscal and monetary policies can have widespread consequences. Effective global economic planning often hinges on understanding U.S. economic movements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the connection between the U.S. economy and financial markets can be complex. Here are answers to some common questions that help simplify this topic.
1. How do changes in interest rates impact the U.S. economy?
Changes in interest rates can significantly influence borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. Lower interest rates make loans cheaper, encouraging spending and investment, which boosts economic growth.
Conversely, higher interest rates increase borrowing costs. This can slow down spending and investment, potentially slowing economic growth. Policymakers use rate changes to manage economic fluctuations and inflation.
2. What role does consumer spending play in the U.S. economy?
Consumer spending is a critical driver of the U.S. economy, accounting for about 70% of total economic activity. When people spend more on goods and services, businesses see higher profits, leading to more jobs and investments.
Lower consumer spending can result in reduced business revenues and potential layoffs or cutbacks on investments. Therefore, monitoring consumer spending trends is vital for predicting economic health.
3. How does the stock market affect everyday Americans?
The stock market affects Americans by influencing their savings and retirement plans like 401(k)s. When stocks perform well, these accounts grow, increasing individual wealth.
Poor performance in the stock market can reduce account values, impacting future financial security for many Americans. Thus, stock market health directly affects personal financial stability for households across the country.
4. What is the significance of bond yields in the U.S. economy?
Bond yields offer clues about investor expectations regarding future economic conditions and interest rates. High bond yields generally suggest strong investor confidence in economic growth.
If bond yields are low, it often indicates that investors seek safer assets due to anticipated economic uncertainty or lower future growth prospects. Tracking bond yield trends helps gauge overall market sentiment.
5. Can global events influence U.S financial markets?
Yes, global events such as geopolitical tensions or international trade agreements can exert significant influence on U.S financial markets by creating uncertainties or opportunities that affect investor decisions globally.
This interconnectedness means events like Brexit or China’s market policies impact American markets by altering trade flows, currency exchange risks, and overall global investor sentiment towards risk versus safety assets.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between the U.S. economy and its financial markets underscores the importance of understanding both systems. These interconnected elements influence global economic stability, affecting investment decisions and policy-making worldwide.
Monitoring key indicators like interest rates, consumer spending, and market trends provides valuable insights into economic health. By staying informed, experts can make more strategic decisions to foster growth and stability in an ever-evolving economic landscape.

