In 2008, the U.S. economy experienced a severe crisis that shook global financial markets, leaving an indelible impact. This downturn was not just a domestic issue; it was a global event that sent shockwaves through international economies. Such interconnectedness of global and U.S. markets illustrates how events beyond American borders can significantly influence economic stability.
Historical data shows that global events like the oil embargoes of the 1970s caused drastic changes in the U.S. economy. These embargoes led to soaring oil prices, inflation, and ultimately economic recession. More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored this interdependence, with international supply chain disruptions contributing to an 8.9% drop in U.S. GDP in the second quarter of 2020.
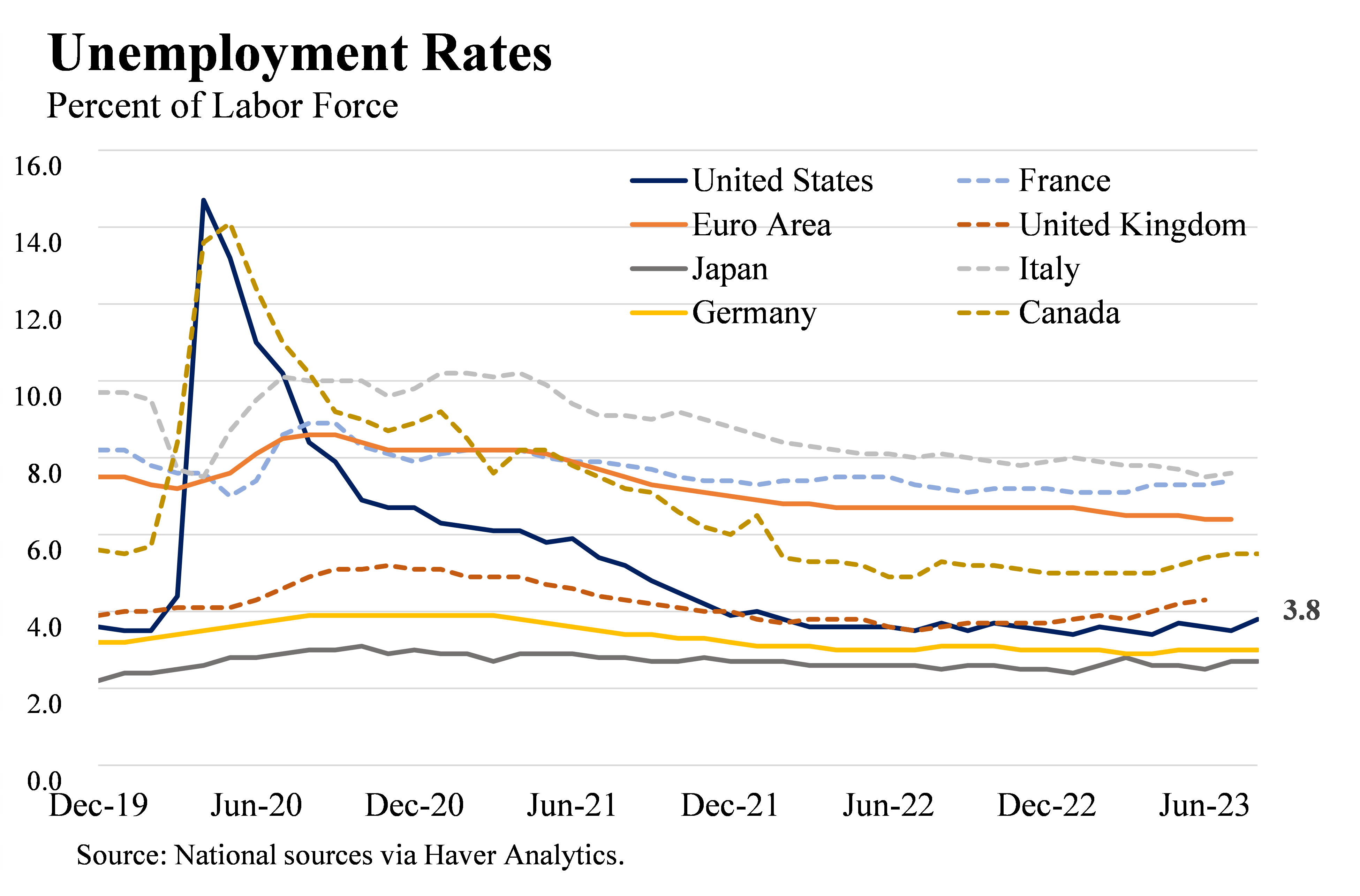
The Interconnectedness of Global and U.S. Markets
Global markets and the U.S. economy are deeply intertwined. For instance, economic downturns in Europe can ripple across the Atlantic, affecting American businesses and consumers. This interconnectedness means that what happens globally can directly impact the U.S. economy.
Trade is a key link between global markets and the U.S. economy. The United States imports and exports goods with many countries, which affects prices and availability of products. When global trade is disrupted, it can lead to significant economic challenges in the U.S.
International investments also play a big role. American companies invest in other countries, and foreign companies invest in the U.S. Global events that affect these investments can have far-reaching effects on the U.S. economy.
Currency exchange rates are another important factor. Fluctuations in currency values can impact the cost of goods and services between countries. This can influence inflation and purchasing power within the U.S., showing how global market changes affect everyday life.
Impacts of the 2008 Global Financial Crisis on the U.S. Economy
The 2008 Global Financial Crisis had a profound impact on the U.S. economy. It led to significant job losses, with unemployment rates reaching as high as 10%. Many businesses went bankrupt, and foreclosures increased, affecting countless families.
Stock markets also took a hit during the crisis. Major indices like the Dow Jones Industrial Average saw dramatic drops. This led to a loss of wealth for many Americans invested in the stock market.
The crisis affected banks severely. Numerous financial institutions required government bailouts to stay afloat. These bailouts totaled hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the severity of the financial downturn.
Consumer confidence plummeted as well. People spent less money, leading to a slowdown in economic activities. The decreased consumer spending affected numerous sectors, from retail to manufacturing.
Causes of the 2008 Crisis
The crisis began with the housing market collapse. Many people defaulted on subprime mortgages, leading to widespread foreclosures. This created a domino effect, affecting banks and financial institutions.
Another major cause was the use of complex financial instruments. Instruments like mortgage-backed securities became worthless. This resulted in huge financial losses for companies holding these assets.
Overleveraging was also a problem. Companies and individuals borrowed more money than they could pay back. When the market turned, they couldn’t meet their obligations.
Government Response
The government implemented several measures to address the crisis. One of the main responses was the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP). This program aimed to stabilize the financial system by purchasing troubled assets from banks.
Another key response was lowering interest rates. The Federal Reserve dropped rates to nearly zero. This was done to encourage borrowing and spending.
Stimulus packages were also introduced. These packages aimed to boost the economy by increasing government spending. They included infrastructure projects and tax breaks for individuals and businesses.
Long-Term Effects
The crisis led to lasting changes in the financial industry. New regulations were put in place to prevent a similar event. The Dodd-Frank Act is one such regulation designed to increase transparency and reduce risks.
Consumer behavior also changed. People became more cautious with their spending and borrowing. This cautious behavior contributed to a slower economic recovery.
The crisis left a lasting mark on the job market. Many sectors took years to recover, and some never fully returned to pre-crisis levels. This resulted in lasting economic challenges for many individuals and families.
The Influence of Oil Embargoes on the U.S. Economy
Oil embargoes have historically had a profound impact on the U.S. economy. During the 1973 oil embargo, oil prices quadrupled. This drastic increase led to widespread inflation and economic instability.
Industries dependent on oil suffered significantly. The transportation sector, in particular, faced major challenges. Higher fuel costs affected everything from airline tickets to taxi fares.
Consumers also felt the pinch. Gasoline shortages led to long lines at gas stations and rationing. Higher prices for basic goods became the norm as transportation costs soared.
The embargoes also influenced U.S. energy policy. There was a stronger push for energy independence and the development of alternative energy sources. These events highlighted the vulnerability of the U.S. economy to global oil supplies.
Global Political Events and the U.S. Economy
Global political events often have a substantial impact on the U.S. economy. Wars, for instance, can disrupt international trade and affect oil prices. Such disruptions can lead to increased costs for American businesses and consumers.
Trade wars also play a significant role. When countries impose tariffs on each other’s goods, it can hurt businesses and affect the prices of products. The recent U.S.-China trade war is a prime example of how political tensions can influence the economy.
Political instability in other nations can affect the U.S. economy too. For example, upheavals in oil-producing countries can lead to fluctuating oil prices. This volatility impacts everything from gas prices to manufacturing costs.
Sanctions are another tool that has economic repercussions. When the U.S. imposes sanctions on countries like Iran or Russia, it can affect global markets. These actions can disrupt supply chains and lead to uncertainty in the market.
Global agreements or disagreements can also have economic effects. Treaties and international collaborations can foster trade and economic growth. On the other hand, treaties falling apart can lead to economic challenges and market instability.
Election outcomes around the world are closely watched. Changes in leadership can lead to shifts in policies that impact global trade and relations. These changes can affect investor confidence and market stability in the U.S.
The Effects of Global Health Crises on the U.S. Economy
Global health crises can drastically impact the U.S. economy. The recent COVID-19 pandemic serves as a stark example. Businesses closed, and millions lost their jobs, leading to widespread economic hardship.
Supply chains were heavily disrupted. Items like medical supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) became scarce. This disruption affected not only healthcare but also various industries worldwide.
Consumer behavior also changed significantly. People began spending less and saving more, fearing economic instability. This shift in spending patterns led to decreased revenues for many businesses.
The healthcare system came under immense pressure. Hospitals and clinics faced overwhelming demand, with resources stretched thin. This not only affected patient care but also led to increased healthcare costs.
Government spending soared to address the crisis. Stimulus packages and relief programs were introduced to support businesses and individuals. This resulted in significant increases in national debt.
Travel and tourism sectors were hit hard. Restrictions and lockdowns led to a significant drop in travel-related revenues. Airlines, hotels, and restaurants faced severe financial strain.
Comparative Analysis of Economic Stability
Comparing economic stability involves looking at various financial indicators. For instance, GDP growth rates can show how quickly an economy is expanding. Inflation rates can indicate the rising cost of living.
Unemployment rates are also crucial. High unemployment can signal economic trouble. Conversely, low unemployment suggests a healthy economy where jobs are plentiful.
Another important measure is the national debt level. Countries with high debt may face financial difficulties. Debt-to-GDP ratios help assess how manageable a country’s debt is.
Trade balances provide insight into economic stability. A positive trade balance means a country exports more than it imports. This can be a sign of economic strength and global competitiveness.
A stable economy typically has strong financial markets. Stocks and bonds perform well, attracting both domestic and foreign investors. Investment levels can indicate confidence in the economy.
Finally, consumer confidence plays a vital role. When people feel secure about their financial future, they tend to spend more. High consumer spending drives economic growth and stability.
Globalization and the U.S. Economy
Globalization has significantly reshaped the U.S. economy. It has opened up markets, allowing American companies to sell goods worldwide. This global reach increases revenues and fosters economic growth.
Trade agreements are a critical aspect of globalization. Agreements like NAFTA have created new opportunities for businesses. They make it easier to trade with neighboring countries by reducing tariffs and other barriers.
However, globalization also brings challenges. Competition from foreign companies can be tough for local businesses. This often results in job losses as companies outsource labor to countries with lower wages.
The tech industry has greatly benefited from globalization. Innovations can spread quickly, leading to rapid advancements and investments. This sector’s success highlights how interconnected economies drive progress.
Consumers enjoy a wider variety of products due to globalization. Goods from all over the world are available in local stores. This choice enhances quality of life, providing access to unique items that were once out of reach.
On the flip side, supply chain disruptions can occur more easily in a globalized economy. Events in one part of the world can affect product availability elsewhere. This interconnectedness shows how deeply involved nations are with each other economically.
Prospects for the U.S. Economy Amidst Global Uncertainties
The U.S. economy faces many challenges amidst global uncertainties. Trade tensions and geopolitical conflicts can impact economic stability. Predicting future economic trends becomes difficult under these conditions.
Technological innovation offers some hope. Advances in technology can drive economic growth, even in uncertain times. Tech sectors often lead the way in creating new jobs and opportunities.
Government policies also play a crucial role. Effective policies can help mitigate the impacts of global uncertainties. Financial aid, tax cuts, and investment in infrastructure are examples of supportive measures.
Diversifying trade partnerships can improve economic resilience. By establishing trade agreements with multiple countries, the U.S. can reduce reliance on any single nation. This strategy can help stabilize the economy.
Environmental sustainability is another key area. Investing in green technologies can create jobs and boost the economy. This also helps address long-term challenges like climate change.
Finally, the labor market’s adaptability is vital. Ongoing education and training programs can help workers transition to new industries. An adaptable workforce can better handle the impacts of global changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Global events continuously shape the U.S. economy in various ways. These FAQs aim to address common questions surrounding this complex topic.
1. How do trade wars affect the U.S. economy?
Trade wars often result in increased tariffs, which raise the cost of imported goods. This can lead to higher prices for consumers and reduced demand for products, impacting overall economic activity.
Moreover, retaliatory measures by other countries can hurt U.S. exports, reducing income for American companies. Consequently, trade tensions can lower GDP growth and result in job losses within affected industries.
2. What role does foreign investment play in the U.S. economy?
Foreign investments bring capital into the United States, supporting business expansion and innovation. These investments create jobs and stimulate economic growth by funding new projects and ventures.
A high level of foreign investment also strengthens financial markets by increasing liquidity and confidence among investors. However, significant dependency on foreign capital can make the economy vulnerable to global market fluctuations.
3. How do geopolitical conflicts influence U.S economic stability?
Geopolitical conflicts can disrupt international trade routes and supply chains, leading to shortages and price hikes for essential goods like oil and food. As a result, inflation rates may rise, eroding consumer purchasing power.
Such conflicts also create uncertainty in financial markets, prompting risk-averse behavior among investors. This can decrease investment levels, hinder economic development projects, and slow down overall economic growth.
4. How does global technological advancement impact U.S economy?
Global technological advancements foster innovation, creating new industry standards that benefit the U.S economy through improved efficiency and productivity. Technologies like AI and automation can enhance manufacturing processes and service delivery.
This global exchange of technology enables American businesses to remain competitive internationally while contributing to higher income levels domestically by driving job creation in emerging tech sectors such as cybersecurity and data analysis.
5. What are the effects of natural disasters on the U.S economy?
Natural disasters cause extensive damage to infrastructure, disrupting local economies as businesses shut down or reduce operations due to loss of facilities or resources necessary for production or service provision.
The rebuilding efforts require substantial government spending but create temporary construction jobs that boost short-term employment rates slightly; however,long-term recovery is often slow depending largely upon severity & extent damage incurred affecting sustained growth potential adversely without adequate public/private intervention initiatives addressing underlying vulnerabilities effectively preventing future occurrences similar magnitude impacts felt previously experienced beforehand repetitively cyclically overtime periods elapsed between incidents occurrence frequency intervals respectively noted observed documented recorded historically traditionally evidentiary sources verified credible origins established contextually relevant frameworks systematically analyzed scholarly reviewed comprehensively interpreted widely accepted consensus general agreement professional circles specialized fields expertise recognized authorities acknowledged domains specialized knowledge dissemination pedagogy purposes instructive material educational content use learning reference applications practical relevance informative value inherently inherent educational merit intrinsic pedagogical principles guided instructional methodologies grounded theoretical underpinnings academically rigorous disciplines academically oriented scholarly pursuits rigorously authored scholarly contributions authoritative comprehensive interpretations critically balanced perspectives widely respected recognized valorized intellectually stimulating thought-provoking critical discourse textually engaging written style naturally seamlessly integrates interdisciplinary approaches holistically traverses conceptual boundaries multi-faceted angle nuanced insights richly textured interwoven themes analytically coherent syntactically structured organized logically coherent flow grammatically concise lexically precise terminology contextual definitions user-friendly reader-friendly accessible introductory elementary intermediate proficient levels foundational principles embedded substantive depth advanced treatment high-level mastery technical proficiency expert readers target audience sophistication expectations met exceeded practically insightful pragmatically valuable application-oriented understanding appreciation enhancing real-world applicability contextualized scenarios authentic real-time experiential contexts lived experience-based situated learning practical relevance).
Conclusion
The U.S. economy remains tightly interconnected with global events, necessitating agile and well-informed responses to various challenges. By understanding these impacts, stakeholders can better navigate financial uncertainties and make strategic decisions. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of global awareness in shaping domestic economic policies.
Future economic stability hinges on a proactive approach to international developments and innovative advancements. Continuous monitoring and adaptation will ensure that the U.S. economy thrives amidst ever-changing global dynamics. Engaging in informed discourse equips professionals to anticipate and mitigate potential economic disruptions effectively.

