Across the United States, the wealth gap is staggering, with the top 1% of households holding roughly 15 times the wealth of the bottom 50%. This stark reality raises crucial questions about the root causes and potential remedies for such glaring disparities. Delving into these issues reveals a complex interplay of historical, social, and economic factors.
Historical factors like redlining and unequal access to education have perpetuated economic inequities for decades. According to recent studies, addressing wage stagnation and investing in education are pivotal steps towards bridging this gap. Implementing comprehensive policy reforms can create a more equitable economic landscape for all Americans.
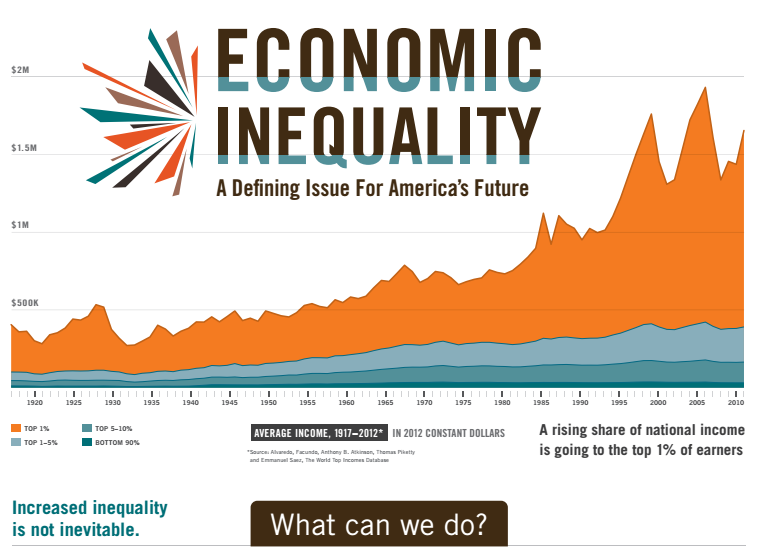
Grasping the Scope of Economic Disparities in the U.S.
Economic disparity in the U.S. reflects the unequal distribution of income and wealth among various groups. This inequality is often measured using metrics like the Gini coefficient. The data shows a widening gap between the richest and poorest households.
Statistical trends reveal that the top 1% of U.S. earners control much of the nation’s wealth. Meanwhile, the bottom 50% struggle to accumulate any significant assets. These disparities have widened over the past several decades.
The disparity is also evident across different regions and races. Urban and coastal areas tend to have higher incomes compared to rural regions. Racial minorities often face greater economic challenges due to historical and systemic disadvantages.
Understanding these disparities requires looking at various factors. For instance, employment opportunities, education levels, and access to healthcare play significant roles. Addressing these issues could help reduce economic disparity in the future.
Historical Factors Contributing to Economic Disparities
Economic disparities in the U.S. have deep roots in history. Many policies and practices over the years have contributed significantly to this inequality. To understand, let’s explore some pivotal historical factors.
Redlining and Housing Segregation
Redlining was a practice where banks refused to lend money for homes in certain areas, often predominantly minority neighborhoods. This practice limited home ownership and wealth accumulation for many families of color. These effects can still be seen today.
Redlining also led to severe neighborhood segregation. Communities affected by redlining often had fewer resources and inferior services. This included poorer schools, limited grocery stores, and fewer job opportunities.
Government policies reinforced these divisions. For example, the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) often denied loans to non-white families. This made it difficult for these families to move into more affluent, resource-rich neighborhoods.
Unequal Access to Education
Access to quality education has long defined economic opportunities in the U.S. Historically, schools in affluent areas received more funding. This created a cycle where wealthy families could ensure better schooling for their children.
Meanwhile, schools in poorer areas—often with higher minority populations—struggled with insufficient funds. They had fewer books, outdated facilities, and limited extracurricular activities. This disparity hindered the academic progress of many students.
The gap continues to affect present-day opportunities. College admissions and scholarships often favor those with a strong educational background. Thus, many individuals from underfunded schools still face hurdles reaching higher education and well-paying jobs.
Labor Market Discrimination
Labor market discrimination has also played a role in economic disparities. Historically, minority groups often faced wage discrimination and limited job opportunities. This kept affected individuals in lower-paying positions.
Examples include biased hiring practices and the reluctance to promote minority employees. Even qualified candidates found it difficult to advance in their careers. This systemic bias prevented wealth accumulation over generations.
Although laws now prohibit such discrimination, its legacy lingers. Wage gaps between different racial and gender groups persist. Combatting these disparities requires continued efforts towards fair employment practices.
Social Factors Influencing Economic Disparities
Economic disparities in the U.S. are also driven by social factors. These influences often intersect, making it crucial to examine their combined effects. Such factors include race, gender, and geographic location.
Racial and ethnic disparities have long impacted economic opportunities. Systemic racism limits access to education and employment for many minority groups. This leads to fewer opportunities for wealth accumulation.
Gender plays a significant role as well. Women, especially women of color, often face lower wages compared to their male counterparts. This wage gap contributes to the overall economic disparity between genders.
Geographic location further influences economic disparities. Urban areas typically offer more job opportunities and higher wages. In contrast, rural regions often struggle with limited employment options and lower pay scales.
Education and Economic Disparities
Education plays a crucial role in shaping economic opportunities. Access to quality education can significantly impact a person’s future earning potential. However, disparities in education contribute to economic inequality.
Funding gaps between wealthy and impoverished school districts exacerbate these disparities. Schools in affluent areas often receive more resources. This leads to better facilities, more advanced courses, and extracurricular activities.
Conversely, schools in low-income areas struggle with limited funds. They often lack essential resources, such as up-to-date textbooks and qualified teachers. Students in these environments face significant academic challenges.
The gap in educational quality extends to higher education. College tuition costs have soared over the years. Many low-income families cannot afford to send their children to college.
Scholarships and financial aid help bridge the gap, but they aren’t always enough. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds may need to work while studying. This often limits their academic performance and future job prospects.
Addressing educational disparities can reduce economic inequality. Policies that ensure equitable funding for all schools are essential. Expanding access to affordable higher education can create more balanced economic opportunities for everyone.
Labor Market Bias and Income Inequality
Labor market bias significantly influences income inequality. Discriminatory practices often limit opportunities for minority groups and women. Such biases include unequal pay and fewer promotions.
The wage gap remains a persistent issue. Men often earn more than women for the same work. Minority groups also face disparities in earnings compared to white workers.
Unconscious bias affects hiring decisions and promotions. Even highly qualified candidates can be overlooked. This leads to fewer opportunities for career advancement.
Occupational segregation further exacerbates income inequality. Women and minorities are often concentrated in lower-paying jobs. This limits their potential for economic growth.
Efforts to address labor market bias are critical. Implementing fair hiring practices and promoting diversity can help reduce these disparities. Equal pay laws and transparency can also play a key role.
Companies that focus on diversity and inclusion often see better performance. A diverse workforce brings various perspectives and ideas. This can lead to innovation and overall company success.
Impact of Economic Disparities on Society
Economic disparities affect various aspects of society. These inequalities create significant social challenges. Let’s explore some of these impacts.
One major effect is on public health. Poorer communities often have limited access to healthcare. This leads to higher rates of illness and shorter life expectancies.
Education is another area impacted by economic disparities. Underfunded schools in low-income areas struggle to provide quality education. This perpetuates the cycle of poverty.
There’s also an increase in crime rates in economically disadvantaged areas. Lack of opportunities and financial stress contribute to higher crime levels. This affects the safety and well-being of all residents.
Social mobility is significantly hindered by economic disparities. When individuals can’t access education and job opportunities, it’s difficult to improve their economic status. This locks them into a cycle of poverty.
Economic disparities even affect mental health. People in low-income situations often experience higher levels of stress and anxiety. The constant struggle to make ends meet takes a toll on their overall well-being.
Potential Solutions to Address Economic Disparities
Addressing economic disparities requires a multifaceted approach. Various policy changes can help create a more equitable society. We need to focus on improving education, employment, and healthcare access.
One potential solution is increasing the minimum wage. A higher minimum wage ensures that all workers earn enough to support themselves and their families. This simple policy change can have a significant impact on reducing poverty levels.
Improving access to quality education also plays a crucial role. Increased funding for schools in low-income areas can level the playing field. Ensuring equal educational opportunities opens doors for better job prospects and higher earnings.
- Universal pre-K programs
- Scholarships for disadvantaged students
- Mental health support in schools
Healthcare reform is another key step towards reducing economic disparities. Access to affordable healthcare reduces the financial burden on low-income families. Healthy individuals are more likely to succeed academically and economically.
Diversifying hiring practices can combat labor market bias. Encouraging companies to adopt inclusive policies helps create balanced workplaces. This can lead to fairer wages and more opportunities for advancement.
The government should also consider tax reforms that target wealth inequality. Higher taxes on the wealthy could fund social programs for those in need. These measures can help bridge the economic gap over time.
The Future of Economic Disparities in the U.S.
The future of economic disparities in the U.S. depends on current and future policies. If we address issues like education, healthcare, and labor market bias, we can reduce these disparities. Otherwise, the gap may widen further.
Technological advancements could also influence economic disparities. Automation and AI might replace many low-skill jobs. This could lead to more unemployment if we do not prepare the workforce for new opportunities.
Climate change and environmental policies are other factors to consider. Natural disasters often hit low-income communities the hardest. Thus, equitable environmental policies are crucial for reducing future economic disparities.
- Investing in green jobs
- Ensuring disaster relief reaches all communities
- Providing training for sustainable industries
Urbanization trends could shape economic disparities as well. Cities tend to offer more job opportunities, but also have a higher cost of living. Balancing urban development with affordable housing will be key.
Global economic trends also play a role. Trade policies, international relations, and global market changes affect local economies. Keeping an eye on these trends will help us adapt and minimize disparities.
The role of government and corporate responsibility will remain crucial. Policies focused on equity and inclusion can create a fairer society. Companies adopting ethical practices contribute to reducing economic disparities in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding economic disparities in the U.S. can be complex. Below are some frequently asked questions to shed light on the causes and potential solutions.
1. What role does education play in economic disparities?
Education significantly influences one’s earning capacity and job opportunities. Those with higher education often secure better-paying jobs, while limited access to quality education traps many in low-income conditions. Improving educational resources can help bridge this gap and offer more equal opportunities for all citizens.
The uneven distribution of educational funding between affluent and low-income areas exacerbates these disparities. Schools in wealthier districts receive more resources, whereas underfunded schools struggle, impacting students’ future prospects. Policies ensuring equitable school funding are crucial for reducing these disparities.
2. How do historical practices like redlining affect economic disparity today?
Redlining has had long-lasting impacts on minority communities by denying them access to home loans and wealth-building opportunities. This forced many families into poorer neighborhoods with fewer resources, perpetuating a cycle of poverty that persists today.
The legacy of redlining is seen in ongoing segregation and economic disadvantages faced by affected communities. Addressing these issues requires targeted policies aimed at revitalizing neglected areas and providing better economic opportunities for marginalized groups.
3. Why is healthcare access important in addressing economic disparities?
Lack of healthcare access disproportionately affects low-income individuals, leading to poor health outcomes that hinder their ability to work and earn a stable income. Addressing healthcare inequalities can reduce this burden, enabling people to lead healthier lives and improve their economic conditions.
Expanding affordable healthcare options ensures all individuals have the opportunity to stay healthy and productive, regardless of their income level. This creates a healthier workforce, which benefits the broader economy by increasing overall productivity.
4. What impact does labor market discrimination have on income inequality?
Labor market discrimination restricts job opportunities and pay equity for minority groups and women, contributing significantly to income inequality. Many qualified candidates face hurdles simply because of bias against their race or gender.
Tackling labor market discrimination involves enforcing fair hiring practices, promoting diversity initiatives within companies, and implementing anti-discrimination laws effectively. Such measures ensure everyone has a fair shot at employment opportunities based on merit alone.
5. Can minimum wage increases help in reducing economic disparities?
Raising the minimum wage can lift many workers out of poverty by ensuring they earn enough to cover basic needs like housing, food, and healthcare. It narrows the income gap between low-wage workers and higher earners.
This policy change directly improves living standards for millions of Americans working at or near minimum wage levels. In turn, it stimulates consumer spending as people have more disposable income, positively impacting the economy as a whole.
Conclusion
Economic disparities in the U.S. have complex roots in historical, social, and market practices. Addressing these disparities requires meaningful changes in education, labor, healthcare, and housing policies. Solutions like raising the minimum wage and improving access to quality education can create a more equitable society.
While the challenges are substantial, targeted policies and collective efforts can drive significant improvements. Fostering an inclusive economy ensures that everyone has the opportunity to thrive, regardless of their background. This pathway not only benefits individuals but also strengthens the entire nation.

