Every dollar spent by U.S. companies on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives translates into remarkable socioeconomic benefits. Whether it’s investing in sustainable practices or philanthropy, the ripple effects are noteworthy. CSR not only enhances corporate reputation but also fosters consumer trust and loyalty, which are pivotal for economic stability.
Tracing back, the concept of CSR has evolved significantly since the early 20th century. Today, nearly 90% of S&P 500 companies publish sustainability reports, a testament to its rising importance. When businesses address social and environmental issues, they not only contribute to societal well-being but also drive innovation and efficiency, ultimately boosting their bottom line and supporting the U.S. economy at large.
Evolution of Corporate Social Responsibility
The idea of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) began in the early 20th century. Businesses started understanding they had more responsibilities beyond just making money. This included being accountable to their employees, communities, and the environment.
By the 1950s, the concept of CSR grew stronger. Companies began to see the value in helping society and not just focusing on profits. CSR became a way to build trust with the public.
The 1980s marked another significant shift. During this time, businesses started publishing reports on their CSR activities. Transparency and accountability became vital aspects of CSR.
Today, nearly 90% of S&P 500 companies publish sustainability reports. This shows how essential CSR has become in the modern world. Companies realize that being socially responsible can lead to financial success.
Early Beginnings of CSR
In the early 1900s, companies were mainly focused on increasing profits. Few thought about their impact on society. However, some forward-thinking leaders saw a need for businesses to act responsibly.
This was the era when labor movements emerged, pushing for better working conditions. Businesses began to respond by improving employee welfare. These actions were the first steps towards modern CSR.
Philanthropy also gained importance. Wealthy business owners started to donate substantial amounts to various causes. This set an early precedent for corporate giving.
The Growth of CSR in the 1950s
The 1950s were a pivotal decade for CSR. Academics began to study and define what it meant for businesses to be socially responsible. This helped in shaping the concept of CSR.
Businesses started realizing that helping society could improve their reputation. Companies began to earn the public’s trust through their community efforts. CSR initiatives expanded beyond just donations; they included employee welfare, environmental care, and customer satisfaction.
Government policies also began promoting socially responsible behavior. Regulations were put in place to ensure that companies met minimum standards for safety and ethics. This was a significant push in the evolution of CSR.
The 1980s: Reporting and Accountability
In the 1980s, CSR took on a new dimension with the rise of accountability. Businesses started publishing CSR reports to showcase their contributions to society. Transparency became a key element of CSR.
These reports highlighted various initiatives, from environmental programs to social welfare projects. It allowed the public to see the positive impact of businesses. This era marked the beginning of structured and documented CSR activities.
Audits and assessments of CSR activities also gained popularity. Companies hired third-party organizations to verify their claims. This added another layer of credibility to their efforts.
CSR in the Modern Era
Today, CSR is an integral part of business operations. Companies create detailed sustainability reports to showcase their efforts in areas like environmental protection and social welfare. Transparency and accountability remain crucial in these reports.
One significant element of modern CSR is the integration with core business strategies. Companies realize that sustainable practices can lead to long-term benefits and profitability. CSR initiatives are not just additional projects but are woven into the business model.
The modern approach also includes stakeholder engagement. Businesses now involve employees, customers, and communities in their CSR efforts. This collective approach enhances the overall impact on society.
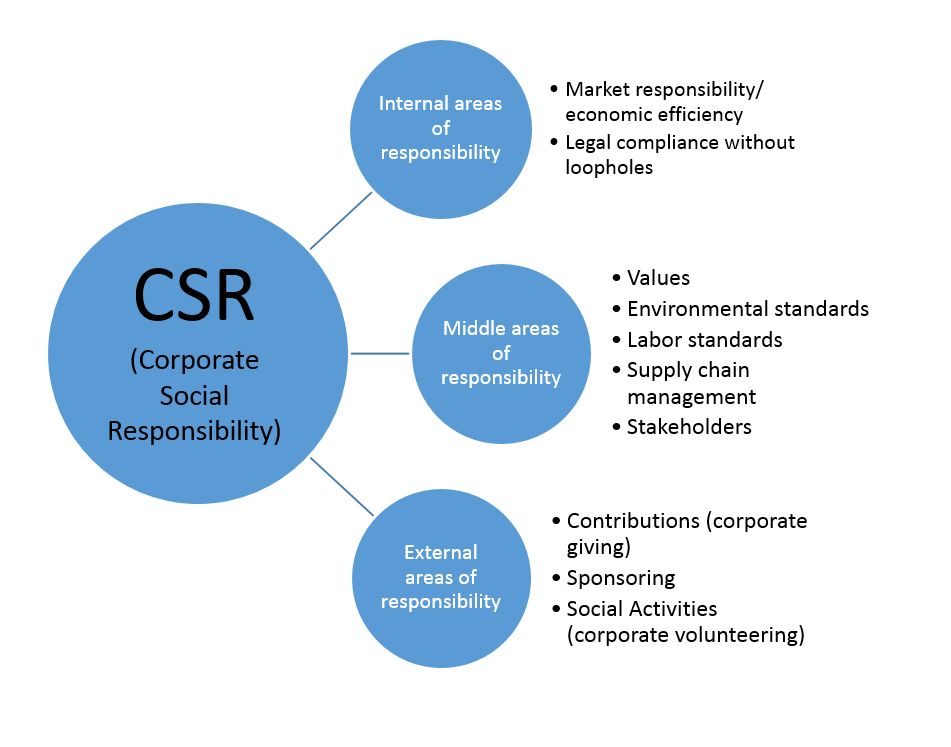
The Concept of Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to a company’s commitment to manage its business processes in a way that has a positive impact on society. This includes ethical practices in areas such as environmental sustainability, employee well-being, and community development. **CSR is about going beyond profit-making to improve society**.
There are four main pillars of CSR: Economic, Legal, Ethical, and Philanthropic responsibilities. Each pillar plays a crucial role in shaping a company’s social responsibility practices. **Businesses must balance these pillars to achieve true CSR.**
Economic responsibility involves being profitable, while ensuring fair practices. Legal responsibility means complying with laws and regulations. Ethical responsibility goes a step further, ensuring actions are morally right. **Philanthropic responsibility includes giving back to society** through donations and community service.
CSR is not just a trend; it’s a necessity in today’s world. Consumers and stakeholders expect companies to be socially responsible. **This expectation drives businesses to adopt sustainable and ethical practices**.
Defining Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility is the idea that businesses should act in a way that benefits society. This means companies should go beyond just making money. They should also contribute to the social and environmental well-being.
CSR includes activities like reducing carbon footprints and improving labor policies. It also involves volunteering in the community and making charitable donations. **These actions help build a positive image for the company**.
Adopting CSR can improve customer loyalty. People prefer to buy from companies that are socially responsible. This can lead to increased sales and customer retention.
The Four Pillars of CSR
CSR is built on four key pillars: Economic, Legal, Ethical, and Philanthropic responsibilities. **Each pillar is essential** for a robust CSR strategy. Understanding these can help businesses implement effective CSR initiatives.
- Economic Responsibility: This focuses on being profitable while maintaining fairness.
- Legal Responsibility: Companies must comply with laws and regulations.
- Ethical Responsibility: Actions should be morally right and fair.
- Philanthropic Responsibility: This involves giving back to society.
Balancing these pillars helps companies achieve their CSR goals. It ensures that they are not only profitable but also ethical and socially conscious. This balance can boost a company’s reputation and success.
Why CSR Matters Today
In today’s world, CSR is more important than ever. Customers and stakeholders expect businesses to act responsibly. **This expectation drives companies to adopt better practices**.
CSR can lead to long-term benefits for a company. It can enhance their reputation and build customer trust. Employees also feel more motivated and satisfied working for a socially responsible company.
Businesses that ignore CSR can face backlash. Negative publicity can harm their image and sales. Therefore, embracing CSR is not just good ethics; it is also good business.
Corporate Social Responsibility and Brand Image
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) plays a crucial role in shaping a company’s brand image. When companies engage in ethical practices and contribute positively to society, they build a strong reputation. **This reputation enhances the trust** consumers have in the brand.
Brands known for their CSR activities often enjoy higher customer loyalty. People prefer to support companies that align with their values. **CSR initiatives like environmental conservation and fair labor practices** are particularly appealing to consumers.
For example, companies like Patagonia and TOMS are celebrated for their CSR efforts. Patagonia’s commitment to sustainability and TOMS’ “One for One” program have significantly boosted their brand images. **These examples show the tangible benefits of CSR** on brand perception.
A positive brand image also opens doors to new opportunities. Companies with strong CSR programs attract partnerships and investments more easily. **This further strengthens their market position** and drives long-term success.
Economic Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility in the U.S.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) significantly influences the U.S. economy. When companies invest in sustainable practices, they often see cost savings in the long run. **These savings can then be reinvested** into the business, fostering growth.
CSR initiatives can also boost employee morale and productivity. Happy employees are more efficient and tend to stay longer with the company. **This reduces turnover costs** and improves overall business performance.
Communities benefit when companies engage in CSR activities. For example, companies that focus on local hiring and development can help reduce unemployment rates. **This creates a more stable and prosperous community**.
Consumers are willing to spend more on products from companies known for CSR. A study showed that 55% of consumers are willing to pay extra for goods from socially responsible companies. **This willingness directly impacts company revenues** and market share.
Investors are increasingly looking at CSR as a factor in their decision-making. Companies with strong CSR programs are often seen as less risky. **This can lead to better access to capital** and more favorable investment terms.
The overall economic impact of CSR is profound. From improving financial performance to enhancing community well-being, the benefits are wide-ranging. **CSR is not just a moral choice**; it’s a smart economic strategy.
Corporate Social Responsibility and Innovation
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) often leads to innovation within companies. When businesses focus on solving social or environmental issues, they develop new products and services. **This drive for solutions can lead to breakthrough innovations**.
Innovative practices related to CSR can improve a company’s efficiency. For example, adopting renewable energy sources can reduce operational costs. **These cost savings can then be used for further innovation and development**.
CSR encourages creative thinking. Employees are motivated to come up with unique solutions to social challenges. **This kind of thinking fosters a culture of innovation** within the organization.
Many companies are now integrating CSR into their core business strategies. This integration leads to the development of sustainable products that meet consumer demand. **For example, companies are creating eco-friendly packaging** or developing new ways to reduce waste.
Collaborative projects between companies and non-profits also spur innovation. By working together, they can pool resources and expertise. **This collaborative effort leads to more impactful solutions**.
An example of CSR-led innovation is seen in the tech industry. Companies are developing energy-efficient devices and sustainable supply chains. **These innovations not only help the environment but also provide a competitive edge** in the market.
The Role of CSR in Business Efficiency
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has a significant impact on business efficiency. When companies adopt ethical practices, they often find ways to streamline operations. **This leads to cost savings and improved processes.**
For instance, using sustainable materials can reduce waste and resource consumption. This not only benefits the environment but also lowers production costs. **Companies can then reinvest these savings** into further improvements.
CSR initiatives also boost employee morale and productivity. Happy and motivated employees work more efficiently. **This enhanced productivity contributes to the overall efficiency of the business.**
Engaging in CSR can lead to innovation that streamlines business activities. By focusing on solving social and environmental issues, companies develop better practices. **These improved practices often lead to increased efficiency.**
Another key area is energy efficiency. Many companies are investing in renewable energy sources. **This reduces their energy costs and environmental footprint.**
CSR can also improve supply chain efficiency. Ethical sourcing and fair labor practices ensure a more reliable and responsible supply chain. **A responsible supply chain can reduce risks and improve overall efficiency.**
Corporate Social Responsibility and Sustainability
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and sustainability go hand in hand. Companies that practice CSR often prioritize sustainable methods. **This means adopting practices that protect the environment** and conserve resources.
Sustainability in CSR includes actions like reducing carbon footprints and minimizing waste. Some companies are investing in renewable energy sources. **These efforts help ensure a better future for the planet**.
Sustainable business practices can also lead to cost savings. For example, using energy-efficient technologies reduces utility bills. **Companies can then allocate these savings to other areas** of the business.
Many consumers prefer brands that focus on sustainability. This preference drives companies to adopt eco-friendly practices. **Strong sustainability initiatives can boost customer loyalty**.
- Energy Conservation: Implementing renewable energy sources like solar or wind power
- Waste Reduction: Using recyclable materials and reducing single-use plastics
- Sustainable Sourcing: Ensuring supply chains use environmentally friendly products
Sustainability also encourages innovation within companies. When businesses seek greener solutions, they often develop new products and technologies. **These innovations not only benefit the environment but also provide a competitive edge**.
Overall, integrating sustainability into CSR strategies leads to numerous benefits. It helps build a positive brand image while ensuring long-term environmental protection. **CSR and sustainability together create a win-win situation** for companies and society.
Case Study: The Positive Economic Impact of CSR
One notable example of CSR’s positive economic impact is the outdoor clothing company, Patagonia. This company is well-known for its commitment to sustainability. **Patagonia’s efforts have not only benefited the environment but also their bottom line**.
Patagonia has implemented various CSR initiatives, such as using recycled materials in their products. They also donate a portion of their profits to environmental causes. **These actions have resonated with consumers**, leading to increased sales.
Their “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign is a prime example. It encouraged consumers to think about the environmental impact of their purchases. This campaign not only raised awareness but also boosted their brand loyalty and sales.
- Recycled Materials: Significant reduction in waste and resource use
- Environmental Donations: Support for global sustainability causes
- Consumer Engagement: More loyal and committed customer base
Another positive impact is seen in their employee retention. Employees at Patagonia are highly motivated by the company’s CSR values. **This leads to lower turnover rates** and higher productivity.
Overall, Patagonia’s CSR initiatives have proven to be economically beneficial. They have managed to align their business goals with social and environmental responsibility. **This alignment has created a sustainable and profitable business model**.
Frequently Asked Questions
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a crucial aspect of modern business. Here are some frequently asked questions that can help you understand its influence better.
1. What are the main components of Corporate Social Responsibility?
Corporate Social Responsibility comprises four main components: Economic, Legal, Ethical, and Philanthropic responsibilities. Economic responsibility involves being profitable while considering societal impacts. Legal responsibility is about complying with laws and regulations governing business practices.
Ethical responsibility means doing what is right even beyond legal obligations. Philanthropic responsibility involves businesses contributing to society through donations and community service. Together, these components make up a robust CSR strategy.
2. How does CSR affect consumer behavior?
Consumers often prefer to buy from companies with strong CSR commitments. Knowing a company invests in social and environmental causes builds trust and loyalty.
This preference translates into higher sales and repeat customers for the business. Many consumers are even willing to pay a premium for products from ethically responsible companies, enhancing profitability.
3. Can CSR lead to innovation within companies?
Yes, CSR can drive innovation by encouraging creative solutions to social or environmental problems. Companies may develop new products or improve existing ones to meet sustainability goals.
This focus on innovation makes the company more competitive. Additionally, businesses often find that sustainable practices lead to cost savings which can be reinvested in further innovation.
4. Does CSR improve employee satisfaction?
CSR initiatives positively impact employee morale and job satisfaction. Employees feel proud working for socially responsible organizations and become more engaged in their roles.
This increased engagement leads to higher productivity and lower turnover rates, which benefits the company’s overall efficiency. Happy employees serve as brand ambassadors, further enhancing the company’s image.
5. How do investors view CSR activities?
Investors increasingly consider CSR when making investment decisions. Companies with strong CSR programs are perceived as less risky investments due to their commitment to ethical practices.
This perception often results in better access to capital and more favorable investment terms for socially responsible companies. In turn, this increased investment helps businesses grow sustainably over time.
Conclusion
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) holds considerable power in shaping the U.S. economy. By integrating ethical, environmental, and social initiatives, companies not only enhance their brand image but also promote consumer loyalty and drive innovation. These factors collectively contribute to a more stable and prosperous economy.
Furthermore, the positive impacts of CSR extend beyond financial gains. Companies engaged in responsible practices attract better talent, retain motivated employees, and foster stronger community ties. Clearly, CSR is a vital strategy for long-term business success and societal well-being.

