Losing $6 trillion to cybercrime annually, the U.S. economy faces an unprecedented threat. This financial hemorrhage is not just a staggering statistic but a wake-up call. It underscores the broader implications of cybersecurity threats on various sectors, from banking to healthcare.
Since the advent of the internet, the U.S. has actively digitized its economic framework, inadvertently escalating its vulnerability. According to a report by McAfee, cybercrime siphons off nearly 1% of the global GDP. Strengthening cybersecurity measures could serve as a bulwark, safeguarding critical infrastructure and economic stability.
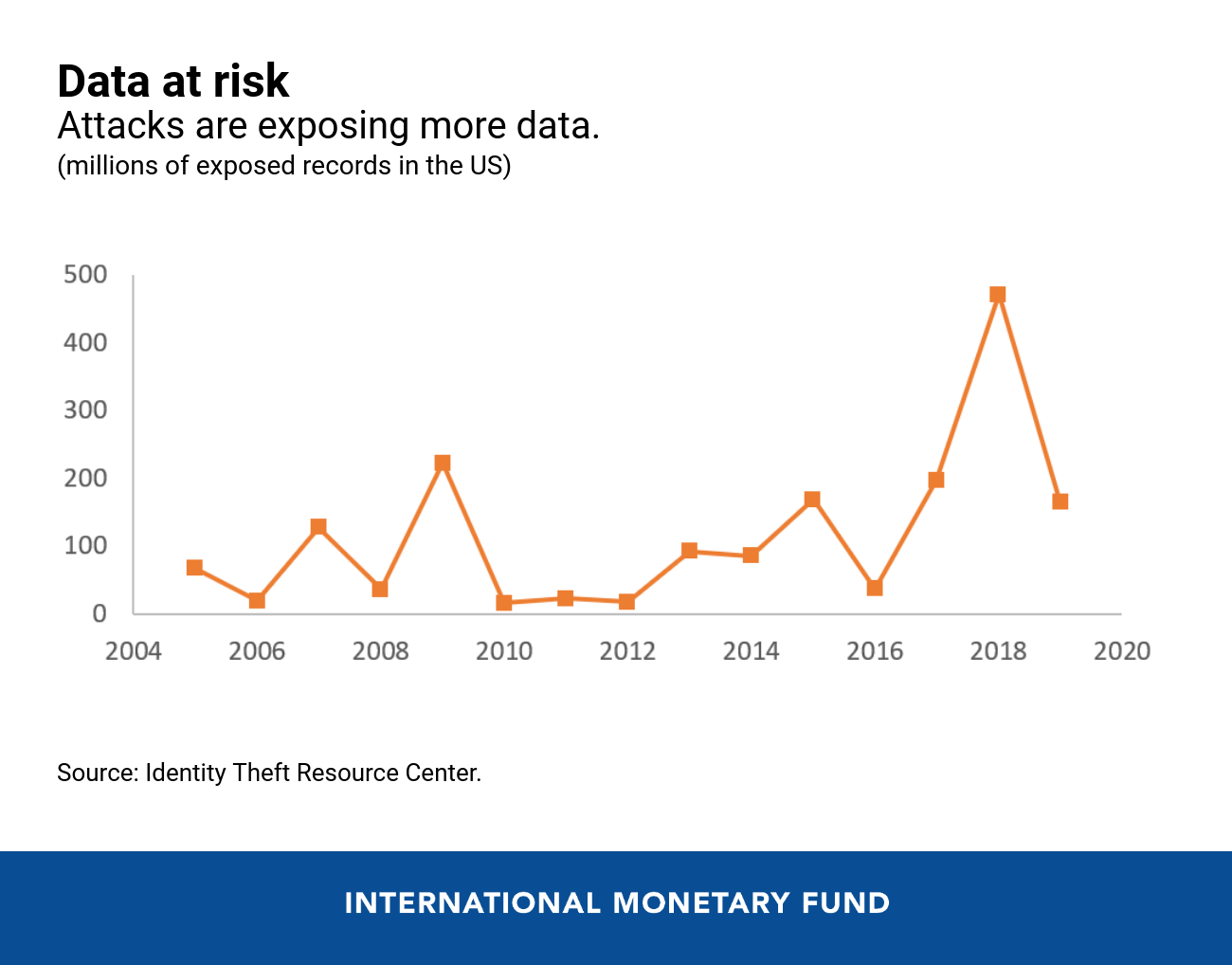
The Growing Threat of Cybercrime on U.S. Economy
Cybercrime is an ever-growing threat. Each year, the U.S. faces billions in losses due to cyber attacks. These breaches can hit businesses, government agencies, and even private citizens.
The risks are escalating as hackers become more sophisticated. A single data breach can cost a company millions, not just in lost revenue but also in reputational damage. This puts immense pressure on organizations to invest heavily in cybersecurity.
Small businesses are especially vulnerable. Many lack the funds to implement strong defenses. Unfortunately, this makes them easy targets for cyber criminals looking to exploit weaknesses.
Cybercrime affects everyone. Consumers face potential identity theft, while companies suffer financial hits. Even the U.S. economy as a whole can slow down due to the pervasive fear and uncertainty.
Why Cybercrime is Surging
The rise of digital transformation has led to an increase in cybercrime. More devices and networks mean more opportunities for hackers. As businesses migrate to digital platforms, they expose themselves to more vulnerabilities.
Ransomware attacks are also on the rise. This is where hackers lock a company’s data and demand a ransom to release it. With growing success, more cyber criminals are adopting this method.
The international nature of the internet complicates policing efforts. It’s hard to track down and prosecute cyber criminals, especially when they operate across borders. This makes cybercrime a low-risk, high-reward endeavor for many hackers.
The Financial Toll on Businesses
Cyber attacks can cripple businesses financially. Responding to a breach requires immediate action, often involving expensive cybersecurity experts. Also, companies may face fines if they fail to protect customer data.
Besides direct costs, companies also deal with long-term impacts. Customer trust diminishes, leading to a drop in sales. Shareholders might lose confidence, causing stock prices to fall.
Moreover, companies have to invest significantly in preventive measures. This includes upgrading security infrastructure and conducting regular audits. These continual investments strain financial resources.
Impact on Employment and Innovation
Job markets are affected by cybercrime as well. Companies may hesitate to expand or hire new employees due to financial strains from handling breaches. Reduced growth translates into fewer job opportunities.
Innovation also takes a hit. Fear of cyber attacks can stifle new investments in technology. Businesses may avoid adopting new tools or platforms, slowing down technological advancement.
This creates a vicious cycle. The less companies innovate, the more they struggle to keep up with evolving cyber threats. This downtrend hurts the economy’s overall health and competitiveness.
The Economic Impact of Cybersecurity Breaches
Cybersecurity breaches cause significant economic damage. They lead to financial losses, declining consumer confidence, and damaged reputations. The overall economy feels the strain from these widespread impacts.
One direct impact is the cost of responding to the breach. Companies must allocate resources to investigate and fix vulnerabilities. This involves hiring experts and implementing advanced security measures.
The aftermath of a breach often includes legal fees and penalties. Businesses may face lawsuits from affected customers. Regulatory fines can further exacerbate their financial burden.
Indirectly, cybersecurity breaches also affect stock prices. Investors lose trust in companies unable to protect their data. This loss of confidence can result in a volatile market.
Immediate Financial Losses
Cyber breaches immediately result in financial losses. Companies must spend quickly to respond and mitigate the effects. These costs cover notifying affected parties, auditing systems, and hiring cybersecurity professionals.
Additionally, businesses often face operational downtime during recovery. This downtime means lost sales and interrupted services. For some companies, the downtime cost can run into millions.
Insurance can help, but it’s not a complete safety net. Cyber insurance policies often have limits. Many expenses can exceed these limits, leaving companies to cover remaining costs.
Reputational Damage and Customer Trust
Reputational damage follows close behind financial loss. When personal data gets exposed, customers lose trust. This diminished trust can lead to a reduced customer base.
Building trust takes time, but losing it happens quickly. The brand image suffers, and regaining it is an uphill battle. Marketing efforts must now focus on rebuilding a tarnished reputation.
Some customers may never return. They may opt for competitors who seem more secure. This shift can result in long-term revenue losses.
Economic Ripple Effects
The impact goes beyond individual companies. Breaches can affect entire supply chains. A compromised supplier can disrupt deliveries, causing further economic strain.
Investors react poorly to news of breaches. Stock sell-offs are common, leading to a drop in market value. This reaction can affect not just the company involved but the market as a whole.
Even on a broader scale, national economic growth can be stunted. Widespread cyber attacks create a sense of insecurity. This can slow investments and innovation, harming overall economic progress.
Cybercrime and its Effect on Different Economic Sectors
Cybercrime significantly impacts various economic sectors. The financial sector is often a primary target due to the direct monetary gain. Banks and financial institutions face constant threats, leading to substantial losses that can affect the whole economy.
The healthcare sector is another key target. Cyber attacks on hospitals can disrupt patient care and access to medical records. This not only endangers lives but also incurs high costs to restore and secure critical systems.
In the retail sector, cybercrime leads to theft of customer data. Breaches can result in massive financial penalties and loss of customer trust. Retailers must invest heavily in cybersecurity to protect their data systems.
Even the public sector is not immune. Government agencies face attacks aimed at stealing sensitive information. These breaches can compromise national security and require extensive resources to address.
A Closer Examination of Notable Cyber Attacks and Their Economic Consequences
Cyber attacks like the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack highlight severe economic damage. Targeting over 200,000 computers in 150 countries, it caused millions in losses. The healthcare industry, particularly the UK’s NHS, was extensively disrupted.
The Equifax breach in 2017 exposed personal data of 147 million people. The company faced heavy fines and legal fees, estimated to cost $1.4 billion. This breach also led to a decline in consumer confidence in credit reporting agencies.
In 2014, Sony Pictures suffered a significant cyber attack. Attackers stole and released sensitive employee data and unreleased films. This caused substantial financial and reputational damage to Sony.
The 2013 Target breach resulted in the theft of 40 million credit and debit card records. Target spent approximately $202 million on legal fees, settlement costs, and security upgrades. Customers’ trust in the retail giant plummeted.
Yahoo experienced multiple breaches between 2013 and 2014, impacting all 3 billion user accounts. The consequence was not only financial loss but a drop in market value by $350 million. It also complicated Yahoo’s sale to Verizon.
The Colonial Pipeline attack in 2021 disrupted fuel supply across the U.S. East Coast. The company paid a ransom of $4.4 million to restore operations. The attack highlighted vulnerabilities in critical national infrastructure.
The Ripple Effect: Indirect Economic Consequences of Cybercrime
Cybercrime extends its impact beyond immediate financial losses. One ripple effect is the loss of consumer trust, which can take years to rebuild. When consumers feel unsafe, they hesitate to engage in online transactions.
Another indirect consequence is the negative impact on job markets. Companies suffering from cyber attacks often slow hiring processes. Some may even lay off employees to balance the financial burden caused by breaches.
Additionally, cybercrime can stifle innovation within affected companies. Instead of investing in new technologies, resources are diverted to security measures. This can hinder overall market progress and technological advancements.
Supply chain disruptions are also a significant concern. A cyber attack on one supplier can halt production lines. This delay affects not only the company but also its partners and customers.
The cost of cyber insurance is another indirect economic impact. As breaches become more frequent, insurance premiums rise. Businesses must allocate more funds to cover these higher costs.
Ultimately, the combined effect of these indirect consequences can lead to a weaker economic outlook. Both individual companies and entire sectors may face prolonged recovery periods. The broader economy absorbs these shocks, leading to slower growth rates.
How the U.S. Economy is Responding to the Cybersecurity Threats
The U.S. economy is increasingly focusing on bolstering its cybersecurity defenses. Both public and private sectors are investing heavily in advanced technologies. With rising cyber threats, this focus has become crucial for economic stability.
Government initiatives play a significant role in response strategies. Agencies like the Department of Homeland Security are implementing stricter regulations. They’ve introduced programs to assist businesses in enhancing their cybersecurity infrastructure.
The private sector is also making strides in cybersecurity. Companies are hiring specialized cybersecurity professionals to safeguard their systems. Cybersecurity training programs for employees are now commonplace.
Investment in research and development is crucial. The U.S. is funding various projects aimed at creating more secure technologies. This includes blockchain solutions and advanced encryption methods.
Cyber insurance has also gained prominence. Businesses are increasingly purchasing policies to cover potential losses from cyber incidents. This trend underscores the serious economic impact of cybersecurity threats.
Collaboration is key in the fight against cybercrime. Many companies are now working with cybersecurity firms for continuous monitoring. Information sharing between private companies and government agencies has improved.
The Role of Cybersecurity Industry in U.S. Economy
The cybersecurity industry is a key player in the U.S. economy. It generates billions of dollars annually, creating a significant economic impact. This industry not only protects but also drives economic growth.
One major contribution is job creation. The demand for cybersecurity professionals is higher than ever. This demand has led to numerous opportunities across various sectors.
Innovation within the industry fuels advancements in technology. Companies invest in developing new tools and software to combat cyber threats. This, in turn, encourages other industries to integrate these innovations.
Cybersecurity firms often collaborate with other businesses. These partnerships ensure continuous monitoring and protection against evolving threats. Such collaborations enhance overall economic resilience.
- Job creation and employment opportunities
- Continuous technological innovation
- Strengthened partnerships with diverse industries
- Pushing economic resilience and growth
The industry also plays a role in education and training. Universities and institutions now offer specialized cybersecurity programs. This helps prepare the next generation of experts to tackle cyber threats effectively.
| Contribution | Impact on Economy |
|---|---|
| Job Creation | Increases employment rates, boosts consumer spending |
| Innovation | Keeps the U.S at the forefront of tech development |
| Partnerships | Adds strength to business ecosystems through collaboration |
Looking Ahead: Future Economic Implications of Cyber Threats
Cyber threats are expected to evolve and become more sophisticated. This will likely lead to increased financial losses. Businesses will need to allocate more resources to cybersecurity measures.
Future regulatory changes could also impact the economy. As cyber threats grow, governments may introduce stricter cybersecurity laws. Compliance with these regulations can be costly for businesses.
The rise of emerging technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) can help combat cyber threats. However, these technologies can also be exploited by cybercriminals.
Consumer confidence might take a hit if cyber threats continue to escalate. Fear of data breaches can deter people from engaging in online transactions. This would impact e-commerce and other digital markets.
Supply chains could face further disruptions. Cyber attacks on key suppliers can halt production and delivery. This can ripple through the economy, affecting various sectors.
Lastly, the focus on cybersecurity might spur job creation. As demand for cybersecurity experts increases, new job opportunities will emerge. This can help mitigate some of the economic impacts of cyber threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cybersecurity threats are a pressing concern, affecting both individuals and the economy. Here are some common questions and detailed answers to help you understand these issues better.
1. What is the main cause of cybersecurity threats?
The primary cause of cybersecurity threats is often the exploitation of vulnerabilities in systems. Hackers use techniques like phishing, malware, and ransomware to gain unauthorized access.
Additionally, human error also plays a significant role. Incorrectly configured systems or weak passwords can provide easy targets for cybercriminals. Continuous education and updates can mitigate these risks.
2. How do cybersecurity breaches impact small businesses?
For small businesses, a cybersecurity breach can be devastating. They face high recovery costs, sometimes leading to bankruptcy.
Moreover, these businesses might lose crucial customer trust. Without strong security measures, small businesses become easy targets for repeated attacks.
3. What industries are most vulnerable to cyber attacks?
Banks and financial institutions are prime targets due to their access to sensitive financial data. Healthcare providers also face significant risks because they store valuable medical records.
The retail industry is another frequent target due to the vast amount of customer data they manage daily. These sectors need robust security protocols to protect against such threats effectively.
4. Why is employee training important in cybersecurity?
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Training them about recognizing phishing emails and safe internet practices reduces vulnerabilities.
This knowledge empowers employees to act more cautiously online and helps prevent accidental data breaches. Regular training sessions ensure that everyone stays updated on best practices.
5. What steps can companies take to improve their cybersecurity posture?
Companies should regularly update their software systems and use strong encryption methods for data protection. Implementing multi-factor authentication also adds an extra layer of security.
Creating a solid incident response plan ensures quick action when a breach occurs. Regular audits and vulnerability assessments help identify potential weaknesses before they’re exploited.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity threats pose significant challenges to the U.S. economy. They affect not only financial stability but also consumer trust and business operations. Addressing these threats proactively is crucial for maintaining economic resilience.
By investing in advanced technologies and strong cybersecurity measures, both private and public sectors can mitigate these risks. Collaboration and continuous education are key. Ensuring robust defenses will help safeguard the nation’s economic future.
