When you walk into your neighborhood bank, have you ever thought about its impact on the broader economy? The evolution of retail banking trends—ranging from the advancement of digital banking to the diversification of financial products—affects not just individual finances but also the entire U.S. economic landscape. This interplay between consumer behavior and banking innovations is a powerful engine driving economic shifts.
Historically, shifts in retail banking have mirrored significant economic changes, with the advent of ATMs in the 1960s and online banking in the late 20th century climbing to the fore. A staggering 56% of Americans now prefer online banking, a trend accelerating economic digitization. Such retail banking advancements not only streamline financial transactions but also boost consumer spending and savings, directly influencing GDP growth.
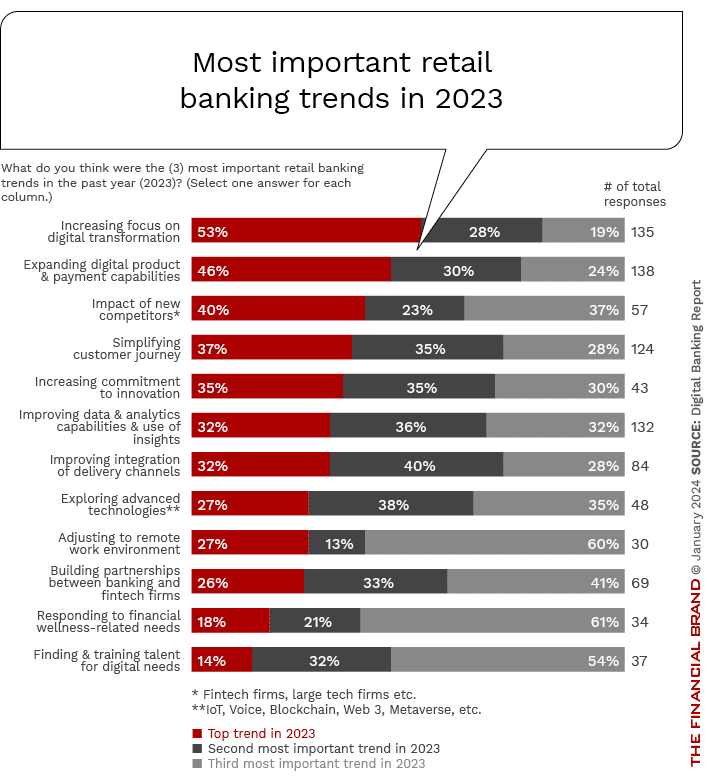
Impact of Digitalization on Retail Banking and U.S. Economy
With the rise of digitalization, retail banking has undergone dramatic changes. Traditional brick-and-mortar banks are now offering extensive online services, making banking more accessible. This shift has significantly influenced consumer banking habits, leading to greater convenience and speed.
One of the major impacts on the economy is the increased efficiency of financial transactions. Digital banking allows for faster and cheaper transactions, boosting economic activities. This accessibility propels business operations and consumer spending, driving economic growth.
Another key aspect is the enhanced data analytics capabilities. Digitalization enables banks to gather and analyze vast amounts of customer data. This leads to personalized financial products and better customer service, which in turn strengthens the economic relationship between banks and consumers.
Moreover, digital platforms have promoted financial inclusion. People in remote areas can now access banking services which were previously out of reach. This inclusivity broadens the economic base, contributing to overall economic stability and growth.
Emerging Trends in Retail Banking
Retail banking is constantly evolving with new trends shaping the future. These trends are transforming how customers interact with banks and how banks operate. Keeping up with these trends is crucial for staying competitive.
Mobile Banking and App Culture
One of the biggest trends in retail banking is mobile banking. Customers increasingly prefer managing finances through their smartphones. This trend enhances convenience and enables 24/7 accessibility.
Banks are now launching sophisticated mobile apps. These apps offer various services such as fund transfers, bill payments, and even loan applications. This shift towards mobile apps has significantly reduced the need for physical bank visits.
Moreover, the app culture is driving personalized banking experiences. Machine learning and AI are used to understand customer behavior. This helps in offering tailor-made financial solutions.
Artificial Intelligence and Chatbots
Artificial intelligence (AI) is making a big impact in retail banking. AI-powered chatbots are becoming a common feature on banking websites. These chatbots provide real-time customer support and answer queries instantly.
AI systems are also used for fraud detection and risk management. They can analyze numerous transactions in seconds and identify suspicious activities. This improves the security of banking services.
Additionally, AI helps in automating routine tasks. Banks can process loans and manage accounts more efficiently. This leads to faster and more accurate service.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is another crucial trend. It offers a high level of transparency and security by decentralizing data storage. Banks are exploring blockchain for secure, fast transactions.
One significant use of blockchain in banking is in verifying identities. It helps in reducing fraud and ensuring compliance. This technology also makes cross-border transactions quicker and cheaper.
Blockchain’s use is expanding beyond payments. Banks are adopting it for smart contracts and record keeping. This has the potential to revolutionize traditional banking systems.
Role of Financial Technology (Fintech) in Retail Banking
Financial technology, or Fintech, is significantly reshaping retail banking. It bridges the gap between technology and financial services, offering innovative solutions. These innovations have streamlined many banking processes.
One of the most notable roles of Fintech is in enhancing customer experience. Mobile payment systems and digital wallets are becoming the norm. This technology makes transactions faster and more convenient.
Fintech also plays a critical role in offering personalized financial services. Advanced algorithms analyze customer data to provide tailored banking solutions. This customization improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Moreover, Fintech is boosting financial inclusion. It provides access to banking services for unbanked and underbanked populations. This inclusivity supports economic growth and stability.
Retail Banking and Consumer Spending
Retail banking plays a vital role in shaping consumer spending habits. When banks offer easy-to-access credit options, consumers are more likely to make purchases. Credit cards and personal loans encourage spending, which boosts the economy.
Savings accounts and investment options impact how much money people save versus spend. Higher interest rates on savings accounts can encourage people to save more. Conversely, lower rates might lead them to spend instead of saving.
Online banking features like budgeting tools help consumers manage their money better. These tools can show spending patterns and help set financial goals. This promotes more responsible spending behavior.
Retail banks also offer incentives like cash-back rewards and discounts. These perks entice customers to use bank services more frequently. This increases both consumer spending and bank profitability.
Access to loans and mortgages from retail banks is crucial for big purchases. Consumers can buy homes, cars, and other high-cost items with these loans. This level of spending fuels different sectors of the economy.
Retail banks also contribute to financial literacy by offering educational programs. These programs teach consumers about budgeting, saving, and investing wisely. Informed consumers tend to make smarter financial decisions, which positively affects the economy.
Changes in Banking Regulations and their Economic Influence
Banking regulations are constantly evolving to ensure financial stability. These changes often impact how banks operate and how consumers interact with them. Regulations aim to protect both the economy and individual consumers.
Stricter lending guidelines can influence consumer borrowing. When banks have to follow more rigorous rules, it becomes harder for people to get loans. This can slow down spending and economic growth.
Changes in capital requirements also affect banks. Higher capital reserves mean banks have to hold more money in reserve. This reduces the amount available for loans, impacting businesses and consumers.
Regulations around digital banking and cybersecurity are critical. Banks must invest in advanced security measures to protect customer data. This ensures trust and stability in the financial system.
New laws on transparency and disclosure can increase consumer confidence. When banks are required to be more transparent, customers feel safer. This can lead to increased banking activities and economic engagement.
Regulatory changes can also incentivize green banking. Encouraging banks to invest in sustainable projects can have a positive environmental and economic impact. This aligns financial goals with broader societal benefits.
The Relationship between Interest Rates and Retail Banking
Interest rates play a huge role in retail banking. They influence how much people borrow and save. Central banks set the baseline rates which retail banks follow.
When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper. Consumers are more likely to take out loans for homes, cars, and other big purchases. This boosts spending and stimulates the economy.
On the flip side, low-interest rates can discourage saving. People are less inclined to put money in savings accounts with lower returns. Instead, they might spend more, further influencing economic activity.
Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive. This can slow down consumer spending as loans become pricier. High rates often encourage saving, as people prefer to earn more interest on their deposits.
The balance between interest rates and inflation is also crucial. Retail banks must navigate changing rates to maintain profitability. They adjust their loan and deposit rates accordingly.
Banks use competitive interest rates to attract customers. Offering better rates than competitors can bring in more deposits and loans. This helps banks grow their customer base and assets.
Influence of Retail Banking on Small Businesses
Retail banking has a significant impact on small businesses. Access to loans and credit is crucial for growth. Banks provide essential financial resources needed for startups and expansions.
Smaller banks often serve as lifelines for local businesses. They offer personalized services tailored to unique needs. This fosters strong community bonds.
Business checking accounts help manage daily transactions. Many banks offer specialized accounts with features like low fees and payroll services. These accounts make business operations smoother.
Banks also provide merchant services, enabling card payments from customers. This boosts sales by making payment options more flexible. Convenience can lead to higher customer satisfaction.
Moreover, retail banks offer advisory services. They guide small businesses on financial planning, investments, and risk management. This expert advice can be invaluable.
Financial technology from banks helps in managing finances efficiently. Apps and online tools simplify everything from invoicing to expense tracking. This frees up time for business owners to focus on growth.
Retail Banking’s Role in Financial Inclusion
Retail banking plays a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion. It provides access to essential financial services for everyone, including underserved and rural communities. This access helps people manage their money more effectively.
One significant way retail banking achieves this is through branch expansion. Banks establish branches in remote areas to offer services like savings accounts and loans. This presence helps integrate more people into the financial system.
Another essential service provided by retail banks is the introduction of basic banking accounts. These accounts require minimal documentation and are easy to open. Such initiatives make banking accessible to low-income individuals.
Digital banking platforms are also enhancing financial inclusion. Mobile banking apps allow people to access banking services right from their phones. This is particularly beneficial for those who can’t easily visit physical branches.
Moreover, retail banks offer financial literacy programs. These programs educate consumers on managing finances, understanding credit, and making investments. Better-informed customers can make smarter financial decisions.
Access to microloans is another way retail banks support financial inclusion. These small loans help individuals and small businesses get started. Microloans can be a stepping stone to greater economic stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore common questions about how retail banking trends shape the U.S. economy. These answers will help you understand the far-reaching impacts of these transformations.
1. What are the key trends in retail banking today?
The key trends in retail banking include digitalization, mobile banking, and artificial intelligence (AI). Digital services streamline operations and offer customers 24/7 access to their finances, boosting efficiency and engagement.
AI helps in personalizing customer experiences by analyzing data for tailored financial solutions. Additionally, blockchain technology is enhancing security and transparency, making financial transactions more secure.
2. How does digitalization impact consumer behavior in retail banking?
Digitalization drastically changes how consumers interact with banks. With online and mobile platforms, users now have convenient access to banking services anytime, anywhere.
This accessibility promotes more regular interaction with financial institutions. It also encourages better financial management through easy-to-use tools like budgeting apps and automated savings plans.
3. How do interest rates affect retail banking and the broader economy?
Interest rates directly influence how much consumers borrow or save money. Lower rates make loans cheaper, encouraging spending on big purchases like homes and cars.
This increased spending stimulates economic growth. In contrast, higher interest rates encourage savings over borrowing, which can slow down economic activity but help control inflation.
4. Why is financial inclusion important for the U.S. economy?
Financial inclusion ensures that everyone has access to essential financial services like savings accounts and credit facilities. This inclusivity boosts overall economic health by enabling more people to contribute to economic activities.
Moreover, when more people are financially included, there is a broader tax base for public investments such as infrastructure development projects that drive further economic growth.
5. What role do banks play in supporting small businesses?
Banks provide crucial support to small businesses through loans and lines of credit necessary for startup capital or expansion efforts. These financial resources are vital for operational sustainability and growth.
Banks also offer various advisory services that guide small business owners on best financial practices such as managing funds efficiently or investing wisely for future gains.
Conclusion
The evolving trends in retail banking have substantial effects on the U.S. economy. Digitalization, fintech innovations, and regulatory changes are reshaping how consumer and business finances operate. These advancements contribute significantly to economic growth and stability.
Moreover, retail banking plays a critical role in promoting financial inclusion and supporting small businesses. By adapting to new technologies and regulatory frameworks, banks can continue to enhance their services. This ensures a more inclusive and robust economy for the future.

