Global infrastructure investment is projected to reach a staggering $94 trillion by 2040. This enormous figure indicates the vast opportunities available for investors seeking to tap into sectors like transportation, energy, and telecommunications. As cities expand and populations grow, the need for modern, efficient infrastructure becomes critical.
Historically, infrastructure projects have been a linchpin for economic development and productivity. For instance, every dollar invested in public infrastructure generates approximately $1.92 in economic activity. By focusing on sustainable and resilient infrastructure, investors can not only achieve impressive returns but also contribute to long-term growth and stability.
Exploring the Investment Landscape in Infrastructure
The Current State of Infrastructure Investment
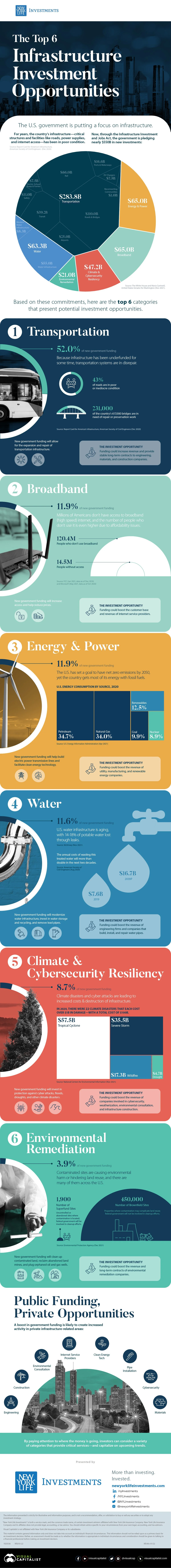
Infrastructure investment is on the rise globally, driven by growing urban populations and the need for modernization. Governments and private companies are pouring funds into projects like roads, bridges, and energy systems. This influx of capital creates numerous opportunities for investors.
In the United States, infrastructure has become a priority, with billions allocated to repair and enhance existing systems. Emerging markets also present fertile ground for investment, offering high growth potential. These regions often need new infrastructure to support their rapid development.
Despite the optimism, challenges remain in securing reliable funding and navigating regulatory landscapes. Changing political climates can affect the pace and scale of infrastructure rolls. Yet, the demand for improved systems remains robust, ensuring continued investment.
Key Sectors for Infrastructure Investment
Transportation is a critical sector, including investments in highways, railways, and airports. Modernizing these systems is essential to support economic activity and mobility.
Energy infrastructure is another vital area, focusing on both traditional and renewable energy sources. With the shift towards sustainability, investors are increasingly interested in green energy projects. This shift is supported by government incentives and public demand for cleaner energy.
Digital infrastructure is becoming as crucial as physical infrastructure. Investments in broadband and wireless networks ensure communities stay connected. These investments are critical for both urban and rural areas to support growth and innovation.
Understanding Risk Factors in Infrastructure Investment
Investing in infrastructure involves several risks, including project delays and cost overruns. Political instability can impact project timelines and funding. Investors need to be aware of these risks and plan accordingly.
Market risks, such as fluctuating demand and economic downturns, can also affect returns. Diversification can help mitigate some of these risks. Spreading investments across different sectors and regions can balance potential losses.
Environmental factors pose another set of risks. Natural disasters can damage infrastructure, leading to unforeseen expenses. Strong risk management strategies are essential for sustainable investment success.
Capitalizing on the Rewards of Infrastructure Investment
The rewards of investing in infrastructure can be substantial, including long-term, stable returns. Public-private partnerships often provide lucrative opportunities. These collaborations leverage both public funds and private expertise.
Infrastructure investments also promote economic growth and job creation. They can stimulate local economies and improve living standards. This dual benefit makes infrastructure an attractive investment avenue.
Sustainable infrastructure projects offer added benefits, including environmental and social impacts. Green projects can attract additional funding and public support. Investors can feel good about contributing to a sustainable future.
The Current State of Infrastructure Investment
Infrastructure investment is increasingly vital as countries modernize and expand. In recent years, both public and private sectors have boosted spending. This trend reflects the growing importance of resilient and efficient infrastructure systems.
Government Initiatives
Many governments are launching ambitious infrastructure plans to spur economic growth. These initiatives include upgrading transportation networks and improving energy systems. Such projects often receive significant funding and policy support.
For example, the U.S. recently passed a substantial infrastructure bill worth billions. This bill aims to repair aging roads and bridges and enhance public transit. Such government actions create vast opportunities for infrastructure investments.
In developing countries, governments focus on building new infrastructure from scratch. These regions need modern facilities to support their rapid growth and urbanization. Hence, they attract global investors looking for high returns.
Private Sector Involvement
Private companies are also major players in infrastructure development. They often enter public-private partnerships to share risks and rewards. These collaborations help accelerate project completion and improve efficiency.
In the energy sector, private investments are driving the shift to renewable energy. Solar and wind projects are attracting substantial capital, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This shift not only offers financial returns but also promotes environmental sustainability.
Additionally, technology firms are investing in digital infrastructure. Broadband expansion, 5G networks, and data centers are key focus areas. These investments are essential for the digital transformation of economies.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite significant progress, infrastructure investment faces various challenges. Political instability and regulatory hurdles can delay projects. Nevertheless, the demand for modern infrastructure continues to grow.
Environmental concerns are another critical factor. Sustainable projects, like green buildings and renewable energy systems, are gaining traction. Investors are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly initiatives.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and IoT offer new opportunities. These can enhance infrastructure efficiency and safety. Investing in smart technologies can provide competitive advantages.
Key Sectors for Infrastructure Investment
Transportation is one of the most crucial sectors for infrastructure investment. This includes roads, railways, and airports. Efficient transportation networks boost economic activity and enhance mobility.
Energy infrastructure is another vital area. Investments in both traditional and renewable energy sources are essential. With increasing focus on sustainability, green energy projects are particularly attractive.
Water management systems also offer substantial investment opportunities. These include water supply networks, sewage treatment facilities, and irrigation systems. Reliable water infrastructure is crucial for public health and agriculture.
Lastly, digital infrastructure is gaining importance. High-speed internet, data centers, and 5G networks are critical for modern economies. These investments support digital transformation and innovation.
Navigating the Risks and Rewards of Infrastructure Investment
Investing in infrastructure comes with both risks and rewards. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions. Balancing risks with potential rewards can lead to successful investments.
One significant risk is project delays. Delays can be caused by regulatory approvals or construction challenges. Such issues can increase costs and impact returns.
Another risk involves budget overruns. Infrastructure projects are complex and often run over budget. This can affect the overall profitability of the investment.
Despite these risks, there are considerable rewards. Infrastructure investments often offer long-term, stable returns. These steady income streams make infrastructure an attractive investment option.
Moreover, public-private partnerships can amplify rewards. These collaborations combine public funding with private expertise. Such partnerships can expedite project completion and enhance efficiency.
Additionally, sustainable infrastructure projects offer unique benefits. Green energy and eco-friendly constructions are increasingly popular. Investors not only gain financial returns but also contribute to a sustainable future.
Understanding Risk Factors in Infrastructure Investment
Investing in infrastructure carries several risks, starting with political instability. Changes in government policies can delay or halt projects. This unpredictability can significantly impact returns.
Another important risk is regulatory hurdles. Compliance with local laws and regulations can be complex and time-consuming. Investors often need to navigate different layers of bureaucracy.
Financial risks are also a major concern. Budget overruns and unexpected costs can erode profit margins. Cost management practices are essential to mitigate these risks.
Natural disasters and environmental factors pose additional risks. Floods, earthquakes, and other events can damage infrastructure. This can lead to significant repair costs and project delays.
Technological risks are becoming increasingly relevant. As infrastructure projects incorporate more technology, the risk of cyber-attacks grows.
- Key risk factors:
- Political instability
- Regulatory hurdles
- Financial risks
- Natural disasters
- Technological risks
Capitalizing on the Rewards of Infrastructure Investment
The rewards of infrastructure investment are often substantial. These projects generally offer long-term, stable returns. This makes them an attractive option for investors seeking reliability.
Public-private partnerships can further enhance these rewards. Combining public funding with private sector expertise can expedite project timelines. This collaboration often leads to higher efficiency and profitability.
Besides financial returns, infrastructure investments contribute to economic growth. Building new roads, bridges, and energy systems stimulates job creation. Communities benefit through improved services and better quality of life.
Investing in sustainable infrastructure adds another layer of rewards. Green projects like renewable energy and eco-friendly buildings attract additional capital. These initiatives also garner public support and can lead to quicker approvals.
Digital infrastructure projects offer high growth potential as well. Investments in high-speed internet and 5G networks enable technological advancements.
- Key rewards of infrastructure investment:
- Stable returns
- Economic growth
- Sustainable impact
- Technological advancement
Case Studies: Successful Infrastructure Investments
One of the most successful infrastructure investments is the Panama Canal expansion. This project doubled the canal’s capacity, allowing it to handle larger ships. The expansion has significantly boosted global trade efficiency.
Another great example is the London Crossrail project. This massive railway construction connects east and west London, reducing travel times. It has spurred economic growth in surrounding areas by improving connectivity.
Renewable energy projects in Denmark have also seen impressive returns. Denmark invested heavily in wind farms, becoming a leader in renewable energy. These investments not only provide sustainable power but also generate revenue through energy exports.
The IDFC’s Digital Infrastructure Fund in India is noteworthy too. By investing in broadband networks across rural areas, it has enhanced internet access and digital services. This initiative has opened up new economic opportunities for remote communities.
- Successful infrastructure investment highlights:
- Panama Canal Expansion
- London Crossrail Project
- Denmark’s Wind Farms
- IDFC’s Digital Infrastructure Fund in India
The Sydney Metro project is another example of effective infrastructure investment. This urban rail system improves Sydney’s public transport network and reduces traffic congestion. Its success demonstrates how well-planned projects can transform cities and enhance quality of life.
Spotlight: Infrastructure Investments in Emerging Economies
Infrastructure investments in emerging economies are creating new opportunities. These regions often have high growth potential and a pressing need for development. Investors are capitalizing on this demand to achieve impressive returns.
China is a prime example, with its Belt and Road Initiative. This massive project aims to enhance trade routes across Asia, Europe, and Africa. It has attracted billions in investment and spurred economic development.
In Africa, countries like Kenya are investing in modern transportation systems. The Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway is a significant project. It has reduced travel time and logistics costs, boosting local economies.
India’s infrastructure sector is also growing rapidly. Projects like the Golden Quadrilateral highway network connect major cities. This network enhances trade and transportation efficiency.
- Key examples in emerging economies:
- Belt and Road Initiative in China
- Mombasa-Nairobi Railway in Kenya
- Golden Quadrilateral in India
Brazil’s renewable energy sector shows promising growth. Investments in wind and solar energy are expanding rapidly. These projects provide sustainable power and create jobs.
Spotlight: Green Infrastructure Investments
Green infrastructure investments are gaining traction worldwide. These projects focus on sustainability and environmental benefits. They offer long-term returns while promoting eco-friendly practices.
One standout example is Norway’s expansion of wind energy. Norway has invested heavily in offshore wind farms. These projects generate substantial clean energy, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
In the United States, green building initiatives are flourishing. Many cities are adopting LEED-certified construction standards. These buildings use less energy and water, making them more sustainable.
Singapore’s commitment to green infrastructure is also noteworthy. The city-state has integrated green spaces into urban design. Rooftop gardens and vertical forests help reduce urban heat and improve air quality.
- Key examples of green infrastructure:
- Norway’s wind farms
- LEED-certified buildings in the U.S.
- Green spaces in Singapore
Germany leads in solar energy investments. The country has implemented numerous solar farms. These initiatives produce renewable energy and generate local employment opportunities.
Shaping the Future with Infrastructure Investments
Infrastructure investments play a crucial role in shaping the future. These projects not only improve current systems but also pave the way for sustainable development. They ensure long-term economic growth and enhanced quality of life.
One key area is smart cities. These urban areas use technology to optimize resources and improve efficiency. Investments in smart infrastructure include sensors, data analytics, and automated systems.
Another important aspect is resilience. Building infrastructure that can withstand natural disasters and climate change is essential. Resilient infrastructure protects communities and reduces future costs.
Transportation advancements are also crucial for the future. High-speed rail networks and electric vehicle infrastructure reduce carbon footprints. These investments make travel faster and more sustainable.
- Future-focused infrastructure projects:
- Smart cities
- Resilient systems
- Advanced transportation
Renewable energy projects will continue to grow. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are key to reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Investments in these sectors contribute to a cleaner, greener future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Investing in infrastructure can seem complex, but breaking it down makes it simpler. Here are common questions and answers to help you understand better.
1. What are the main benefits of investing in infrastructure?
Investing in infrastructure brings long-term stability and profits. It creates jobs and boosts economic growth, making communities stronger.
Additionally, well-planned projects like renewable energy can protect the environment. Infrastructure investment also improves daily life by upgrading public services such as transport and utilities.
2. How does government support impact infrastructure investment?
Government support is crucial for large-scale infrastructure projects. It provides essential funding and policy backing that attracts private investors.
Support from the government ensures smoother approvals and regulatory compliance. This backing helps mitigate risks, making investment more appealing to stakeholders.
3. Why is digital infrastructure becoming a vital investment sector?
Digital infrastructure includes internet networks and data centers, essential in our tech-driven world. Investing here supports faster communication, innovation, and business growth.
It also levels the playing field by connecting rural areas with urban hubs. High-speed internet enables remote work and access to global information resources.
4. What risks should investors consider when investing in green infrastructure?
The primary risks involve technological changes and regulatory shifts. New regulations could alter project viability or profitability over time.
Sustained technological innovation is critical yet uncertain. Investors must stay updated on advancements to ensure long-term project success in green sectors like renewable energy.
5. How do public-private partnerships (PPPs) function in infrastructure investments?
P Public-Private Partnerships combine resources from both sectors for efficient project execution.. The public sector often offers funding or land, while private entities bring technical expertise/
This collaboration reduces financial burden on each party involved while maximizing benefits.Some notable PPP examples include highways built with private construction firms or airports managed through public oversight but operated privately.Such initiatives accelerate progress without compromising quality..