Consider this: the top 1% of global earners control almost 50% of the world’s wealth. This stark reality forces us to question the mechanisms underpinning economic equity. How can macroeconomics play a role in bridging this gaping chasm?
Macroeconomics, with its focus on broad economic factors and policies, has the potential to promote economic justice. The Keynesian Revolution, for example, highlighted the importance of government intervention in economic inequalities. By examining fiscal policies, redistribution mechanisms, and employment strategies, we can forge a path towards a more equitable economic landscape.
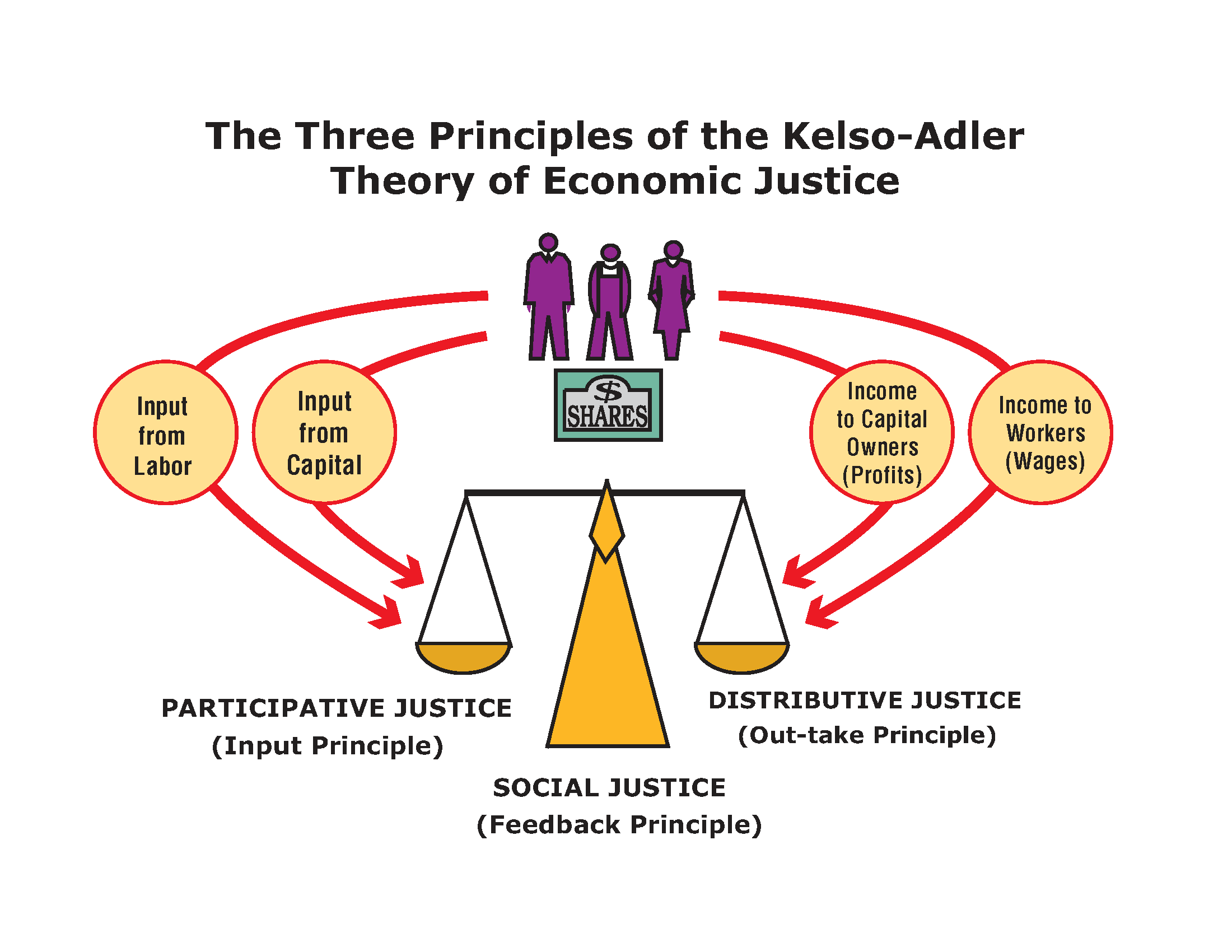
Exploring the Link Between Macroeconomics and Economic Justice
Economic justice means everyone gets a fair chance to succeed. It’s not just about wealth but also about opportunities and rights. Macroeconomics plays a crucial role in this process.
Macroeconomics studies the health of the entire economy. It focuses on big factors like GDP, unemployment, and inflation. These elements can significantly impact economic justice.
Fiscal policy is one way macroeconomics influences economic justice. When the government adjusts taxes and spending, it can help reduce inequality. For instance, higher taxes on wealthy individuals can fund programs for the less fortunate.
Monetary policy also matters. By controlling interest rates and money supply, central banks can influence economic stability. This, in turn, affects jobs and income distribution.
Defining Economic Justice in a Macroeconomic Context
Economic justice involves creating a system where everyone has equal economic opportunities. This includes ensuring fair wages and eliminating discrimination. In a macroeconomic context, it means using policy tools to balance the economy.
A fair economy leads to a more stable society. Programs like social security and minimum wage laws are examples of economic justice in action. They help reduce poverty and provide safety nets for the vulnerable.
Education and access to healthcare are also crucial. When everyone can afford school and medical care, they have better chances to succeed. These aspects boost productivity and, ultimately, the economy.
The Role of Macroeconomic Policies in Shaping Economic Justice
Macroeconomic policies can either help or hinder economic justice. Effective policies aim to reduce inequality and support growth. They must be carefully designed and implemented.
- Fiscal policies like progressive taxes.
- Government spending on social programs.
- Monetary policies that promote stable inflation.
Balancing these factors is tricky but essential. The goal is to create a fair and thriving economy for all. Policymakers must continuously adapt to changing conditions.
Challenges to Achieving Economic Justice Through Macroeconomics
There are many hurdles to economic justice. Political resistance and economic constraints often slow progress. External factors like trade wars can also throw a wrench in the works.
Moreover, achieving balance is difficult. Policies need constant monitoring and adjustment. Unexpected economic downturns can derail even the best plans.
Despite these challenges, striving for economic justice is vital. A fairer economy benefits everyone. It leads to a more harmonious and productive society.
Defining Economic Justice in a Macroeconomic Context
Economic justice means fairness in the way economic policies impact people. It ensures everyone has equal opportunities to succeed and thrive. In a macroeconomic context, this involves broad policies that influence the whole economy.
The Principles of Economic Justice
Economic justice rests on key principles like fairness and equal opportunity. Policies must ensure that resources are fairly distributed. This helps reduce disparities in wealth and income.
Social programs and progressive taxation are tools used to achieve economic justice. These measures support those in need and promote economic stability. By addressing inequality, they contribute to a more balanced economy.
Other principles include access to education, healthcare, and employment. When everyone has equal access to these resources, the economy becomes stronger. These principles are essential for a just economic system.
Impact of Macroeconomic Policies on Economic Justice
Macroeconomic policies can significantly affect economic justice. Fiscal policies, for example, involve government spending and taxation. These policies can either reduce or increase economic disparities.
- Tax cuts for low-income families.
- Increased spending on public services.
- Subsidies for affordable housing.
Monetary policies are also crucial. These include controlling interest rates and money supply. Effective monetary policies can promote stable economic growth and reduce inequality.
Challenges in Ensuring Economic Justice
There are many obstacles to achieving economic justice. Political resistance can hinder the implementation of fair policies. Economic constraints also pose challenges.
For example, balancing the budget while addressing inequality is difficult. External factors like global trade tensions can impact economic stability. These challenges require careful and continuous policy adjustments.
Despite these difficulties, pursuing economic justice is essential. It leads to a fairer, more stable society. Effective macroeconomic policies can make a significant difference.
The Role of Macroeconomic Policies in Shaping Economic Justice
Macroeconomic policies have a significant impact on economic justice. They can determine how wealth and resources are distributed. Effective policies aim to reduce inequality and promote fairness.
Fiscal policies are crucial in this regard. By adjusting taxes and government spending, policymakers can help level the playing field. For example, higher taxes on the wealthy can fund social programs for those in need.
Monetary policies also play a role. Central banks control interest rates and money supply to stabilize the economy. These actions can influence employment and income distribution.
- Progressive taxation to reduce wealth gaps.
- Subsidies for essential services like healthcare and education.
- Monetary measures to keep inflation in check.
Impact of Fiscal Policies on Economic Justice
Fiscal policies are powerful tools that shape economic justice. They involve government spending and taxation. These policies can influence the distribution of wealth and resources.
Progressive taxation is one such policy. It means higher-income individuals pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. This helps reduce income inequality and funds social programs.
Government spending plays a crucial role too. By investing in healthcare, education, and social services, the government can support those in need. These investments create a safety net for the vulnerable.
- Affordable housing programs.
- Subsidized healthcare services.
- Free or low-cost education.
Fiscal policies can also target employment. Job creation programs and subsidies for small businesses can reduce unemployment. This promotes economic stability and fairness.
Effective fiscal policies require careful planning and execution. Balancing the budget while addressing inequality is challenging. Yet, these efforts are essential for achieving economic justice.
Role of Monetary Policies
Monetary policies are essential in managing a country’s economy. These policies control the money supply and interest rates. Central banks, like the Federal Reserve, are responsible for implementing them.
One key function is regulating interest rates. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper. This can lead to increased spending and investment, boosting economic activity.
Another tool is adjusting the money supply. By printing more money or reducing it, central banks can control inflation. Low inflation helps maintain the value of money and ensures stability in the economy.
- Setting benchmark interest rates.
- Buying or selling government bonds.
- Changing reserve requirements for banks.
Monetary policies can also impact employment. By promoting steady economic growth, these policies help create jobs. This leads to reduced unemployment and greater stability.
Effective monetary policies require careful monitoring. Central banks must be responsive to changes in the global economy. Their decisions can have wide-reaching consequences for both individuals and businesses.
Case Studies: Macroeconomics Leading to Economic Justice
Several countries have successfully used macroeconomic policies to achieve economic justice. These case studies show how strategic decisions can make a big difference. Let’s look at a few examples.
Sweden is often cited as a model for economic justice. Through progressive taxation and extensive social programs, Sweden has narrowed the income gap. The country invests heavily in education and healthcare, benefiting all citizens.
Another example is Germany. After reunification, Germany implemented policies to boost economic activity in the East. These measures included infrastructure investments and job creation programs, which helped reduce regional inequalities.
- Affordable housing initiatives
- Workforce training programs
- Support for small businesses
Brazil has also made strides in economic justice, especially through the Bolsa Família program. This social welfare program provides financial aid to low-income families. It aims to reduce poverty and improve health and education outcomes.
These case studies demonstrate the power of thoughtful macroeconomic policies. By focusing on fairness and equity, countries can create more just and stable economies. These examples offer valuable lessons for policymakers worldwide.
The Keynesian Revolution and Economic Justice
The Keynesian Revolution was a significant shift in economic thinking. It introduced the idea that government intervention can stabilize the economy. This change aimed to address issues like unemployment and inequality.
John Maynard Keynes, the movement’s founder, argued for active fiscal policies. He believed that government spending could boost demand during economic downturns. This approach aimed to create jobs and support those affected by recessions.
- Increased public works projects.
- Expanded social welfare programs.
- Progressive taxation to fund these initiatives.
The New Deal in the United States is a classic example of Keynesian policies in action. Introduced during the Great Depression, it included various social and economic programs. These measures helped reduce poverty and improve living standards.
Other countries adopted similar approaches, leading to widespread acceptance of Keynesian economics. By focusing on government intervention, these policies promoted more balanced growth. They provided safety nets for vulnerable populations while stimulating economic activity.
The legacy of the Keynesian Revolution remains relevant today. Many modern economies rely on its principles during crises. Its focus on economic justice through policy intervention continues to inspire governments worldwide.
Challenges to Achieving Economic Justice Through Macroeconomics
Achieving economic justice through macroeconomics is difficult. Political resistance often slows progress. Many policies face opposition from different interest groups.
Economic constraints also pose significant challenges. Governments must balance budgets while addressing inequality. This requires careful and strategic planning.
External factors like global trade tensions can impact domestic economic stability. For instance, trade wars can harm local industries and increase unemployment. These external pressures complicate policy implementation.
- Fluctuating global markets.
- Natural disasters affecting economies.
- Sudden shifts in consumer behavior.
Another challenge is maintaining policy effectiveness over time. Economic conditions change, requiring constant adjustment. Policymakers must stay adaptable to new data and trends.
Socioeconomic disparities can also make implementation difficult. Different regions may require tailored approaches. This complexity adds another layer to achieving economic justice through macroeconomic policies.
The Struggles of Implementing Sustainable Fiscal Policies
Creating sustainable fiscal policies is challenging. Balancing short-term needs with long-term goals requires careful thought. Politicians often face pressure to deliver quick results, making sustainability harder to achieve.
One major hurdle is political resistance. Different parties have varying priorities, leading to conflicts. These disagreements can delay or alter important policies.
Economic conditions also play a role. In times of recession, governments may need to increase spending. However, this can lead to budget deficits, complicating sustainability efforts.
- Maintaining balanced budgets.
- Deciding on spending cuts or tax increases.
- Managing public debt.
Public opinion is another factor. People may resist changes that affect their daily lives. For example, raising taxes to fund sustainable programs can be unpopular.
Global influences can disrupt plans. International trade, currency fluctuations, and foreign policies can impact domestic fiscal policies. Policymakers must be adaptable to these changes.
The Future: Macroeconomics and the Pursuit of Economic Justice
The future of economic justice lies in innovative macroeconomic policies. Governments must focus on inclusivity and sustainability to ensure fairness. Emerging technologies can also play a crucial role in this transformation.
Global collaboration is essential. Countries need to work together to address common economic challenges. This includes tackling issues like climate change and income inequality.
- Investing in renewable energy.
- Supporting global education initiatives.
- Creating fair trade agreements.
Technological advancements offer new opportunities. Automation and AI can boost productivity but must be managed wisely. Policies should aim to distribute the benefits of technology evenly.
Public awareness and education are also key. People need to understand the importance of economic justice. An informed public can advocate for better policies and hold leaders accountable.
Looking ahead, the balance between growth and equity will be crucial. Policymakers must be flexible and responsive to changing global dynamics. The pursuit of economic justice will require continuous effort and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Macroeconomics plays a crucial role in shaping economic justice. Here are some commonly asked questions to help you understand this relationship better.
1. What is the difference between fiscal and monetary policies?
Fiscal policy involves government spending and taxation decisions. It’s used to influence the economy by managing levels of spending and taxation. For instance, increasing taxes on the wealthy can fund social programs for those in need.
Monetary policy, on the other hand, deals with controlling the money supply and interest rates. It’s managed by a country’s central bank, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States. Low-interest rates can encourage borrowing and investing, stimulating economic activity.
2. How does progressive taxation promote economic justice?
Progressive taxation means higher-income individuals pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes compared to low-income earners. This approach helps reduce income inequality by redistributing wealth through government services and welfare programs.
The collected tax revenue funds essential services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure development. When these services are accessible to everyone, it creates a fairer society where opportunities aren’t limited by financial status.
3. Can macroeconomic policies reduce unemployment?
Yes, macroeconomic policies can target job creation to reduce unemployment rates. Government spending on public works projects or subsidies for businesses can create new jobs and boost employment levels.
Moreover, lowering interest rates through monetary policy can encourage investment in new ventures, leading to more job openings. Higher employment contributes to economic stability and reduces poverty.
4. What role do international trade agreements play in economic justice?
International trade agreements can significantly influence economic justice by opening markets and creating job opportunities. Fair trade practices ensure that developing countries benefit from globalization while protecting workers’ rights.
A well-designed trade agreement promotes sustainable development by reducing tariffs on essential goods and encouraging investment in underdeveloped regions. This helps balance global inequality and supports inclusive growth worldwide.
5. How does public opinion impact macroeconomic policies?
Public opinion often shapes government priorities regarding economic policies. When there is strong support for measures addressing inequality and fairness, policymakers are more likely to implement such initiatives.
An informed public advocates for effective fiscal policies like progressive taxation or increased social spending. Thus, understanding citizens’ needs fosters better decision-making aimed at achieving long-term economic justice goals.
Conclusion
Macroeconomics and economic justice are deeply interconnected. Effective policies can reduce inequality and promote fairness in society. By addressing the root causes of economic disparity, we pave the way for a more equitable future.
The journey towards economic justice requires constant effort and adaptation. Policymakers must balance short-term needs with long-term goals. With the right strategies, we can create a stable and just economy for all to thrive in.
