It’s fascinating to note that, according to the International Monetary Fund, global GDP contracted by 4.4% in 2020, the sharpest decline since the Great Depression. This statistic underscores the critical role of macroeconomics in understanding and navigating economic tumult. By examining aggregate indicators like GDP, unemployment rates, and inflation, macroeconomists provide essential insights for policymakers.
Macroeconomics has evolved significantly since John Maynard Keynes published his groundbreaking work in the 1930s. Measuring economic performance has since become increasingly sophisticated, integrating complex models and diverse data sources. For instance, real-time economic tracking now offers a more nuanced view, aiding in more timely and effective policy decisions.
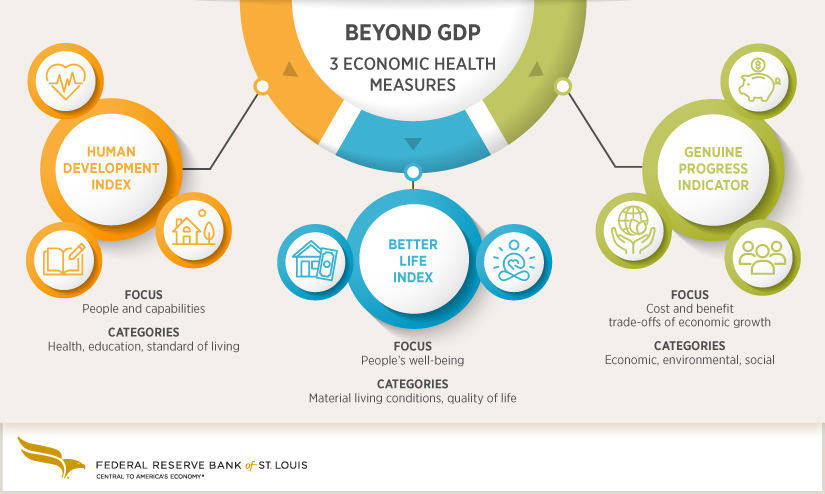
Exploring the World of Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the economy as a whole. It looks at big-picture factors like national productivity and the total amount of goods and services produced. This helps in understanding economic growth and stability.
Macroeconomics also examines total investment and savings in an economy. These factors influence interest rates and financial markets. By studying these, economists can make predictions about future economic trends.
Another critical area is the analysis of governmental fiscal policies, like taxes and spending. These policies can boost or slow down the economy. Understanding how these policies work helps in creating effective economic strategies.
The study of international economics is a crucial aspect. It involves understanding trade between countries and exchange rates. This knowledge is essential for assessing a country’s economic performance in a global context.
The Role of Macroeconomics in Economic Analysis
Macroeconomics plays a vital role in shaping government policies. By examining economic indicators, policymakers make informed decisions. This can lead to stabilizing the economy during uncertain times.
Businesses also rely on macroeconomic analyses to plan their strategies. For example, knowing the trend in consumer spending can help businesses adjust their production levels. This ensures efficient resource allocation.
Macroeconomic studies are crucial for investment decisions. Investors look at economic data to decide whether to buy or sell assets. Understanding macroeconomic trends helps investors minimize risk and maximize returns.
Key Concepts and Principles of Macroeconomics
One fundamental concept in macroeconomics is Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP measures the total economic output of a country. This indicator is essential for assessing economic health.
Another key principle is the unemployment rate. It shows the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed but actively seeking work. High unemployment rates usually signal economic distress.
Inflation is another important concept. It measures how prices for goods and services rise over time. Understanding inflation helps in predicting purchasing power and cost of living.
The Role of Macroeconomics in Economic Analysis
Macroeconomics helps us understand the bigger picture of the economy. It examines factors like national income, employment, and inflation. These insights are crucial for making informed decisions.
By analyzing macroeconomic data, governments can design better policies. They use this data to decide on things like taxes and spending. Effective policies can stabilize the economy and promote growth.
Businesses also rely on macroeconomic analysis. It helps them forecast demand and make investment choices. Better understanding of economic trends can lead to more profitable outcomes.
Investors use macroeconomic indicators to guide their decisions. For example, they might look at GDP growth rates or inflation trends. This information helps them minimize risk and maximize returns.
Measuring Economic Performance
Economic performance is measured using various indicators. The most common is Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP tells us the total value of goods and services produced in a country.
Unemployment rate is another critical measure. It indicates the percentage of people actively seeking work but unable to find jobs. High unemployment usually signals economic trouble.
Inflation rate is also vital. It measures how quickly prices for goods and services are rising. High inflation can erode purchasing power and savings.
The Impact of Fiscal Policies on Economy
Fiscal policies, such as government spending and taxation, directly affect the economy. By increasing spending, the government can stimulate growth. Conversely, higher taxes can slow down economic activity.
Governments often use fiscal policies to combat economic downturns. For instance, they may lower taxes to encourage spending. More spending can kickstart economic recovery.
However, fiscal policies must be carefully balanced. While increased spending can boost the economy, it can also lead to higher debt. Finding the right balance is crucial for sustainable growth.
The Role of Monetary Policies
Monetary policies are managed by a country’s central bank. These policies control the money supply and interest rates. Lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending.
The central bank can also use policies to control inflation. By adjusting interest rates, they can influence how much people save or spend. Effective monetary policies help stabilize the economy.
Monetary policies are especially important during economic crises. Quick adjustments can provide immediate relief and set the stage for recovery. Central banks play a crucial role in maintaining economic stability.
Key Concepts and Principles of Macroeconomics
One key concept in macroeconomics is Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country. It serves as an essential indicator of economic health.
Another important principle is the unemployment rate. The unemployment rate represents the percentage of the labor force that is jobless but actively seeking work. A high unemployment rate usually indicates economic problems.
Inflation is also critical in understanding macroeconomics. Inflation measures how the prices of goods and services rise over time. It affects purchasing power and can influence economic policies.
Interest rates are another fundamental aspect. They determine the cost of borrowing money. Lower interest rates generally encourage borrowing and spending.
Understanding Economic Performance Measurement
Economic performance measurement is crucial for assessing a country’s economic health. It involves using various indicators to evaluate how well an economy is functioning. These indicators help in making informed decisions.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the most common measurement. GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced. A growing GDP usually indicates a healthy economy.
The unemployment rate is another vital indicator. It shows the percentage of people actively seeking work but unable to find jobs. High unemployment rates often signal economic distress.
Inflation rate is also an essential measure. It tracks how quickly prices for goods and services are rising. Understanding inflation helps in planning and policy-making.
Other important indicators include interest rates and trade balances. Interest rates affect the cost of borrowing money. Trade balances show the difference between exports and imports.
These measurements are often presented in economic reports. Governments, businesses, and investors rely on these reports to make strategic decisions. Accurate economic measurements are key to effective planning and growth.
Significance of Economic Performance Indicators
Economic performance indicators are crucial for assessing an economy’s health. They provide valuable data that helps in understanding various economic aspects. These indicators guide policymakers, businesses, and investors.
Indicators like GDP and unemployment rate offer insights into economic growth and job market health. GDP shows the total value of goods and services, while unemployment rate indicates joblessness levels. Both are essential for planning and policy-making.
Inflation rate is another significant indicator. It measures how quickly prices for goods and services are rising. High inflation impacts purchasing power and can lead to economic instability.
Interest rates influence borrowing and spending habits. Lower interest rates usually encourage borrowing and stimulate economic activity. Conversely, higher rates can cool down an overheating economy.
Trade balance is also important. It shows the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A positive trade balance indicates more exports than imports, which is generally favorable.
By analyzing these indicators, we can make informed decisions. For example, businesses can adjust their strategies based on economic forecasts. Reliable economic performance indicators are key to successful planning and growth.
Methods of Measuring Economic Performance
Measuring economic performance involves various methods and indicators. The most well-known is Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP measures the total economic output of a country.
Another method is the unemployment rate. This indicator shows the percentage of people who are actively seeking work but cannot find jobs. High unemployment usually signals economic issues.
Inflation rate is also crucial. It measures how quickly prices for goods and services rise over time. A steady inflation rate is generally a sign of a healthy economy.
Interest rates set by the central bank play a significant role. Lower interest rates usually stimulate economic growth by encouraging borrowing. Higher rates can slow down the economy to prevent inflation.
Trade balance is another important metric. It compares the value of exports to imports. A positive trade balance means a country exports more than it imports.
These methods collectively provide a comprehensive view of economic health. Policymakers, businesses, and investors rely on them to make informed decisions. Accurate measurement is key to effective economic planning and growth.
In-Depth Look at GDP as an Economic Performance Metric
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a key measure of economic activity. It represents the total value of goods and services produced in a country over a specific period. This makes it a crucial indicator for evaluating economic health.
GDP can be calculated using three approaches: production, income, and expenditure methods. The production approach sums the value of outputs produced minus inputs used. The income approach totals all incomes earned by residents.
The expenditure method is perhaps the most common. It adds up consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports (exports minus imports). This method provides insights into how different sectors contribute to the economy.
An increasing GDP typically signifies economic growth and prosperity. However, it’s important to consider other factors like income inequality and environmental costs. GDP does not account for these issues or social well-being.
Countries with higher GDPs generally have more resources for education, healthcare, and infrastructure. These investments further stimulate economic growth and development. This creates a positive cycle of prosperity.
| Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Production | Value of outputs minus inputs |
| Income | Total incomes earned by residents |
| Expenditure | Adds up consumption, investment, government spending, net exports |
Calculating GDP: The Formula and Components
Calculating Gross Domestic Product (GDP) involves adding up various components of a nation’s economy. The most common formula is GDP = C + I + G + (X – M). Each letter represents a different part of economic activity.
C stands for consumption, which is the total value of goods and services consumed by households. This is typically the largest part of GDP. It includes spending on items like food, clothing, and entertainment.
I is for investment, representing business and government investments in capital goods. This includes spending on new buildings, machinery, and infrastructure projects. Investments are crucial for future economic growth.
G stands for government spending, which covers all government expenditures on goods and services. This includes things like defense, education, and public services. Government spending plays a key role in stimulating the economy.
(X – M) represents net exports, which is the value of a country’s exports minus its imports. A positive net export number boosts GDP, while a negative number reduces it. This component shows how a nation interacts with the global economy.
| Component | Explanation |
|---|---|
| C (Consumption) | Household spending on goods and services |
| I (Investment) | Business and government spending on capital goods |
| G (Government Spending) | Government expenditures on public services |
| (X – M) | Net exports, exports minus imports |
Strengths and Shortcomings of GDP as a Prosperity Indicator
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a widely used indicator of economic prosperity. One major strength is that GDP provides a clear measure of a country’s total economic output. This helps compare the economic performance of different nations.
Another strength of GDP is its ability to track economic growth over time. By measuring changes in GDP, one can see if an economy is expanding or contracting. This makes it useful for policy-making and economic planning.
However, GDP has its shortcomings. It does not account for income inequality. A high GDP might hide the fact that wealth is unevenly distributed.
GDP also fails to consider environmental costs. Economic activities that harm the environment can still increase GDP. This makes GDP an incomplete measure of well-being.
Another limitation is that GDP does not measure the informal economy. Many economic activities, like household work or black-market transactions, are not included. This can lead to an underestimation of a country’s actual economic activity.
Despite its limitations, GDP remains a crucial tool for assessing economic performance. It provides invaluable insights but should be used alongside other indicators for a well-rounded view. Combining GDP with other measures can offer a more accurate picture of prosperity.
Other Vital Economic Performance Indicators
Besides GDP, several other indicators are crucial for assessing economic health. One important measure is the unemployment rate. It shows the percentage of people without jobs but actively looking for work.
The inflation rate is another key indicator. It measures how fast prices for goods and services are rising. High inflation can reduce purchasing power and savings.
Interest rates also play a significant role in the economy. Managed by a country’s central bank, they influence borrowing and spending habits. Lower interest rates usually encourage economic activity.
The trade balance measures the difference between exports and imports. A positive trade balance indicates more exports, which is generally good for the economy. This shows a country’s competitiveness in global markets.
Consumer confidence is yet another vital indicator. It reflects how optimistic consumers are about the economy. High consumer confidence often leads to increased spending, boosting economic activity.
These indicators together offer a comprehensive view of economic performance. Relying on multiple measures provides a more accurate picture. Good policy decisions depend on understanding all these aspects of the economy.
Unemployment Rates: Interpretation and Impact
The unemployment rate is a vital economic indicator. It measures the percentage of the labor force that is jobless but actively seeking work. A high unemployment rate usually signifies economic problems.
Lowering the unemployment rate is crucial for economic stability. Jobs provide incomes that people spend on goods and services. This spending boosts the economy.
High unemployment can lead to various social issues. When people are out of work for long periods, they may experience financial hardship and lower well-being. This can increase poverty levels and strain social services.
Governments use different policies to manage unemployment rates. They may create job programs or offer tax incentives to businesses that hire more workers. These actions can help reduce unemployment.
Unemployment rates also affect investor confidence. High unemployment can make investors wary of economic stability. Lower rates generally make a country more attractive for investment.
| Effect | Impact |
|---|---|
| High Unemployment | Economic instability, increased poverty |
| Low Unemployment | Economic growth, higher investor confidence |
Inflation Rates: Understanding Its Effects
The inflation rate measures how quickly prices for goods and services are rising. A moderate inflation rate is normal and can be a sign of a growing economy. However, high inflation can be problematic.
High inflation reduces purchasing power. When prices rise quickly, the money you have buys less. This can make everyday items more expensive.
Low inflation or deflation (falling prices) is also problematic. It can lead to reduced business investment and spending. People may delay purchases, expecting lower prices in the future.
Central banks use monetary policies to manage inflation. They might raise interest rates to reduce spending and cool down the economy. Lowering interest rates can stimulate economic activity and help control deflation.
Inflation rates affect different groups in various ways. While borrowers may benefit from decreasing real debt, savers can lose value on their savings. This creates a complex economic landscape.
- High Inflation: Reduces purchasing power.
- Low Inflation: Can slow down the economy.
- Central Bank Actions: Tools to manage and control inflation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Macroeconomics is a fascinating field that deals with the big picture of the economy. Below are some commonly asked questions to help you understand this complex subject better.
1. What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
Gross Domestic Product, or GDP, measures the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period. It’s crucial because it helps gauge the economic health of a nation.
A growing GDP indicates economic prosperity, while a shrinking one can signal economic trouble. Policymakers use GDP figures to make informed decisions and craft strategies for growth.
2. How does inflation impact the economy?
Inflation refers to the rate at which prices for goods and services rise. High inflation reduces purchasing power, making everyday items more expensive for consumers.
This can lead to wage demands and sometimes even an economic slowdown if unchecked. Central banks often adjust interest rates to control inflation, aiming for stable economic growth.
3. Why is unemployment an important economic indicator?
The unemployment rate measures how many people in the labor force are jobless but seeking employment. High unemployment suggests an underperforming economy and can lead to social issues like increased poverty.
Conversely, low unemployment usually signifies robust economic health but could also indicate impending labor shortages. Governments focus on this metric when crafting policies to foster job creation.
4. What role do interest rates play in macroeconomics?
Interest rates set by central banks influence borrowing costs for individuals and businesses. Lower rates typically encourage spending and investment, boosting economic activity.
On the other hand, higher interest rates aim to cool down an overheating economy by discouraging excessive spending and borrowing. Understanding these dynamics helps economists predict trends.
5. How does trade balance affect a country’s economy?
The trade balance compares the value of exports with imports. A positive trade balance means more goods are being exported than imported, generally seen as favorable for economic health.
A negative balance could indicate dependency on foreign goods and services, affecting domestic industries negatively. Policymakers watch this closely to support balanced international trade relations.
Conclusion
Understanding macroeconomics and economic performance measurement is vital for navigating the complexities of modern economies. These insights help governments, businesses, and investors make informed decisions. By focusing on key indicators like GDP, unemployment rates, and inflation, we can better comprehend economic trends.
While each indicator has its strengths and weaknesses, using them together offers a more complete picture. Therefore, effective economic strategies require a balanced approach. Constantly updating and analyzing these metrics ensures adaptive and resilient economic policies.
