Consider the ripple effect of an unexpected interest rate hike by the central bank: a mere 1% increase can lead to substantial shifts across financial markets. For instance, investors may withdraw from riskier stocks and flock towards safer bonds. The dynamic interplay between interest rates and investments essentially reshapes the economic landscape in ways that demand continuous analysis.
Historically, periods of low interest rates have spurred significant investment in equities and real estate, driving economic growth. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis saw central banks slashing interest rates to near zero to stimulate investment. Conversely, a 2022 report indicated that even moderate rises in interest rates could increase the cost of capital, potentially reducing corporate investment by up to 10%.
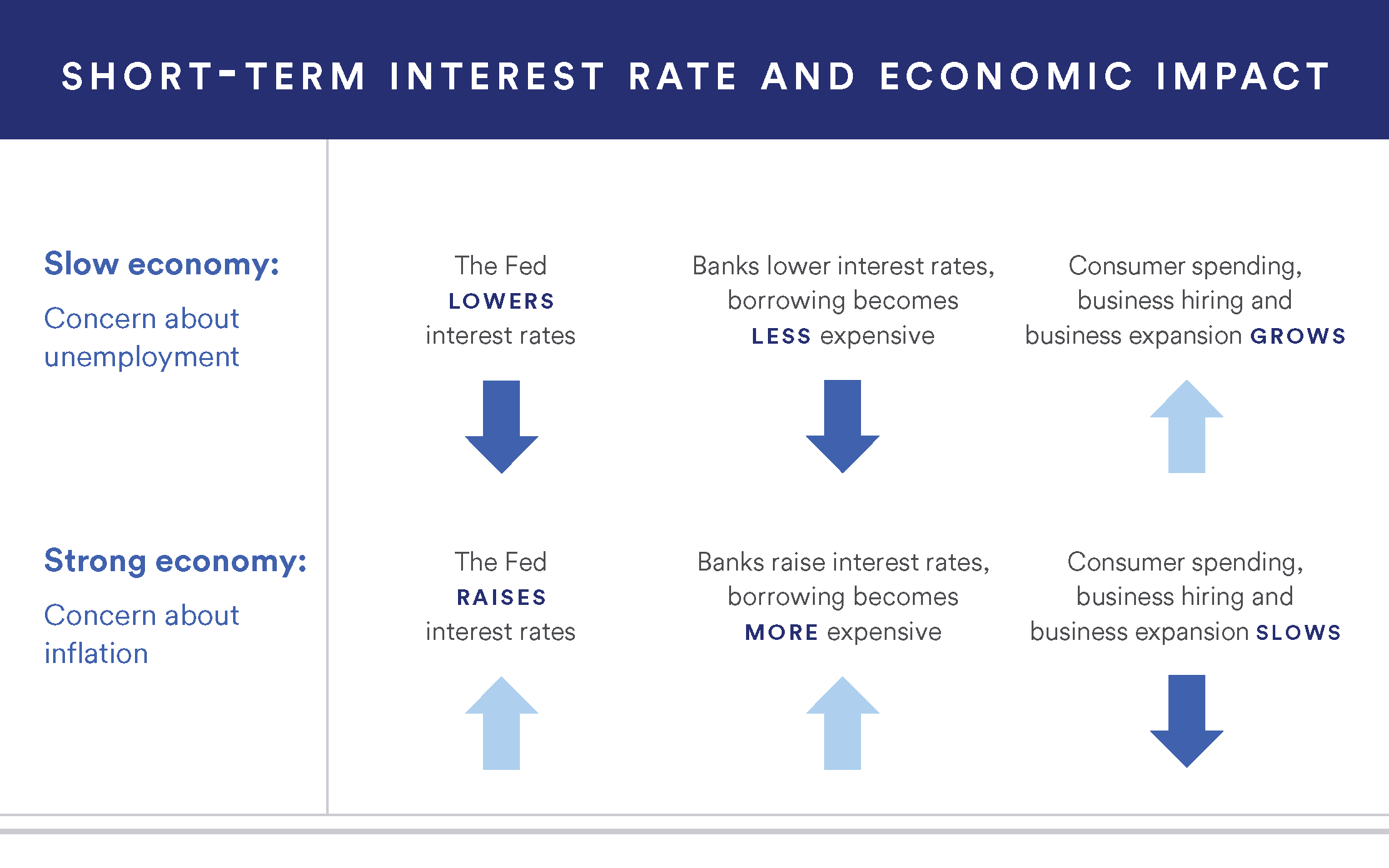
The Relationship between Interest Rates and Investments
The Basic Principle: Why Interest Rates Affect Investment Decisions
When interest rates change, they directly influence the amount people borrow or save. For instance, higher interest rates make borrowing costlier, reducing investment in new projects. Lower rates encourage more spending and investment.
The change in interest rates also affects asset prices. If rates go up, bonds become more attractive, making stocks less appealing. This can cause stock prices to fall.
Similarly, when interest rates drop, loans for homes and businesses become cheaper. Investors are then more likely to invest in higher-risk stocks for better returns.
The Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Stocks and Bonds
As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases. This can discourage companies from taking on new debt. Consequently, they may scale back on expansion plans.
For stocks, higher rates often mean lower earnings. Investors might sell off stocks, driving prices down. Bonds, however, can become more appealing, as they offer stable returns.
Higher interest rates also mean higher returns on savings accounts. Investors might shift money from stocks to these safer options.
The Effect of Declining Interest Rates on Real Estate and Equities
When interest rates fall, borrowing costs decrease, making it cheaper to buy homes and invest in businesses. This boosts the real estate market. Home prices can rise as demand increases.
For the stock market, lower rates can lead to higher corporate profits. Companies benefit from cheaper loans, allowing more investment in projects. This often leads to higher stock prices.
Additionally, investors seek better returns in a low-rate environment. They may turn to equities over bonds, pushing stock prices even higher. This dynamic helps boost overall economic growth.
The Basic Principle: Why Interest Rates Affect Investment Decisions
Interest rates directly influence decisions about borrowing, saving, and investing. When rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, so fewer people take out loans. Conversely, lower rates encourage borrowing and spending.
This change in borrowing costs affects how businesses and individuals allocate their money. Higher rates typically mean less investment in new projects. Lower rates can stimulate economic growth by promoting spending and investment.
Interest rates also play a pivotal role in determining asset prices. If rates increase, bonds become more attractive, often leading to a drop in stock prices. This is because investors seek safer returns.
Additionally, declining interest rates make alternative investments like real estate and equities more appealing. Businesses expand more and consumers spend more. This usually leads to higher profits for companies and higher stock prices.
How High Interest Rates Affect Borrowing and Spending
When interest rates rise, loans and credit become costlier. Mortgages, car loans, and credit card debt all incur higher interest charges. This decreases disposable income and spending.
Businesses also feel the pinch with higher borrowing costs. Funds for expansion or new projects become pricier. This can lead companies to delay or cancel investments.
The impact is felt across multiple sectors. Consumers hold back on big purchases, and businesses restrict growth. The overall economy can slow down as a result.
The Role of Central Banks in Setting Interest Rates
Central banks, like the Federal Reserve, control the base interest rate. They adjust rates to manage economic conditions. Raising rates can curb inflation, while lowering them can spur growth.
These decisions are based on various economic indicators. Employment data, consumer spending, and inflation rates play significant roles. The goal is to maintain a balanced economy.
Central bank policies directly impact financial markets. Investors closely watch rate announcements. A change in interest rates can bring about immediate shifts in stock and bond prices.
How Investors Adapt to Changing Interest Rates
Investors often shift strategies based on interest rate changes. In a high-rate environment, bonds become more attractive. Stocks may see lower demand as a result.
Conversely, low interest rates push investors to seek higher returns in stocks. Real estate and other high-yield investments gain appeal. This dynamic reshapes the investment landscape.
Some savvy investors diversify their portfolios. Balancing bonds, stocks, and real assets can mitigate risks. This approach helps navigate through varying interest rate conditions.
The Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Stocks and Bonds
As interest rates go up, the stock market often reacts negatively. Companies face higher borrowing costs, which can lead to reduced profits. This makes stocks less attractive to investors.
Bonds, on the other hand, may become more appealing when rates rise. They offer fixed returns, which become more attractive compared to volatile stocks. Higher interest rates typically drive more investment into bonds.
However, existing bonds with lower interest rates can lose value. Investors prefer new bonds offering higher returns, leading to a drop in the market value of older bonds. This shift can create challenges for long-term bondholders.
This interest rate hike can also affect consumer behavior. With higher interest rates, saving accounts and bonds become more attractive. People might shift their money away from stocks to these safer investments.
The Effect of Declining Interest Rates on Real Estate and Equities
When interest rates decline, real estate markets often see a boom. Lower rates mean cheaper mortgages, making homes more affordable. This increase in demand can push home prices higher.
For businesses, lower interest rates reduce borrowing costs. Companies can then finance new projects at a lower expense, boosting growth. This leads to more hiring and higher profits.
In the stock market, lower rates make bonds less attractive. Investors seek higher returns from equities. This influx of investment typically drives stock prices up.
Declining rates also encourage consumer spending. With cheaper loans, people are more likely to buy big-ticket items. This boost in spending benefits retail and manufacturing sectors.
However, low interest rates can create asset bubbles. Real estate prices may rise too quickly, potentially leading to market corrections. Both investors and policymakers need to watch for these risks.
In summary, while lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth, they also bring challenges. Balancing the benefits and risks is crucial for sustained prosperity. Investors must stay informed to make the best decisions.
Interest Rates Change and Economic Consequences
Interest rate changes have a ripple effect across the economy. When rates rise, borrowing costs increase, which can slow economic activity. Consumers and businesses spend less due to higher loan expenses.
Conversely, lower rates make borrowing cheaper. This often stimulates growth as more people and companies take out loans. Increased spending boosts demand, driving economic expansion.
The labor market is also affected by interest rate changes. Higher rates usually lead to slower job growth. Employers may cut back on hiring due to increased financial burdens.
Inflation can be controlled through interest rates. Central banks like the Federal Reserve raise rates to cool down an overheating economy. This helps keep prices stable, protecting purchasing power.
Changes in interest rates impact global trade. Stronger economies might attract foreign investments. This can affect exchange rates and trade balances, altering international economics.
Financial markets quickly react to interest rate decisions. Stocks, bonds, and currencies experience volatility with each change. Investors adjust their strategies in response to central bank policies.
The Macro Perspective: Interest Rates and the Wider Economy
Interest rates set by central banks shape the entire economy. Higher interest rates tend to slow economic growth. Companies invest less due to higher borrowing costs.
Conversely, lower rates boost economic activity. Cheaper loans encourage businesses and consumers to spend. This increases demand for goods and services.
Global trade also feels the effects of interest rate changes. Countries with higher rates may attract foreign investment. This impacts currency exchange rates.
Employment rates are linked to interest rate levels. Higher rates can lead to job cuts, as businesses face increased costs. Conversely, lower rates often boost hiring.
Interest rates also influence housing markets. Lower rates make mortgages more affordable, driving up home purchases. This can lead to higher real estate prices.
The stock market reacts swiftly to changes in interest rates. Investors adjust portfolios based on rate expectations. This creates volatility in financial markets.
Interest Rates Effect on Corporate Decisions
Interest rates play a crucial role in corporate decision-making. When rates are high, borrowing costs increase, making expansions and new projects less attractive. Companies may delay or cancel investments as a result.
Lower interest rates create an environment conducive to growth. Cheaper loans allow companies to finance new projects more easily. This leads to increased hiring and business expansion.
The cost of financing affects the overall operational budget. Higher interest payments reduce available funds for other needs. Firms must balance debt repayment with daily operations.
Savings and investments are also influenced by interest rates. Companies prefer lower-cost options for holding cash reserves. Higher rates may push them toward more conservative financial decisions.
- High-interest environment: Increased financing costs, reduced investment
- Low-interest environment: Easier access to funds, more investment
The impact extends to stock market valuations too. Investors consider interest rates when estimating future corporate profits. This can lead to fluctuations in stock prices based on rate changes.
Investor Strategies in Varying Interest Rate Conditions
Investors need to adapt their strategies based on fluctuating interest rates. In a high-rate environment, bonds become more attractive because they offer stable returns. This makes stocks less appealing, leading to a shift in investment portfolios.
When interest rates are low, investors often turn to equities for better returns. Lower borrowing costs encourage corporate growth, boosting stock prices. Real estate investments also become more appealing due to cheaper mortgages.
Diversification is a key strategy for managing risk in varying interest rate conditions. Balancing investments in stocks, bonds, and real estate can help mitigate risk. This approach ensures that some assets perform well, regardless of rate changes.
- High-rate environment: Prioritize bonds, reduce stock exposure
- Low-rate environment: Increase stock and real estate investments
- Diversified portfolio: Balance across various asset classes
Investors should also consider the economic cycle. During growth periods, interest rates generally rise, making bonds safer. In economic downturns, lower rates boost stocks and real estate.
Adapting Your Investment Strategy to Rising Interest Rates
When interest rates rise, adjusting your investment strategy is crucial. High interest rates make borrowing more expensive. This often leads to reduced corporate profits. It is essential to consider safer investments like bonds.
Diversifying your portfolio is another key strategy. Spread your investments across various asset classes like stocks, bonds, and real estate. This approach can help protect against market volatility.
Investing in sectors that typically perform well during rising rates can also be beneficial. For example, financial stocks often fare better. Banks can charge more for loans, increasing their profits.
- Bonds: Offer stability and steady returns
- Financial stocks: Benefit from higher loan rates
- Diversified portfolio: Reduces risk and volatility
Lastly, keeping an eye on inflation is important. Higher interest rates are often used to control rising prices. Understanding this relationship can help you make informed investment decisions.
Investing Successfully in a Low-Interest Rate Environment
Investing in a low-interest rate environment requires a strategic approach. Equities often become more attractive as bonds yield lower returns. Investors should consider diversifying their portfolios into stocks.
Real estate investments can also be lucrative. Low-interest rates mean cheaper mortgages. This can drive up property values and rental incomes.
It’s essential to seek out high-dividend stocks. These stocks provide a steady income, compensating for the lower returns from savings accounts and bonds. Steady dividends can offer financial stability.
- Equities: Offer higher returns compared to bonds
- Real estate: Benefits from cheaper mortgages and high demand
- High-dividend stocks: Provide a reliable income stream
Consider investing in sectors that benefit from low borrowing costs. Technology and consumer goods often perform well. These sectors capitalize on increased consumer spending and investment.
Finally, global investments can offer additional opportunities. Countries with varying interest rates can present new avenues for growth. Diversifying internationally can help mitigate local market risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Interest rates play a crucial role in shaping investment decisions. Understanding their impact can help investors make strategic choices.
1. How do interest rate hikes affect bond prices?
When interest rates go up, existing bonds with lower rates become less appealing. Investors prefer new bonds offering higher returns, which can lead to a drop in the market value of older bonds.
This decrease happens because the fixed interest payments from existing bonds are less attractive. Therefore, their prices fall to align with the new, higher-yielding bonds available in the market.
2. Why might stock prices decline when interest rates rise?
Higher interest rates mean increased borrowing costs for companies, reducing their profit margins. This decrease in profitability often leads investors to sell off stocks, causing prices to drop.
Additionally, higher rates make bonds and savings accounts more attractive due to better returns. Investors may move money out of stocks and into these safer options.
3. What is the effect of low-interest rates on real estate investments?
Low-interest rates make mortgages cheaper, encouraging more people to buy homes. This increased demand usually drives up home prices and boosts real estate market activity.
For investors, cheaper loans mean lower financing costs for property purchases and developments. This scenario can lead to higher rental incomes and greater property appreciation.
4. How do central banks influence interest rates?
Central banks like the Federal Reserve set base interest rates to control economic stability. By raising or lowering these rates, they aim to manage inflation and stimulate economic growth or slow down an overheating economy.
Their decisions are informed by various economic indicators such as employment, inflation, and consumer spending data. These adjustments directly impact financial markets and overall economic conditions.
5. What strategies should investors use in a high-interest rate environment?
Diversification becomes essential when interest rates rise. Balancing investments between stocks, bonds, and real estate can mitigate risks associated with fluctuating markets caused by rising borrowing costs.
Bonds often become more attractive as they offer steady returns despite high-rate conditions. Investing in sectors like finance that benefit from higher loan yields can also be advantageous during such times.
How does raising interest rates control inflation?
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of interest rates on investments is crucial for making informed decisions. Whether rates are rising or falling, each scenario presents unique opportunities and challenges. By adapting strategies accordingly, investors can optimize their portfolios for various economic conditions.
Interest rates influence every aspect of the financial market, from bonds to stocks to real estate. Keeping an eye on these changes helps investors stay ahead of market trends. Ultimately, informed decision-making leads to better financial outcomes and long-term success.
