In 2022, the U.S. real estate market contributed more than $4 trillion to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), illustrating its pivotal role in the economy. The significance of this sector cannot be understated, as it encompasses residential, commercial, and industrial properties. This diverse portfolio impacts job creation, wealth accumulation, and even government revenue through property taxes.
The roots of real estate’s influence date back to post-World War II, when suburban housing boomed and fueled economic growth. Today, core metropolitan areas generate substantial economic activity. With nearly 5.4 million existing homes sold in 2021, the housing market continues to be a bellwether of economic health, reflecting broader trends and cyclical shifts in the economy.
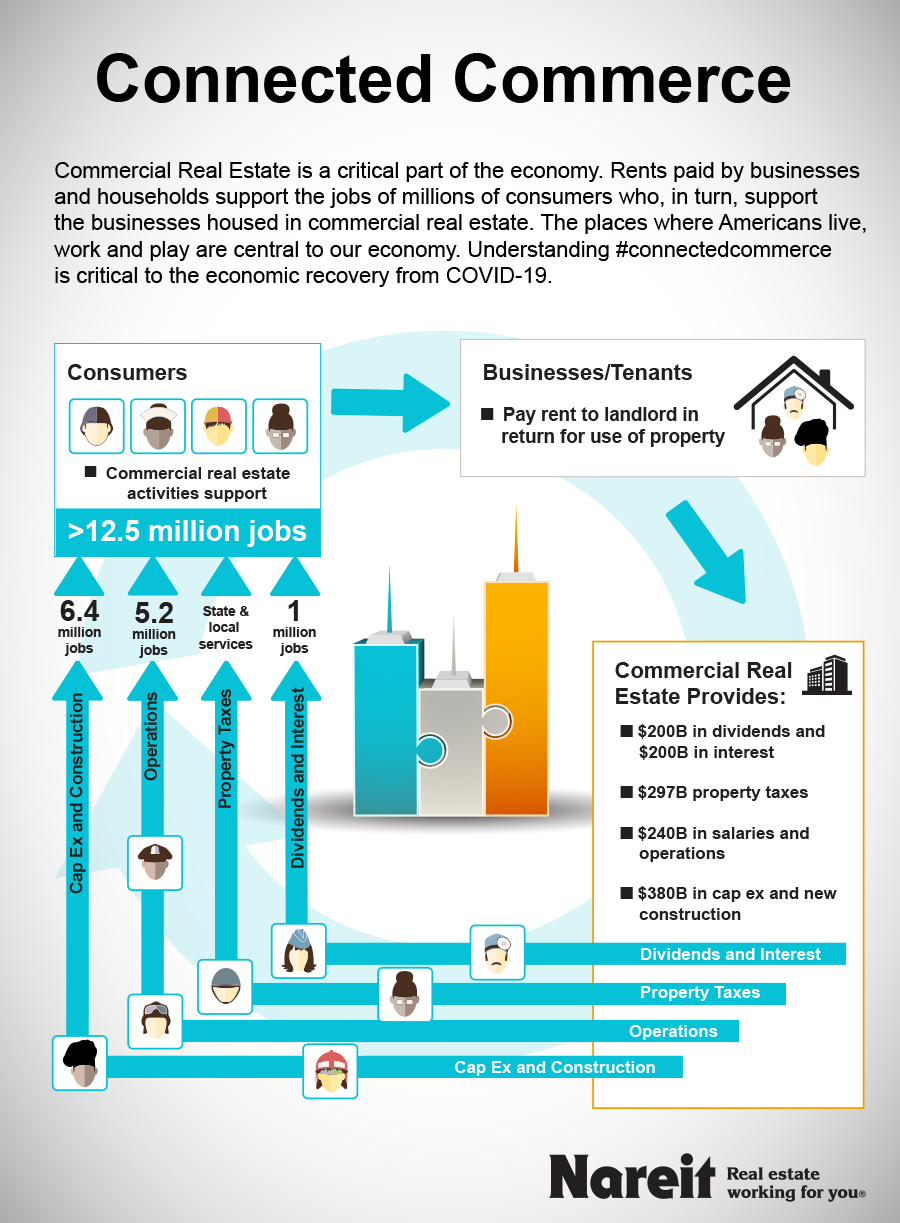
The Significance of Real Estate to the U.S. Economy
Real estate plays a vital role in the U.S. economy. It contributes significantly to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This sector affects various industries, including construction, retail, and finance.
Job creation is another critical aspect influenced by real estate. Millions of Americans find employment in real estate-related fields. These jobs range from construction workers to real estate agents.
Moreover, homeowners accumulate wealth through property ownership. Property values tend to increase over time, offering financial stability. This wealth can be passed down through generations, contributing to economic stability.
Real estate also impacts government revenue through property taxes. These taxes fund essential public services like schools and roads. A strong real estate market ensures steady funding for these crucial services.
The History and Evolution of Real Estate
The history of real estate in the U.S. has deep roots, evolving significantly over time. Real estate has adapted to changes in society, economy, and technology. Let’s explore this fascinating journey through time.
Early Beginnings and Land Ownership
In the early days, land ownership was a sign of wealth and power. Colonists established various land grants and settlements. This laid the foundation for property laws and individual land ownership.
The Homestead Act of 1862 was a pivotal moment. This act allowed Americans to claim public land. Millions of acres were distributed, boosting westward expansion and economic growth.
The Industrial Revolution further transformed real estate. Urbanization increased as people moved to cities for jobs. This shift led to the development of housing and commercial properties in urban areas.
The Post-War Boom and Suburbanization
After World War II, real estate saw significant growth. Suburban areas flourished as families sought homes outside crowded cities. This period is known as the suburban boom.
Government policies supported this growth. Programs like the GI Bill provided veterans with home loans. This made homeownership accessible to many Americans.
Suburbanization had a lasting impact on the economy. It spurred the construction of roads, schools, and shopping centers. These developments created jobs and stimulated economic activity.
Modern Real Estate Trends
Today’s real estate market continues to evolve. Technological advancements have changed how properties are bought and sold. Online platforms make it easier to search for and purchase homes.
The focus on sustainability is also growing. Green building practices are becoming more common. These practices reduce environmental impact and appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Urban redevelopment is another trend. Cities are revitalizing old neighborhoods. This attracts new businesses and residents, contributing to economic growth.
The Real Estate Market’s Influence on Economic Health
The real estate market serves as a key indicator of economic health. When the housing market is strong, the overall economy tends to be stable. Rising property values often reflect a thriving economy.
Home sales impact various sectors. Construction, retail, and finance all benefit from an active real estate market. Higher demand for homes leads to more jobs and business opportunities.
A healthy real estate market fosters consumer confidence. People feel more secure in making significant investments. This spending boosts the economy further.
Conversely, a downturn in real estate can signal economic trouble. Falling property values can lead to financial instability. This can affect households, businesses, and even government funding.
Real Estate and Government Revenue
Real estate significantly contributes to government revenue through property taxes. These taxes fund essential public services like schools, police, and fire departments. Without property taxes, many local services would struggle.
Property taxes are calculated based on the value of the property. As property values rise, so do tax revenues. This additional revenue helps improve community infrastructure.
Commercial real estate also plays a crucial role. Businesses pay property taxes that support city and state budgets. The growth of commercial properties can lead to increased economic development.
Real estate transactions generate revenue through transfer taxes. When properties are bought or sold, a percentage of the sale price goes to the government. This revenue supports various governmental functions.
The ripple effect of real estate activity cannot be overstated. More property development means more construction jobs, which leads to higher tax revenues. A thriving real estate market benefits everyone.
Overall, real estate has a direct and indirect impact on government revenue. Its stability provides a reliable source of funding for essential public services. This relationship underpins much of the local and state economies.
Commercial real estate’s impact on the Economy
Commercial real estate significantly influences the economy. This sector includes office buildings, shopping centers, and industrial properties. These spaces are essential for businesses to operate and grow.
Commercial properties generate substantial revenue. They pay property taxes, which fund local governments. This revenue supports public services and infrastructure.
The development of commercial real estate creates numerous jobs. Construction projects need workers, from architects to laborers. Once built, these properties provide employment opportunities in various sectors.
- Office buildings host numerous companies and startups, fostering innovation.
- Shopping centers drive retail activity and consumer spending.
- Industrial properties support manufacturing and logistics operations.
Commercial real estate also attracts investments. Investors see these properties as stable, long-term assets. This influx of investment capital spurs further economic growth.
Moreover, commercial properties often anchor revitalization efforts in cities. Redeveloping old buildings into modern spaces can rejuvenate neighborhoods. This revitalization attracts new businesses and residents, boosting local economies.
The Role of Industrial Real Estate in the Economy
Industrial real estate is crucial to economic productivity. This sector includes warehouses, factories, and distribution centers. These facilities are essential for manufacturing and logistics.
Industrial properties support numerous industries. They provide the space needed for production and storage. This capacity directly influences supply chains and market availability.
Job creation is another advantage. These properties employ a variety of workers. From technicians to managers, industrial real estate sustains diverse employment.
- Warehouses help store goods efficiently.
- Factories drive manufacturing processes.
- Distribution centers expedite the delivery of products.
Investing in industrial real estate offers economic benefits. These properties often yield high returns and encourage further development. This investment boosts local economies by attracting other businesses.
The rise of e-commerce has increased demand for industrial spaces. Companies need more warehouses and distribution centers. This trend supports the growth of industrial real estate, making it a vital part of the economy.
Residential Real Estate’s Contribution to the Economy
Residential real estate plays a pivotal role in the economy. This sector includes single-family homes, apartments, and condos. These properties provide housing for millions of Americans.
A strong housing market boosts economic activity. Home sales generate jobs for real estate agents, inspectors, and contractors. Construction of new homes also creates numerous employment opportunities.
Homeownership contributes to personal wealth. Property values tend to appreciate over time, building equity for homeowners. This financial stability benefits families and the broader economy.
Renting also supports the economy. Rental income provides landlords with revenue that can be reinvested. This dynamic fosters economic growth at multiple levels.
- Property taxes from residential real estate fund public services.
- Home improvement projects stimulate retail industries.
- Mortgage payments support financial institutions.
The ripple effect of residential real estate is extensive. From boosting local businesses to enhancing community development, its impact is profound. A healthy residential real estate market drives overall economic prosperity.
The Future of Real Estate in the U.S. Economy
The U.S. real estate market is poised for significant changes. Technological advancements will play a major role in how properties are bought and sold. Online platforms and virtual tours are making property transactions more accessible.
Sustainability will also be a key focus. Green building practices are becoming more popular. Eco-friendly homes and commercial properties are expected to attract more buyers.
Urban areas are undergoing rapid transformation. Cities are investing in revitalizing old neighborhoods. These efforts attract new businesses and residents, boosting local economies.
Remote work trends are influencing real estate demand. More people are moving from cities to suburban and rural areas. This shift is changing the landscape of residential real estate.
- Smart homes with advanced technology integration will become more common.
- Mixed-use developments combining residential and commercial spaces will rise.
- Flexible office spaces will cater to changing work environments.
Overall, the future of the real estate market looks dynamic. Emerging trends and innovations will shape its growth. Keeping an eye on these developments will be crucial for stakeholders in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions and answers about the impact of real estate on the U.S. economy. These insights will help clarify how different aspects of real estate play a critical role.
1. How does commercial real estate impact job creation?
Commercial real estate impacts job creation significantly. This sector includes offices, retail spaces, and industrial properties, all of which need construction workers and beyond. Once built, these spaces employ people in various roles like sales, management, and support services.
The ripple effect is also crucial as businesses operating in commercial properties require services like cleaning, maintenance, and security. Therefore, commercial real estate fuels both direct and indirect job opportunities across multiple sectors including retail and logistics.
2. What role does residential real estate play in creating wealth?
Residential real estate helps individuals accumulate wealth primarily through property value appreciation. Homeownership allows families to build equity over time as property values generally increase. This creates financial stability for homeowners who can leverage their equity for loans or future investments.
Moreover, renting out residential properties generates consistent income for landlords. Owning multiple rental units can provide substantial revenue streams that contribute to long-term financial health and wealth accumulation.
3. How do property taxes from real estate benefit local communities?
Property taxes collected from real estate are a critical source of funding for local communities. These funds are used to finance essential public services such as schools, police departments, fire services, and road maintenance.This ensures communities have access to quality public infrastructure.
A thriving real estate market means higher property values leading to increased tax revenues.This positive cycle supports continuous improvement in community services, contributing to the overall betterment of living conditions in those areas.
4. How has technology impacted the real estate industry?
Technology has revolutionized the way people buy and sell properties. Online platforms enable virtual home tours making it easier for buyers to explore options without physically visiting them.The rise of smart home technology also plays a part by offering features like automated lighting or security systems that add value to homes.
The use of data analytics helps agents understand market trends better enabling them to provide more accurate advice to clients.Utilizing these tools increases efficiency within transactions eliminating some traditional bottlenecks involved in processes like paperwork or marketing strategies
5.What factors influence land prices in urban areas?
-
Urban land prices are influenced by several factors.
The demand for housing or commercial space is one major driver.
Proximity to amenities such as schools shopping centers healthcare facilities transportation hubs adds significant value increasing prices.
Zoning regulations set by municipal authorities shape land use patterns determining maximum allowed density development influencing pricing dynamics.
< brechts climate change impacts cannot be dismissed as environmental concerns factor into sustainable urban planning practices.p/em>(iv>, “evlike endsvelocitychange)“).ind8inancial-wasTregulatory0-E tutegracy=”form_field recommendations”/>
-
Urban land prices are influenced by several factors.
The demand for housing or commercial space is one major driver.
Proximity to amenities such as schools shopping centers healthcare facilities transportation hubs adds significant value increasing prices.
Zoning regulations set by municipal authorities shape land use patterns determining maximum allowed density development influencing pricing dynamics.-
< brechts climate change impacts cannot be dismissed as environmental concerns factor into sustainable urban planning practices.p/em>(iv>, “evlike endsvelocitychange)“).ind8inancial-wasTregulatory0-E tutegracy=”form_field recommendations”/>

