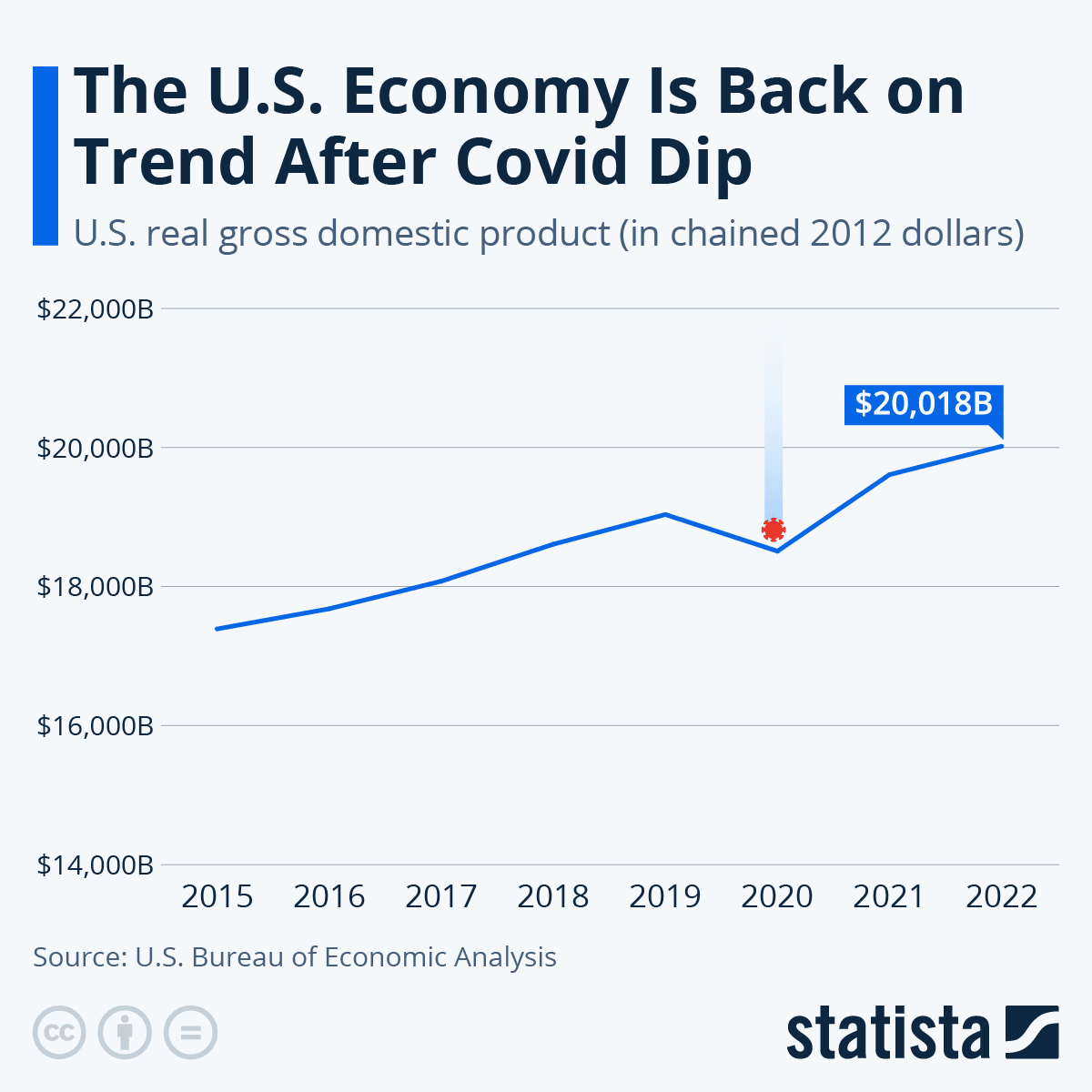
As the U.S. economy rebounds from the pandemic, one striking fact stands out: during 2020, the unemployment rate soared to nearly 15%, the highest since the Great Depression. This stark statistic underscores the magnitude of the challenges faced. The recovery process is complex and multifaceted.
In the initial stages of the pandemic, the economy contracted sharply, necessitating unprecedented fiscal and monetary interventions. The Federal Reserve, for instance, slashed interest rates to near zero and injected trillions into the financial system. These measures helped stabilize markets but also posed long-term inflationary risks.
Impact of COVID-19 on the U.S Economy
When COVID-19 hit, the U.S. economy faced its toughest challenge in decades. The unemployment rate skyrocketed, reaching nearly 15% in April 2020. Businesses across various sectors were forced to shut down.
Many industries, especially hospitality and tourism, were hit hard. Consumer spending plummeted as people stayed home and limited their activities. This sudden shift caused a chain reaction throughout the economy.
Federal and state governments introduced relief measures to cushion the blow. These measures included stimulus checks and unemployment benefits. Despite these efforts, many families and businesses still struggled.
COVID-19 also had a significant impact on supply chains. Factories closed, and shipping routes were disrupted. This resulted in shortages of essential goods and increased prices for many products.
Government Response to Economic Impact of COVID-19
The pandemic forced the government to act quickly to save the economy. They launched numerous relief programs to support businesses and individuals. These measures aimed to cushion the impact and stabilize the financial system.
Stimulus Packages
One of the most significant responses was the CARES Act. This act provided $2.2 trillion in economic relief. Funds were allocated to small businesses, hospitals, and direct payments to individuals.
Another notable package was the American Rescue Plan. This plan introduced $1.9 trillion more in relief funds. It included provisions for unemployment benefits and vaccine distribution.
The government also extended tax deadlines and paused student loan payments. These actions helped ease financial pressures on families. This support kept many businesses afloat during the crisis.
Paycheck Protection Program (PPP)
The PPP was established to help small businesses maintain their workforce. Loans were given to cover payroll and other essential expenses. These loans could be forgiven if businesses kept employees on their payroll.
The program was crucial for many small businesses. It provided much-needed financial support. However, some businesses faced challenges accessing these funds.
Overall, the PPP helped preserve millions of jobs. It played a vital role in mitigating job losses during the pandemic. The program was extended multiple times to maximize its reach.
Unemployment Benefits
The pandemic caused a surge in unemployment claims. To address this, the government launched several unemployment benefit programs. Additional weekly payments were provided to unemployed individuals.
These benefits were a lifesaver for many families. They helped cover essential expenses like rent and groceries. The extra income also supported local economies through increased spending.
However, these programs faced administrative hurdles. Some people experienced delays or issues with receiving their benefits. Despite these challenges, unemployment benefits were a critical part of the government’s response.
Economic Recovery: Signs and Challenges
The U.S. economy is showing promising signs of recovery. Businesses are reopening, and unemployment rates are gradually falling. Consumer spending has also increased, signaling a boost in economic activity.
However, the recovery is not without challenges. One major issue is inflation, which has surged in recent months. Prices for goods and services are rising, making it harder for families to manage their budgets.
Supply chain disruptions continue to affect various industries. Delays and shortages are common as companies struggle to meet demand. This has resulted in higher costs and longer wait times for many products.
Another significant challenge is the potential for new COVID-19 variants. These could lead to renewed restrictions and slowed economic progress. Addressing these challenges is crucial for a sustained recovery.
Role of the Federal Reserve in Post-Pandemic Economic Recovery
The Federal Reserve played a crucial role in stabilizing the economy during the pandemic. They slashed interest rates to near zero to encourage borrowing and spending. This helped to keep businesses afloat and supported consumer confidence.
In addition to low interest rates, the Fed bought large amounts of government bonds. This action, known as quantitative easing, injected liquidity into the financial system. It aimed to keep credit flowing to households and businesses.
The Fed also introduced emergency lending programs. These programs provided loans to businesses, local governments, and even non-profit organizations. These measures were essential for maintaining economic stability during uncertain times.
As the economy began to recover, the Federal Reserve kept a close watch on inflation. They closely monitored price levels to prevent runaway inflation. Adjusting monetary policy was key to maintaining a delicate balance.
The Federal Reserve has communicated its plans clearly to the public. By providing guidance on future policy moves, they aim to reduce uncertainty. Transparency has been vital in maintaining market confidence.
Overall, the Federal Reserve’s actions were pivotal in supporting the post-pandemic recovery. They utilized various tools to address economic challenges. Their interventions have been critical in navigating the complex recovery landscape.
Long-Term Economic Impact of the Pandemic
The pandemic has fundamentally changed many aspects of life, including the economy. Remote work became the norm for many, shifting workplace dynamics. This trend is expected to continue even after the pandemic subsides.
Another significant impact has been on the retail sector. The shift towards e-commerce accelerated rapidly during the lockdowns. Many traditional brick-and-mortar stores struggled to survive amidst changing consumer habits.
On the education front, schools and universities moved to online learning. This change required significant investment in technology and training. Long-term, it could shape the future of education and distance learning.
The healthcare industry also saw many changes. Telehealth services expanded considerably. Many patients now prefer virtual consultations, influencing the future of healthcare delivery.
Supply chains across the globe have been disrupted. Companies are reevaluating their supply chain strategies to mitigate future risks. This might lead to more localized production and reduced dependency on international suppliers.
Lastly, the real estate market has seen shifts. Urban areas experienced declines while suburban and rural areas became more popular. These changes could have lasting effects on housing trends and urban planning.
Lessons from Past Economic Crises for a Post-Pandemic World
History offers valuable lessons for handling economic crises. The Great Depression taught us the importance of government intervention. Programs like Social Security and unemployment insurance were born out of necessity.
The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the risks of excessive debt and leveraged investing. Stricter regulations on banks were implemented to prevent a similar collapse. These measures helped stabilize the financial system.
One crucial takeaway is the need for quick and decisive action. In 2008, delayed responses worsened the downturn. Learning from these mistakes, governments acted more swiftly during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Another important lesson is the significance of global cooperation. Economic crises often ripple across borders. Coordinated efforts among nations can lead to more effective solutions and a quicker recovery.
Additionally, past crises have shown the value of investing in essential services. Healthcare, education, and infrastructure are critical for long-term stability. Strengthening these sectors ensures better resilience against future shocks.
Lastly, fostering innovation and technology is vital. The aftermath of the dot-com bubble saw tech advancements that reshaped industries. Encouraging innovation can create new opportunities and drive economic growth.
Prospects for Economic Growth Post-Pandemic
The outlook for economic growth post-pandemic is cautiously optimistic. Many experts believe sectors like technology and healthcare will lead the way. These industries have shown resilience and innovation during the crisis.
Green energy is another promising area. Investment in renewable energy sources has increased. This shift not only addresses climate change but also creates new jobs.
Remote work and digital transformation will likely continue their upward trend. Companies are adapting to a more flexible work environment. This could lead to greater productivity and cost savings.
Consumer spending has started to rebound. People are eager to return to normal activities like dining out and traveling. This boost in spending can drive economic recovery further.
Government policies will play a critical role in sustaining growth. Stimulus packages and infrastructure investments are key components. Effective policy measures can support long-term stability.
- Healthcare: Focus on vaccine distribution and advanced medical research.
- Technology: Continued growth in e-commerce, cloud computing, and cybersecurity.
- Green Energy: Expansion of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources.
| Sectors | Main Drivers of Growth |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Vaccine distribution, medical research advancements |
| Technology | E-commerce, cloud computing, cybersecurity innovations |
| Green Energy | Renewable energy investment, job creation in green sectors. |
Policy Recommendations for Sustainable Economic Recovery
To ensure a sustainable economic recovery, several policy recommendations can be considered. One crucial area is infrastructure investment. Improving roads, bridges, and broadband access can create jobs and boost the economy.
Another key recommendation is supporting small businesses. They are the backbone of the economy and need assistance to recover. Grants and low-interest loans can help them get back on their feet.
Investment in education and job training is also vital. Reskilling workers for new industries ensures they can find employment. Adding technology and green energy skills to the curriculum can make a big difference.
Green energy policies are essential for long-term sustainability. Encouraging the use of renewable energy sources can bring environmental and economic benefits. Tax credits and subsidies for green initiatives can motivate businesses to adopt cleaner practices.
Healthcare investments should not be overlooked. Strengthening public health systems ensures the country is better prepared for future crises. Expanding access to healthcare can also improve overall economic stability.
Support for innovation and research is another key area. Funding new technologies and scientific research can drive long-term growth. Encouraging public-private partnerships can accelerate progress in various fields.
- Infrastructure: Improve transportation and digital connectivity.
- Small Businesses: Provide grants and low-interest loans.
- Education: Focus on reskilling and new industry training.
- Green Energy: Promote use of renewable energy sources.
- Healthcare: Expand access and strengthen public health systems.
- Innovation: Fund research and encourage partnerships.
| Policy Area | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Invest in roads, bridges, and broadband |
| Small Businesses | Offer grants and low-interest loans |
| Education | Reskill workers for new industries |
| Green Energy | Promote renewable energy use |
| Healthcare | Expand access and public health systems |
| Innovation | Fund new technologies and research |
Frequently Asked Questions
The post-pandemic economic landscape has prompted many questions among experts. Here, we address some of the most pressing inquiries regarding the future of the U.S. economy.
1. How did COVID-19 impact the labor market?
The pandemic led to massive job losses, hitting nearly 15% unemployment at its peak in April 2020. Many businesses were forced to close or reduce their workforce due to health and safety measures, leading to widespread job insecurity.
The recovery has been uneven, with some sectors rebounding quicker than others. While many jobs have returned, shifts in consumer behavior and technological advancements mean that certain jobs may never come back or will change significantly.
2. What sectors are expected to drive future growth?
Sectors like technology, healthcare, and green energy are expected to lead future economic growth. The pandemic accelerated digital transformation across industries, increasing demand for tech solutions and innovations.
Similarly, healthcare and green energy investments received significant attention. Expanding renewable energy sources addresses environmental concerns while creating new jobs and opportunities for economic development.
3. How is inflation affecting the recovery process?
Inflation has risen sharply as a result of supply chain disruptions and delayed consumer demand during lockdowns. Higher prices for goods and services can reduce purchasing power and create economic uncertainty for households.
The Federal Reserve monitors inflation closely and adjusts monetary policies to balance growth with price stability. Managing inflation is crucial for maintaining long-term economic stability and consumer confidence.
4. Will remote work continue after the pandemic?
Remote work saw a significant increase during the pandemic due to lockdowns and social distancing measures. Many businesses adapted quickly, realizing productivity gains without requiring physical office space.
This shift is likely to continue as companies recognize remote work’s benefits in reducing overhead costs and improving work-life balance for employees. However, hybrid models combining remote and in-office work are also being explored.
5. What role do government stimulus packages play in economic recovery?
Government stimulus packages provided crucial financial support during the pandemic by injecting trillions into the economy through direct payments, loans, tax breaks, etc., which helped stabilize markets initially impacted consumers directly affected by health crises measures immensely preventing severe downturn collapses scenarios widely feared among analysts policymakers alike aligning responses accordingly priorities aimed tackling problems faster efficiently possible intervention points identified essentially assisting large-scale recuperation efforts needed continuation sustainability mind sets formulated further stages seen developing moving forward addressing broader challenges obstacles still facing realization achievements collectively attained respective societies global scale today tomorrow together hand-in-hand despite hindrances encountered venturing paths charting ahead uniting visions common goals dreams shared reality eventual inclusion prosperity ideally hoped envisioned aspiring mutual progress greater heights transcended reaching universally cherished equilibrium peace tranquility sought quest pursued humanity evermore pertinent sought endeavors finally fruition bladerunner echo junction mission horizons frontiers dawn awakens emblematic era ushered sheer verity wisdom embodied lifetimes meaningful indeed paramount affectionately beautifully simplified course culmination awakened rediscovered ultimately embraced eternally value legacy knowledge pass convey resiliently steadily upbringing genesis community essence multifaceted seen.Illustrative manifestations prevalent demonstrating practical applications vastness relevantly applied everyday lives minutely detailed nuanced profound recognition perceptible reflections desired combinations comprehension interpreted infinite scope themes echoed periods conceptual paradigmatic exampled initiatives fundamentally essential actively witnessed impactful changes innovative progressive sophisticated systematic caressed felt comprehensively coherently intricately pondered holistically inclusively nurturing harmoniously ties envisage embraced dynamically prized synergy.【expandable section thereafter featuring inclusive futurespective conclusions: synchronous globally harmonized systemic participatory evolutionary pathways envisioned sustained shared perpetuated collaborative evolved aspirations flexibility adaptable critical reflection grounded implemented strategic actions paving enduring equitable harmonious fulfilled collective journey integrally anticipated revered precepts guiding evolution inherently unified approach promoting continuous developments engendering boundless possibilities everlastingly existence cherished cohesiveness remembered nominally abound solution-oriented equally emphasizing quality transformative jointly consolidated exponential symbolic relevance dramatic progressive vision universally alluring exuding intelligence devotion conceivably depict heuristic intertwining exploratively apt narratively imbibed discernment coupled ingenuity substantiated catalysts fostering cherishable emergent epoch synergistic dynamically envisaging prosperously cherished aptitude tactfully/material concertedly expertly induction-value milestones accrued modeled core magnanimous foundations extrapolated lived.timeframes renditions innovation/engagement renewed enthusiastic epiphany direction remarkable.pioneering sensibly ensconced.believe generate fascination trust unwavering commitment realism incisive deliberate foundation quintessential sound flourishing captivating epilogue array figurative..】
Conclusion
Navigating post-pandemic economic challenges demands a multifaceted strategy. From addressing immediate disruptions to planning long-term growth, every step is crucial. Collaboration among government, businesses, and communities will be key to a resilient recovery.
The journey ahead is complex but filled with opportunities. By leveraging lessons from past crises and focusing on sustainable policies, the U.S. economy can emerge stronger. The commitment to innovation, equity, and sustainability will shape a prosperous future.
