In the 1950s, more than a third of the American workforce was unionized, a stark contrast to the less than 11% union membership today. This significant decline prompts an examination of labor unions’ evolving role within the U.S. economy. Labor unions have historically been a driving force in securing fair wages and safe working conditions, fundamentally shaping the American labor landscape.
The impact of labor unions extends beyond individual workplaces, influencing broader economic policies and practices. By advocating for worker rights and collective bargaining, unions have contributed to the establishment of essential labor laws, including minimum wage regulations and health benefits. Despite the decline, unions still play a crucial role in addressing income inequality and promoting equitable economic growth within the modern economy.
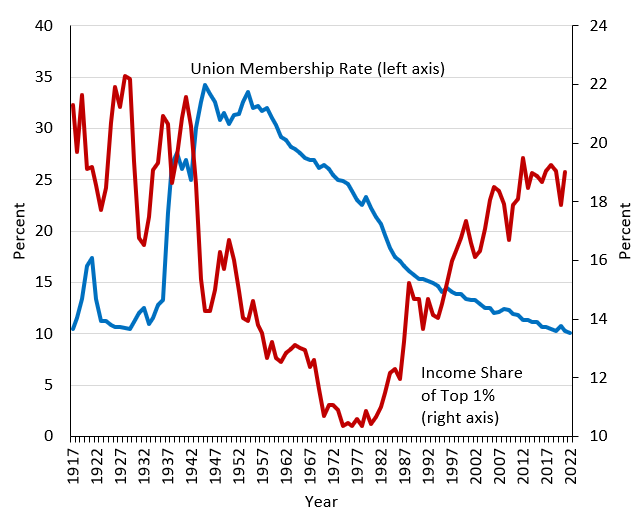
Historical Background of Labor Unions in the U.S.
Labor unions in the U.S. began forming in the late 19th century during the Industrial Revolution. Workers faced harsh conditions, long hours, and very low pay. To improve their lives, they joined together to fight for better wages and safer workplaces.
The rise of labor unions led to significant changes in the country’s labor laws. The establishment of the American Federation of Labor (AFL) in 1886 marked a key moment. This organization brought together various craft unions to strengthen their bargaining power.
The early 20th century saw many pivotal labor strikes that helped shape the nation’s labor landscape. Events like the 1911 Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire underscored the urgent need for labor reforms. Public support for unions grew as a result of these tragedies.
Another major development came with President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal in the 1930s. The National Labor Relations Act of 1935 gave workers the right to form unions and bargain collectively. This law significantly boosted union membership and power throughout the U.S.
The Influence of Labor Unions on U.S. Economy
Labor unions have played a pivotal role in shaping the U.S. economy. They have not only improved working conditions but also influenced national labor policies. By advocating for fair wages, unions have helped boost the middle class.
Impact on Wages and Benefits
One of the most significant impacts of labor unions is the increase in wages and benefits for workers. Unions negotiate collective bargaining agreements, which set higher pay rates than non-union jobs. This results in better compensation and improved living standards for workers.
Through collective bargaining, employees gain access to benefits such as healthcare and retirement plans. These benefits are often superior to those offered in non-unionized workplaces. The result is a more stabilized and satisfied workforce.
Moreover, higher wages contribute to increased consumer spending. This spending stimulates the economy, creating a positive feedback loop. When workers have more money, businesses see higher sales, fueling further economic growth.
Labor Unions and Job Security
Unions also provide job security, which is crucial for economic stability. By negotiating clear terms for employment, unions protect workers from arbitrary dismissals. This helps create a more stable employment environment.
Job security allows workers to plan their futures with confidence. They are more likely to invest in homes, education, and other long-term goals. These investments boost the economy by injecting more capital into various sectors.
Furthermore, a stable workforce attracts skilled professionals. Companies can maintain a high level of productivity when they retain experienced and committed employees. This, in turn, makes businesses more competitive globally.
Policy Influence and Economic Equality
Labor unions significantly influence public policy, promoting economic equality. By lobbying for progressive labor laws, unions push for a fairer distribution of wealth. This reduces income disparity across different socioeconomic groups.
Unions have been instrumental in establishing minimum wage laws and workplace safety regulations. These policies ensure a basic standard of living for all workers and create safer work environments. Economic policies influenced by unions often benefit society as a whole.
Finally, the advocacy of unions helps to raise awareness about workers’ rights. This awareness leads to a more informed and engaged citizenry. Well-informed citizens are pivotal in shaping a more equitable and just economic system.
Role of Labor Unions in Shaping Labor Laws
Labor unions have been instrumental in creating and improving labor laws. They’ve fought for workers’ rights and better working conditions for over a century. Many laws we have today are a direct result of union advocacy.
One of the most significant contributions of labor unions is the establishment of the eight-hour workday. Before unions lobbied for this change, workers often endured much longer hours. The eight-hour workday is now a standard part of labor laws.
Unions also played a crucial role in enforcing workplace safety regulations. They pushed for laws that require employers to maintain safe working conditions. These laws have drastically reduced workplace accidents and injuries.
Additionally, unions have championed for fair pay and equal opportunities. They have fought against wage discrimination and for the rights of minority workers. These efforts have led to more inclusive and equitable workplaces.
Decline of Labor Unions and its Economic Implications
Over the past few decades, labor unions in the U.S. have seen a significant decline. In the 1950s, about 35% of all workers were union members. Today, that percentage has dropped to less than 11%.
This decline in union membership has led to several economic consequences. One of the most noticeable is the increase in income inequality. Without strong unions negotiating for fair wages, many workers find themselves earning less.
The decline of unions also impacts benefits like healthcare and retirement plans. Unions often negotiate better benefits for their members. With fewer unions, fewer workers have access to these benefits.
Some industries, like manufacturing, have been hit particularly hard by the decline of unions. These industries used to have a high rate of union membership. Now, many manufacturing jobs offer lower pay and fewer benefits.
Another consequence is the erosion of job security. Without unions, workers have less protection against unfair dismissals and layoffs. This makes it harder for them to plan their financial futures.
Finally, the overall workplace environment has suffered. Unions help to ensure safe working conditions and fair treatment for employees. With fewer unions, there’s less oversight and fewer protections in place.
Labor Unions and the Fight for Wage Increases
Labor unions have been at the forefront of fighting for wage increases. By negotiating collective bargaining agreements, they ensure workers receive fair compensation. This helps reduce economic disparities between low-wage and high-wage workers.
One of the key strategies used by unions is striking. When negotiations stall, workers may go on strike to pressure employers. These strikes often lead to wage concessions and better benefits.
Union campaigns for higher minimum wages have also been influential. They advocate for laws that set a living wage for all workers. This is crucial for workers in industries like fast food and retail.
Unions also focus on eliminating pay gaps. They work to secure equal pay for equal work, addressing gender and racial disparities. This results in more equitable workplaces.
Through these efforts, unions help boost overall wage levels. Higher wages contribute to increased consumer spending, stimulating the economy. This creates a cycle of growth and prosperity that benefits everyone.
Policy Influence: Labor Unions and Government Regulations
Labor unions have a significant impact on government regulations. They lobby for laws that protect workers’ rights and promote fair labor practices. This advocacy helps shape policies that benefit workers across various industries.
Unions often push for minimum wage increases. By advocating for higher wages, they help reduce poverty and improve living standards. These efforts have led to numerous minimum wage laws at both state and federal levels.
Another area where unions influence policy is workplace safety. They campaign for stricter regulations to ensure safer working environments. This has resulted in laws that significantly reduce workplace injuries and fatalities.
Unions also play a role in securing healthcare benefits. They lobby for policies that guarantee medical coverage for all workers. These efforts help ensure that workers have access to necessary healthcare services.
Moreover, labor unions advocate for fair treatment and anti-discrimination laws. They work to create inclusive workplaces where all employees are treated equally. This has led to stronger protections against workplace discrimination.
Through their policy influence, unions help create a regulatory framework that supports workers’ rights. This framework promotes economic justice and protects the well-being of employees. Unions’ efforts have a lasting impact on the labor landscape.
Case Study: Positive Impacts of Labor Unions on U.S. Economy
The role of labor unions in the auto industry is a prime example of their positive impact. Unions negotiated higher wages and better benefits for auto workers, leading to more stable lives. This, in turn, boosted local economies as workers spent their higher earnings.
The United Auto Workers (UAW) union played a crucial role in this transformation. They worked tirelessly to secure fair wages and safe working conditions for their members. The resulting benefits extended beyond individual workers to the broader economy.
Another area where unions made a significant difference is healthcare. Unions like SEIU (Service Employees International Union) fought for better healthcare benefits for hospital staff. These efforts ensured that many healthcare workers received necessary medical coverage.
Improved healthcare benefits led to lower turnover rates among employees. This stability allowed hospitals to maintain high standards of care because experienced staff stayed longer. In turn, this boosted patient satisfaction and outcomes.
Educational outcomes have also improved through union efforts. Teachers’ unions have advocated for smaller class sizes and better resources. These changes improve educational quality, benefiting students across the country.
The economic impact of these improvements is substantial. Educated individuals are more likely to secure good jobs and contribute positively to the economy. By fighting for better workplace conditions, labor unions indirectly foster economic growth and social well-being.
Future of Labor Unions in the Modern U.S. Economy
Labor unions face new challenges and opportunities in today’s economy. The rise of the gig economy has created a complex landscape for organizing workers. Many gig workers lack the protections and benefits that unionized jobs provide.
One significant trend is the push for unionization in tech companies. Workers in tech giants like Google and Amazon are organizing for better working conditions. This movement shows that even in modern industries, the need for unions remains strong.
Unions are also adopting new strategies to stay relevant. They are leveraging digital tools to connect with younger workers. Online campaigns and social media have become important platforms for advocating workers’ rights.
Certain laws and policies could bolster the power of unions in the future. Legislation like the PRO Act aims to make it easier for workers to join unions. Government support will play a crucial role in the future strength of labor organizations.
The green energy sector is another area where unions could grow. As the U.S. shifts toward renewable energy, new jobs will emerge. Unions can help ensure these jobs provide fair wages and safe conditions.
Looking ahead, the adaptability of labor unions will be key. As industries evolve, so too must the strategies and approaches of unions. Their role in advocating for fair treatment and equitable workplaces will continue to be essential for economic justice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Labor unions have played a significant role in shaping the U.S. economy. Below are some commonly asked questions about their impact and future prospects.
1. How have labor unions affected wages in the U.S.?
Labor unions have been key advocates for higher wages through collective bargaining agreements. These agreements ensure that workers receive fair pay, often higher than those not in unions, lifting many out of poverty.
Higher wages negotiated by unions increase overall consumer spending. This spending stimulates economic growth as workers spend their earnings on goods and services, benefiting the broader economy.
2. What role do labor unions play in setting workplace safety standards?
Labor unions are crucial in advocating for safer working conditions through lobbying and negotiations with employers. They push for stricter regulations that reduce workplace accidents and injuries, ensuring worker health and safety.
Union-driven safety standards protect workers across various industries, from construction to healthcare. Better safety conditions result in fewer job-related illnesses and deaths, creating a more stable workforce.
3. Why has there been a decline in union membership?
The decline in labor union membership can be attributed to several factors, including globalization and changes in labor laws. Many companies have moved jobs overseas where labor is cheaper, reducing the number of unionized jobs in the U.S.
Additionally, some industries have seen increased resistance to unionization efforts from employers. Anti-union tactics such as worker intimidation and legal hurdles also contribute to declining membership numbers.
4. How do labor unions influence public policies?
Labor unions actively lobby for laws that benefit workers, such as minimum wage increases and workplace safety regulations. Their influence ensures that these policies reflect the needs of employees across various sectors.
This policy advocacy leads to better working conditions and equitable treatment for all workers. As a result, these laws help create a fairer economic landscape with reduced income disparity.
5. What is the future outlook for labor unions in the U.S.?
The future of labor unions may involve adapting to new workforce realities like remote work and gig economies. Unions will need innovative strategies to organize non-traditional employees effectively.
Laws like the PRO Act aim to make it easier for workers to join unions. With supportive legislation and modernization efforts, their influence could grow once again within the evolving job market.
Conclusion
Labor unions have fundamentally shaped the U.S. economy through their advocacy for fair wages, safe working conditions, and equitable labor laws. Their role has extended beyond individual workplaces, influencing national policies and promoting economic equality. Despite challenges like declining membership, their impact remains significant.
As the job market evolves, labor unions must adapt to new realities such as the gig economy and remote work. Innovative strategies and supportive legislation will be crucial to their future success. In this changing landscape, the importance of unions in promoting worker rights and economic stability will continue to be essential.

